|
Naṟṟiṇai
''Naṟṟiṇai'' ( ta, நற்றிணை meaning ''excellent tinai''), is a classical Tamil poetic work and traditionally the first of the Eight Anthologies (''Ettuthokai'') in the Sangam literature. The collection – sometimes spelled as Natrinai or Narrinai – contains both ''akam'' (love) and ''puram'' (war, public life) category of poems. The ''Naṟṟiṇai'' anthology contains 400 poems, mainly of 9 to 12 lines, but a few with 8 to 13 lines each. According to Takanobu Takahashi – a Tamil literature scholar, the ''Naṟṟiṇai'' poems were likely composed between 100–300 CE based on the linguistics, style and dating of the authors. While Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature and history scholar , dates some poems to the 1st century BCE. The ''Naṟṟiṇai'' manuscript colophon states that it was compiled under the patronage of the Pandyan king named ''Pannatu Tanta Pantiyan Maran Valuti'', but the compiler remained anonymous. The ''Naṟṟiṇai'' poems ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eight Anthologies
The Eight Anthologies, known as Eṭṭuttokai ( ta, எட்டுத்தொகை) or "Eight Collections" in the literature, is a classical Tamil poetic work that forms part of the Eighteen Greater Texts (''Patiṉeṇmēlkaṇakku'') anthology series of the Sangam Literature. The Eight Anthologies and its companion anthology, the Ten Idylls (''Pattuppāṭṭu''), is the oldest available Tamil literature. According to Kamil Zvelebil, a scholar of Tamil literature and history, dating these Eight Anthologies or their relative chronology is difficult, but the scholarship so far suggested that the earliest layers were composed sometime between the 1st century BCE and 2nd century CE, while the last layers were completed between 3rd and 5th century CE. Contents of the anthologies The Eight Anthologies consist of 2,371 poems varying from small stanzas of three lines in Ainkurnuru to stanzas of forty lines in Purananuru. The following poems form the Eight Anthologies: * '' Ainkurunu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
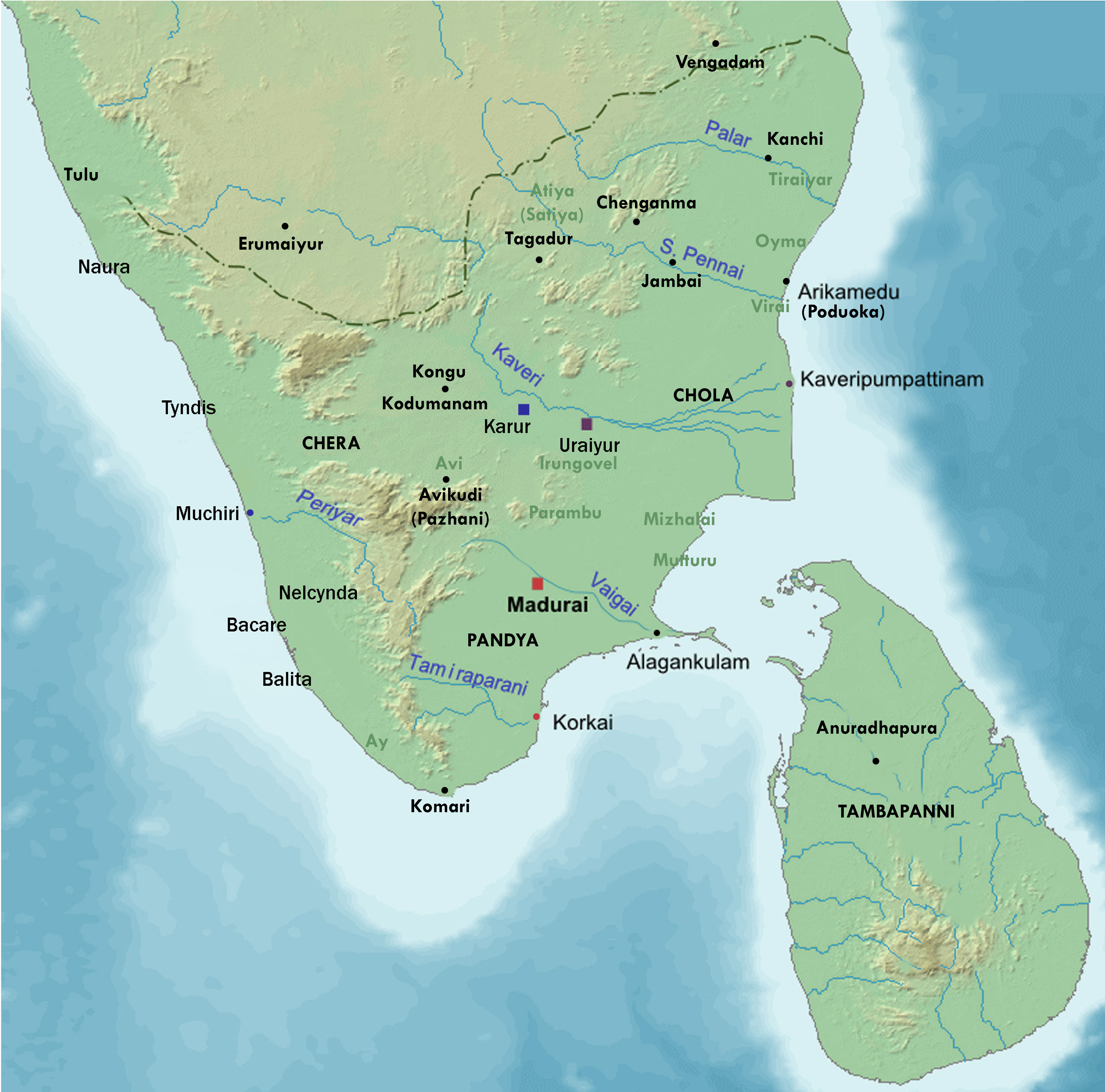
Sangam Literature
The Sangam literature (Tamil: சங்க இலக்கியம், ''caṅka ilakkiyam'';) historically known as 'the poetry of the noble ones' (Tamil: சான்றோர் செய்யுள், ''Cāṉṟōr ceyyuḷ'') connotes the ancient Tamil literature and is the earliest known literature of South India. The Tamil tradition and legends link it to three literary gatherings around Madurai and Kapāṭapuram ( Pandyan capitals): the first over 4,440 years, the second over 3,700 years, and the third over 1,850 years before the start of the common era. Scholars consider this Tamil tradition-based chronology as ahistorical and mythical. Most scholars suggest the historical Sangam literature era spanned from c. 300 BCE to 300 CE, while others variously place this early classical Tamil literature period a bit later and more narrowly but all before 300 CE. According to Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature and history scholar, the most acceptable range for the Sangam l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silappatikaram
''Cilappatikāram'' ( ta, சிலப்பதிகாரம் ml, ചിലപ്പതികാരം,IPA: ʧiləppət̪ikɑːrəm, ''lit.'' "the Tale of an Anklet"), also referred to as ''Silappathikaram'' or ''Silappatikaram'', is the earliest Tamil epic. It is a poem of 5,730 lines in almost entirely ''akaval'' (''aciriyam'') meter. The epic is a tragic love story of an ordinary couple, Kannaki and her husband Kovalan. The ''Silappathikaram'' has more ancient roots in the Tamil bardic tradition, as Kannaki and other characters of the story are mentioned or alluded to in the Sangam literature such as in the ''Naṟṟiṇai'' and later texts such as the ''Kovalam Katai''. It is attributed to a prince-turned-monk Iḷaṅkõ Aṭikaḷ, and was probably composed in the 5th or 6th century CE. The ''Silappatikaram'' is set in a flourishing seaport city of the early Chola kingdom. Kannaki and Kovalan are a newly married couple, in love, and living in bliss. Over time, Kova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thinai
In Tamil poetics, thinnais (Tamil: திணை tiṇai "genre", "type") is a type of poetical mode or theme. A thinai consists of a complete poetical landscape - a definite time, place, season in which the poem is set - and background elements characteristic of that landscape - including flora and fauna, inhabitants, deities and social organisation. These collectively provide imagery for extended poetic metaphors ("ullurai", literally "inner meaning"), which set the mood of the poem. Classical authors recognised two broad categories of thinais. Akam thinais (literally, "the inner genre") consisted of modes used in love poetry, associated with specific aspects of a relationship or specific stages in the development of a relationship. Puram thinais (literally, "the outer genre") consisted of modes that corresponded closely to the akam modes, but were used in heroic, philosophical and moral poetry, to describe the stages of a battle or particular patterns of thought. Later co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Literature
Tamil literature has a rich and long literary tradition spanning more than two thousand years. The oldest extant works show signs of maturity indicating an even longer period of evolution. Contributors to the Tamil literature are mainly from Tamil people from South India, including the land now comprising Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Eelam Tamils from Sri Lanka, as well as the Tamil diaspora. The history of Tamil literature follows the history of Tamil Nadu, closely following the social, economical, political and cultural trends of various periods. The early Sangam literature, dated before 300 BCE, contain anthologies of various poets dealing with many aspects of life, including love, war, social values and religion.Akananuru (1, 15, 31, 55, 61, 65, 91, 97, 101, 115, 127, 187, 197, 201, 211, 233, 251, 265, 281, 311, 325, 331, 347, 349, 359, 393, 281, 295), Kurunthogai (11), and Natrinai (14, 75) are dated before 300 BCE. This was followed by the early epics and moral literature, author ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamil Zvelebil
Kamil Václav Zvelebil (November 17, 1927 – January 17, 2009) was a Czech scholar in Indian literature and linguistics, notably Tamil, Sanskrit, Dravidian linguistics and literature and philology. Life and career Zvelebil studied at the Charles University in Prague from 1946 to 1952 where he majored in Indology, English, literature and philosophy. After obtaining his PhD in 1952 and until 1970 he was a senior research fellow in Tamil and Dravidian linguistics and literature at the Oriental Institute of the Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences. He held the role of associate professor of Tamil and Dravidian at Charles University in Prague until 1968, when he and his family (including his son, the later archaeologist, Marek Zvelebil) were forced to flee after the Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia. They fled to the United States at first, but later settled in the Netherlands. During the late 1960s, he made many field trips including those to South India. From 1965 to 1966, he w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Old Indo-Aryan language varieties. The most archaic of these is the Vedic Sanskrit found in the Rig Veda, a colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tirukkural
The ''Tirukkuṟaḷ'' ( ta, திருக்குறள், lit=sacred verses), or shortly the ''Kural'' ( ta, குறள்), is a classic Tamil language text consisting of 1,330 short couplets, or Kural (poetic form), kurals, of seven words each. The text is divided into three books with aphoristic teachings on virtue (''aram''), wealth (''porul'') and love (''inbam''), respectively. Considered one of the greatest works ever written on ethics and morality, it is known for its universality and secularity, secular nature. Its authorship is traditionally attributed to Thiruvalluvar, Valluvar, also known in full as Thiruvalluvar. The text has been dated variously from 300 BCE to 5th century CE. The traditional accounts describe it as the last work of the third Sangam literature, Sangam, but linguistic analysis suggests a later date of 450 to 500 CE and that it was composed after the Sangam period. The Kural text is among the earliest systems of Indian epistemology and meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manimekalai
''Maṇimēkalai'' ( ta, மணிமேகலை, ), also spelled ''Manimekhalai'' or ''Manimekalai'', is a Tamil-Buddhist epic composed by Kulavāṇikaṉ Seethalai Sataṉar probably around the 6th century. It is an "anti-love story", a sequel to the "love story" in the earliest Tamil epic ''Silappadikaram'', with some characters from it and their next generation. The epic consists of 4,861 lines in ''akaval'' meter, arranged in 30 cantos. The title ''Manimekalai'' is also the name of the daughter of Kovalan and Madhavi, who follows in her mother's footsteps as a dancer and a Buddhist nun. The epic tells her story. Her physical beauty and artistic achievements seduces the Chola prince Udayakumara. He pursues her. She, a nun of Mahayana Buddhism persuasion, feels a commitment to free herself from human ties. She rejects his advances, yet finds herself drawn to him. She hides, prays and seeks the help of her mother, her Buddhist teacher Aravana Adikal and angels. They teach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannagi (Tamil Mythology)
Kannagi ( ta, கண்ணகி) sometimes spelled Kannaki, is a legendary Tamil woman who forms the central character of the Tamil epic ''Cilappatikaram''. Kannagi is described as the chaste woman who stays with her husband despite his unfaithfulness, their attempt to rebuild their marriage after her husband had lost everything but repented, how her husband is falsely framed then punished without the due checks and processes of justice. Kannagi proves and protests the injustice, then curses the king and city of Madurai leading to the death of the unjust Pandyan King of Madurai, who had wrongfully put her husband Kovalan to death. The society that had made her suffer, suffers in retribution as the city Madurai is burnt to the ground because of her curse. In the Chera (Kerala) and Tamil tradition, Kannagi has been deified as the symbol – sometimes as goddess – of chastity, with sculptures or reliefs in Hindu temples iconographically reminding the visitor of her breaking h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |