|
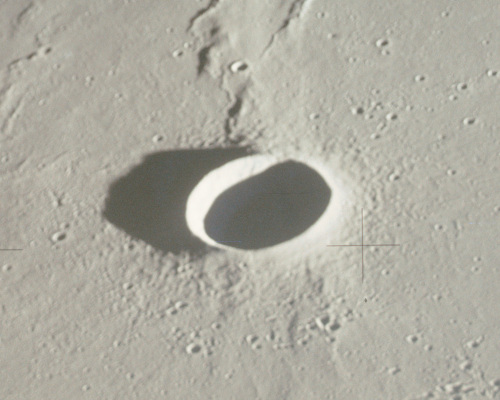
Naumann (crater)
Naumann is a lunar impact crater located on the Oceanus Procellarum in the northwest sector of the Moon. It is a bowl-shaped, symmetrical crater with a relatively high- albedo rim. There are no notable impact craters overlaying the rim edge or the interior. The nearest named craters are Lichtenberg to the southwest and Nielsen to the southeast. Otherwise it is located in a region of lunar mare which is devoid of significant features. Satellite craters By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Naumann. References Bibliography * * * * * * * * * * * * {{refend Impact craters on the Moon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Orbiter 4
Lunar Orbiter 4 was a robotic U.S. spacecraft, part of the Lunar Orbiter program, Lunar Orbiter Program, designed to orbit the Moon, after the three previous orbiters had completed the required needs for Project Apollo, Apollo mapping and site selection. It was given a more general objective, to "perform a broad systematic photographic survey of lunar surface features in order to increase the scientific knowledge of their nature, origin, and processes, and to serve as a basis for selecting sites for more detailed scientific study by subsequent orbital and landing missions". It was also equipped to collect selenodetic, radiation intensity, and micrometeoroid impact data. Mission Summary The spacecraft was placed in a Free-return trajectory, cislunar trajectory and injected into an elliptical near polar high lunar orbit for data acquisition. The orbit was with an inclination of 85.5 degrees and a period of 12 hours. After initial photography on May 11, 1967 problems started occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Friedrich Naumann
Georg Amadeus Carl Friedrich Naumann (30 May 1797 – 26 November 1873), also known as Karl Friedrich Naumann, was a German mineralogist and geologist. The crater Naumann on the Moon is named after him. Life Naumann was born at Dresden, the son of a distinguished musician and composer. He received his early education at Pforta, studied at Freiberg under Werner, and afterwards at Leipzig and Jena. He graduated at Jena, and was occupied in 1823 in teaching in that town and in 1824 at Leipzig. In 1826 he succeeded Mohs as professor of crystallography Crystallography is the experimental science of determining the arrangement of atoms in crystalline solids. Crystallography is a fundamental subject in the fields of materials science and solid-state physics (condensed matter physics). The wor ..., in 1835 he became professor also of geognosy at Freiberg; and in 1842 he was appointed professor of mineralogy and geognosy in the University of Leipzig. At Freiberg he was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Craters
Lunar craters are impact craters on Earth's Moon. The Moon's surface has many craters, all of which were formed by impacts. The International Astronomical Union currently recognizes 9,137 craters, of which 1,675 have been dated. History The word ''crater'' was adopted from the Greek word for "vessel" (, a Greek vessel used to mix wine and water). Galileo built his first telescope in late 1609, and turned it to the Moon for the first time on November 30, 1609. He discovered that, contrary to general opinion at that time, the Moon was not a perfect sphere, but had both mountains and cup-like depressions. These were named craters by Johann Hieronymus Schröter (1791), extending its previous use with volcanoes. Robert Hooke in ''Micrographia'' (1665) proposed two hypotheses for lunar crater formation: one, that the craters were caused by projectile bombardment from space, the other, that they were the products of subterranean lunar volcanism. Scientific opinion as to the origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Crater
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Lunar impact craters range from microscopic craters on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program and small, simple, bowl-shaped depressions in the lunar regolith to large, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth. Impact craters are the dominant geographic features on many solid Solar System objects including the Moon, Mercury, Callisto, Ganymede and most small moons and asteroids. On other planets and moons that experience more active surface geological processes, such as Earth, Venus, Europa, Io and Titan, visible impact craters are less common because they become eroded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanus Procellarum
Oceanus Procellarum ( la, Ōceanus procellārum, lit=Ocean of Storms) is a vast lunar mare on the western edge of the near side of the Moon. It is the only one of the lunar maria to be called an "Oceanus" (ocean), due to its size: Oceanus Procellarum is the largest of the maria ("seas"), stretching more than across its north–south axis and covering roughly , accounting for 10.5% of the total lunar surface area. Characteristics Like all lunar maria, Oceanus Procellarum was formed by ancient volcanic eruptions resulting in basaltic floods that covered the region in a thick, nearly flat layer of solidified magma. Basalts in Oceanus Procellarum have been estimated to be as young as one billion years old. Unlike the other lunar maria, however, Oceanus Procellarum may or may not be contained within a single, well-defined impact basin. Around its edges lie many minor bays and seas, including Sinus Roris to the north, and Mare Nubium and Mare Humorum to the south. To the northeast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synodic period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albedo
Albedo (; ) is the measure of the diffuse reflection of sunlight, solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation, to 1, corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation. Surface albedo is defined as the ratio of Radiosity (radiometry), radiosity ''J''e to the irradiance ''E''e (flux per unit area) received by a surface. The proportion reflected is not only determined by properties of the surface itself, but also by the spectral and angular distribution of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. These factors vary with atmospheric composition, geographic location, and time (see position of the Sun). While bi-hemispherical reflectance is calculated for a single angle of incidence (i.e., for a given position of the Sun), albedo is the directional integration of reflectance over all solar angles in a given period. The temporal resolution may range from seconds (as ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichtenberg (crater)
Lichtenberg is an isolated lunar impact crater located in the western part of the Oceanus Procellarum. The nearest crater of note is Briggs to the south. Lichtenberg has a small system of rays, a characteristic of Copernican age craters. The rays extend to the north and west of the crater but not elsewhere. The remaining flanks of the surface about the crater exhibit the low albedo of the lunar mare, and the mare deposits have overlaid the existing rays on the east and south sides of the crater. These are thus among the youngest deposits of basaltic lava on the Moon, and are believed to be less than 1 billion years in age. However, the most recent lunar geologic map (2020) does not show the mare next to Lichtenberg as being Copernican in age - it is mapped as Upper Imbrian. Lunar scientist Paul Spudis advocates an unmanned sample-return mission to the young mare to obtain an absolute radiometric date that would constrain the time period of the formation of the maria on the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nielsen (crater)
Nielsen is a lunar impact crater on the Oceanus Procellarum. It is located north-east of Montes Agricola on the western hemisphere of the Moon. To the east-southeast is the crater Wollaston. Nielsen is a bowl-shaped formation that lies astride a small ridge that runs north-northwestwards towards the Mons Rümker. The latter is an unusual raised formation of lunar dome A lunar dome is a type of shield volcano that is found on the surface of the Earth's Moon. They are typically formed by highly viscous, possibly silica-rich lava, erupting from localized vents followed by relatively slow cooling. Lunar domes are ...s. The crater is named jointly after the Danish astronomer Axel Nielsen (1902-1970) and the Danish–American physicist Harald Herborg Nielsen (1903-1973). References * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * * * http://www.lunarrepublic.com/atlas/sections/c2.shtml {{Authority control Impact craters on the Moon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Mare
The lunar maria (; singular: mare ) are large, dark, basaltic plains on Earth's Moon, formed by ancient asteroid impacts on the far side on the Moon that triggered volcanic activity on the opposite (near) side. They were dubbed , Latin for 'seas', by early astronomers who mistook them for actual seas. They are less reflective than the "highlands" as a result of their iron-rich composition, and hence appear dark to the naked eye. The maria cover about 16% of the lunar surface, mostly on the side visible from Earth. The few maria on the far side are much smaller, residing mostly in very large craters. The traditional nomenclature for the Moon also includes one (ocean), as well as features with the names ('lake'), ('marsh'), and ('bay'). The last three are smaller than maria, but have the same nature and characteristics. The names of maria refer to sea features (Mare Humorum, Mare Imbrium, Mare Insularum, Mare Nubium, Mare Spumans, Mare Undarum, Mare Vaporum, Oceanus Procellarum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

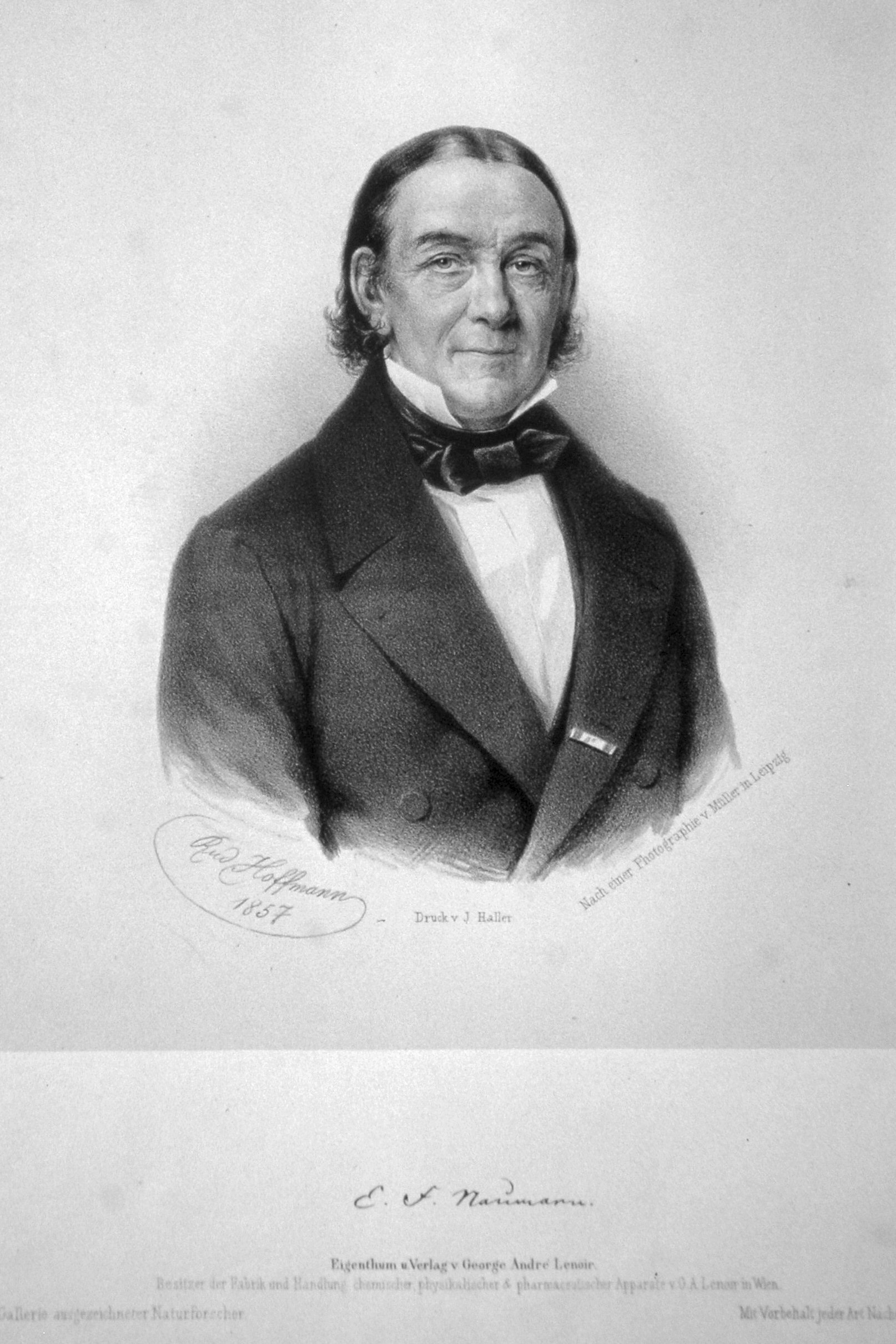


.png)


