|
Naukratis Painter
Naucratis or Naukratis (Ancient Greek: , "Naval Command"; Egyptian: , , , Coptic: ) was a city and trading-post in ancient Egypt, located on the Canopic (western-most) branch of the Nile river, south-east of the Mediterranean sea and the city of Alexandria. Naucratis was the first and, for much of its early history, the only permanent Greek colony in Egypt, serving as a symbiotic nexus for the interchange of Greek and Egyptian art and culture. The modern villages of Kom Gi’eif, el-Nibeira and el-Niqrash cover the archaeological site, which has become a find of the highest significance. The site is also the source of many objects of art that now are contained in many museums of the world, and is an important source of some of the earliest Greek writing in existence (according to inscriptions on the pottery). The sister port of Naucratis was the harbour town of Heracleion, which was discovered in 2000. Background Archaeological evidence suggests that the history of the ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beheira Governorate
Beheira Governorate ( ar, محافظة البحيرة ', , "the governorate of the Lake") is a coastal governorate in Egypt. Located in the northern part of the country in the Nile Delta, its capital is Damanhur. Overview Beheira Governorate enjoys an important strategical place, west of the Rosetta branch of the Nile. It comprises four important highways, namely the Cairo-Alexandria desert road, the Cairo agricultural road, the international road, and the circular road. Beheira Governorate is also home to a number of the most important Coptic monasteries in Wadi El Natrun (Scetes). Beheira consists of 13 centers and 14 cities, and contains important industries such as cotton, chemicals, carpets, electricity, and fishing. The governorate has a noteworthy number of archaeological sites, including at Abu El Matamir, Abu Hummus, Damanhour, Rosetta (Rashid), and Kafr El Dawwar. Coins, lamps, animal bones, and pottery from Roman and later Eastern Roman (Byzantine) eras are some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Dark Ages
The term Greek Dark Ages refers to the period of Greek history from the end of the Mycenaean palatial civilization, around 1100 BC, to the beginning of the Archaic age, around 750 BC. Archaeological evidence shows a widespread collapse of Bronze Age civilization in the Eastern Mediterranean world at the outset of the period, as the great palaces and cities of the Mycenaeans were destroyed or abandoned. At about the same time, the Hittite civilization suffered serious disruption, as cities from Troy to Gaza were destroyed. In Egypt, the New Kingdom fell into disarray, which led to the Third Intermediate Period of Egypt. Following the collapse, fewer, smaller settlements suggest extensive famine and depopulation. In Greece, the Linear B script used by Mycenaean bureaucrats to write the Greek language ceased, with the Greek alphabet not developing until the beginning of the Archaic Period. The decoration on Greek pottery after about 1100 BC lacks the figurative d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buto
Buto ( grc, Βουτώ, ar, بوتو, ''Butu''), Bouto, Butus ( grc, links=no, Βοῦτος, ''Boutos'')Herodotus ii. 59, 63, 155. or Butosus was a city that the Ancient Egyptians called Per-Wadjet. It was located 95 km east of Alexandria in the Nile Delta of Egypt. What in classical times the Greeks called Buto, stood about midway between the Taly ( Bolbitine) and Thermuthiac ( Sebennytic) branches of the Nile, a few kilometers north of the east-west Butic River and on the southern shore of the Butic Lake ( el, Βουτικὴ λίμνη, ''Boutikē limnē''). Today, it is called Tell El Fara'in ("Hill of the Pharaohs"), near the villages of Ibtu (or Abtu), Kom Butu, and the city of Desouk ( ar, دسوق). History Buto was a sacred site in dedication to the goddess Wadjet and was an important cultural site during prehistoric Egypt, from the Paleolithic to 3100 BC. Buto-Maadi culture was the most important Lower Egyptian prehistoric culture, dating from 4000 - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leto
In ancient Greek mythology and Ancient Greek religion, religion, Leto (; grc-gre, Λητώ , ''Lētṓ'', or , ''Lātṓ'' in Ancient Greek dialects#Provenance, Doric Greek) is a goddess and the mother of Apollo, the god of music, and Artemis, the goddess of the hunt.Hesiod, ''Theogony'404–409/ref> She is the daughter of the Titan (mythology), Titans Coeus and Phoebe (Titaness), Phoebe, and the sister of Asteria (Titaness), Asteria. In the Olympian scheme, the king of gods Zeus is the father of her twins, Apollo and Artemis, which Leto conceived after her hidden beauty accidentally caught the eye of Zeus. Classical Greek myths record little about Leto other than her pregnancy and search for a place where she could give birth to Apollo and Artemis, since Hera, the wife of Zeus, in her jealousy ordered all lands to shun her and deny her shelter. Hera is also usually the one to have sent the monstrous Python (mythology), Python, a giant serpent, against Leto to pursue and harm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oracle
An oracle is a person or agency considered to provide wise and insightful counsel or prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by deities. As such, it is a form of divination. Description The word ''oracle'' comes from the Latin verb ''ōrāre'', "to speak" and properly refers to the priest or priestess uttering the prediction. In extended use, ''oracle'' may also refer to the ''site of the oracle'', and to the oracular utterances themselves, called ''khrēsmē'' 'tresme' (χρησμοί) in Greek. Oracles were thought to be portals through which the gods spoke directly to people. In this sense, they were different from seers (''manteis'', μάντεις) who interpreted signs sent by the gods through bird signs, animal entrails, and other various methods.Flower, Michael Attyah. ''The Seer in Ancient Greece.'' Berkeley: University of California Press, 2008. The most important oracles of Greek antiquity were Pythia (priestess to Apoll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twenty-sixth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XXVI, alternatively 26th Dynasty or Dynasty 26) dynasty was the last native dynasty to rule Egypt before the Persian conquest in 525 BC (although others followed). The dynasty's reign (664–525 BC) is also called the Saite Period after the city of Sais, where its pharaohs had their capital, and marks the beginning of the Late Period of ancient Egypt.Aidan Dodson, Dyan Hilton. ''The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt''. The American University in Cairo Press, London 2004 History This dynasty traced its origins to the Twenty-fourth Dynasty. Psamtik I was probably a descendant of Bakenranef. Following the Assyrian conquest of Egypt by the Neo-Assyrian Empire during the reigns of Taharqa and Tantamani, and the subsequent collapse of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, Psamtik I was recognized as sole king over all of Egypt. Psamtik formed alliances with King Gyges of Lydia, who sent him mercenaries from Caria and ancient Greec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psammetichus I
Wahibre Psamtik I ( Ancient Egyptian: ) was the first pharaoh of the Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt, the Saite period, ruling from the city of Sais in the Nile delta between 664–610 BC. He was installed by Ashurbanipal of the Neo-Assyrian Empire, against the Kushite rulers of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty, but later gained more autonomy as the Assyrian Empire declined. Name The Egyptian name , pronounced as , was a short form of , meaning "the man of (the Libyan deity) Meṯek." His name was rendered by the Assyrians as Pishamilki (Akkadian: ), by the Ancient Greeks as (), and by the Romans as . Psamtik was also called Nabu-shezibanni (Akkadian: and ), meaning "O Nabu, save me!" by the Assyrians. Background In 671 BCE, the Assyrian king Esarhaddon invaded Egypt. This invasion was directed against the Kushite rulers of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, who had been in control of Upper Egypt, rather than against the native Egyptian rulers. The Assyrians created an adminis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
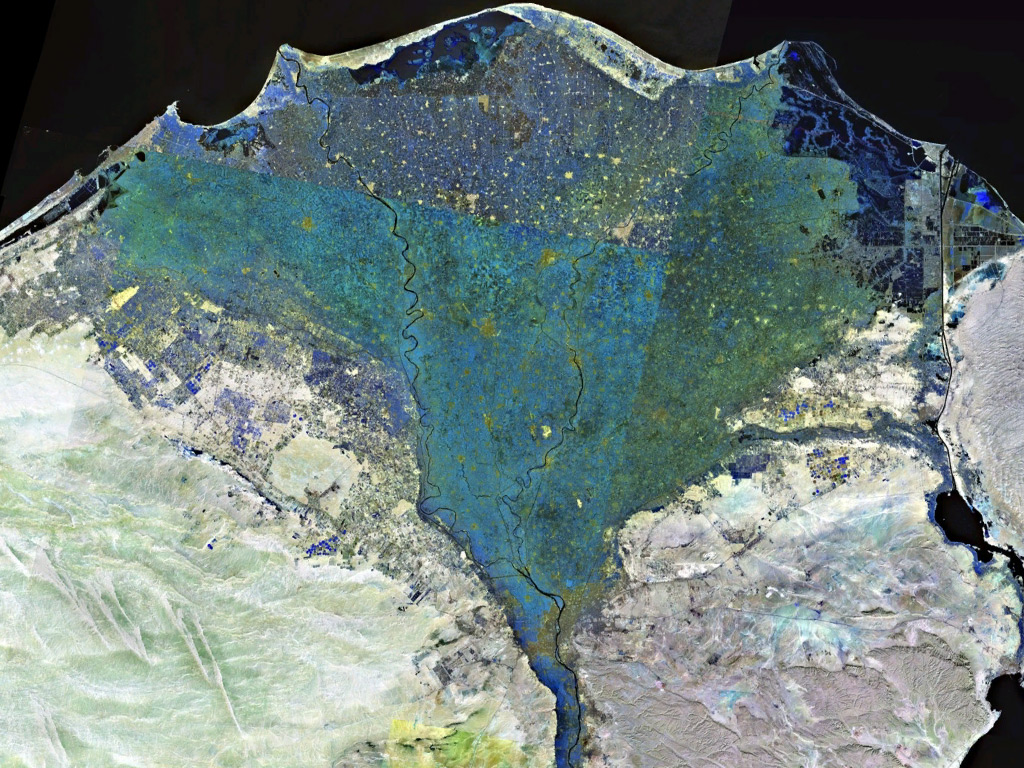
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers of Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same name. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta and enters the coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, vessels used for piracy are pirate ships. The earliest documented instances of piracy were in the 14th century BC, when the Sea Peoples, a group of ocean raiders, attacked the ships of the Aegean and Mediterranean civilisations. Narrow channels which funnel shipping into predictable routes have long created opportunities for piracy, as well as for privateering and commerce raiding. Historic examples include the waters of Gibraltar, the Strait of Malacca, Madagascar, the Gulf of Aden, and the English Channel, whose geographic structures facilitated pirate attacks. The term ''piracy'' generally refers to maritime piracy, although the term has been generalized to refer to acts committed on land, in the air, on computer networks, and (in scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
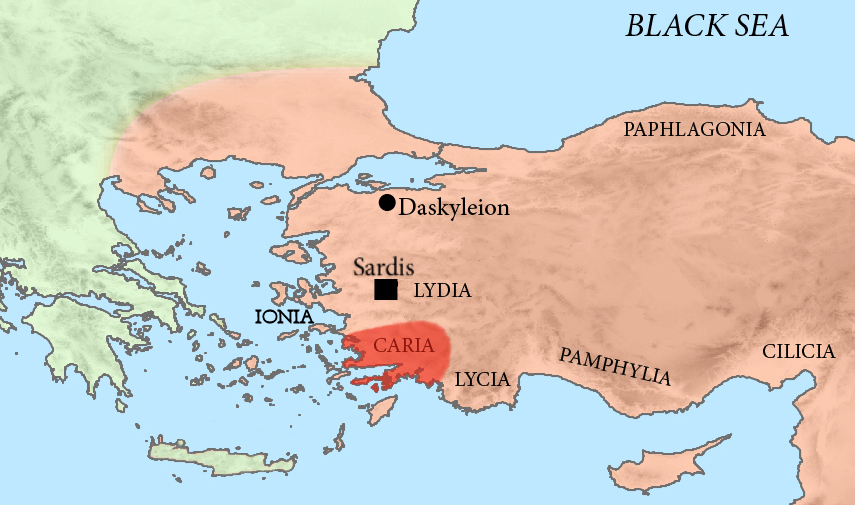
Carians
The Carians (; grc, Κᾶρες, ''Kares'', plural of , ''Kar'') were the ancient inhabitants of Caria in southwest Anatolia. Historical accounts Karkisa It is not clear when the Carians enter into history. The definition is dependent on corresponding Caria and the Carians to the "Karkiya" or "Karkisa" mentioned in the Hittites, Hittite records. Bronze Age Karkisa are first mentioned as having aided the Assuwa League against the Hittite King Tudhaliya I. Later in 1323 BC, King Arnuwandas II was able to write to Karkiya for them to provide asylum for the deposed Manapa-Tarhunta of "the land of the Seha River", one of the principalities within the Luwians, Luwian Arzawa complex in western Anatolia. This they did, allowing Manapa-Tarhunta to take back his kingdom. In 1274 BC, Karkisa are also mentioned among those who fought on the History of the Hittites, Hittite Empire side against the Egyptians in the Battle of Kadesh. Taken as a whole, Hittite records seem to point at a Luw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionians
The Ionians (; el, Ἴωνες, ''Íōnes'', singular , ''Íōn'') were one of the four major tribes that the Greeks considered themselves to be divided into during the ancient period; the other three being the Dorians, Aeolians, and Achaeans. The Ionian dialect was one of the three major linguistic divisions of the Hellenic world, together with the Dorian and Aeolian dialects. When referring to populations, “''Ionian''” defines several groups in Classical Greece. In its narrowest sense, the term referred to the region of Ionia in Asia Minor. In a broader sense, it could be used to describe all speakers of the Ionic dialect, which in addition to those in Ionia proper also included the Greek populations of Euboea, the Cyclades, and many cities founded by Ionian colonists. Finally, in the broadest sense it could be used to describe all those who spoke languages of the East Greek group, which included Attic. The foundation myth which was current in the Classical p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for having written the '' Histories'' – a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars. Herodotus was the first writer to perform systematic investigation of historical events. He is referred to as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus has been criticized for his inclusion of "legends and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |