|
National Unemployed Workers' Movement
The National Unemployed Workers' Movement was a British organisation set up in 1921 by members of the Communist Party of Great Britain. It aimed to draw attention to the plight of unemployed workers during the post First World War slump, the 1926 General Strike and later the Great Depression, and to fight the Means Test. Activities The NUWM was founded by Wal Hannington, and led in Scotland by Harry McShane. From 1921 until 1929 it was called the National Unemployed Workers' Committee Movement. The NUWM became the foremost body responsible for organising the unemployed on a national basis in the interwar period, these years being characterised by high levels of unemployment. A central element of its activities was a series of hunger marches to London, organised in 1922, 1929, 1930, 1932, 1934 and 1936. The largest of these was the National Hunger March, 1932, that was followed by some days of serious violence across central London with 75 people being badly injured, which in turn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Party Of Great Britain
The Communist Party of Great Britain (CPGB) was the largest communist organisation in Britain and was founded in 1920 through a merger of several smaller Marxist groups. Many miners joined the CPGB in the 1926 general strike. In 1930, the CPGB founded the ''Daily Worker'' (renamed the ''Morning Star'' in 1966). In 1936, members of the party were present at the Battle of Cable Street, helping organise resistance against the British Union of Fascists. In the Spanish Civil War the CPGB worked with the USSR to create the British Battalion of the International Brigades, which party activist Bill Alexander commanded. In World War II, the CPGB mirrored the Soviet position, opposing or supporting the war in line with the involvement of the USSR. By the end of World War II, CPGB membership had nearly tripled and the party reached the height of its popularity. Many key CPGB members became leaders of Britain's trade union movement, including most notably Jessie Eden, Abraham Lazarus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Unionism
Industrial unionism is a trade union organizing method through which all workers in the same industry are organized into the same union, regardless of skill or trade, thus giving workers in one industry, or in all industries, more leverage in bargaining and in strike situations. Industrial unionism contrasts with craft unionism, which organizes workers along lines of their specific trades. History Early history Eugene Debs formed the American Railway Union (ARU) as an industrial organization in response to limitations of craft unions. Railroad engineers and firemen had called a strike, but other employees, particularly conductors who were organized into a different craft, did not join that strike. The conductors piloted scab engineers on the train routes, helping their employers to break the strike. In June 1894, the newly formed, industrially organized ARU voted to join in solidarity with an ongoing strike against the Pullman company. The sympathy strike demonstrated the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organizations Disestablished In 1946
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose. The word is derived from the Greek word ''organon'', which means tool or instrument, musical instrument, and organ. Types There are a variety of legal types of organizations, including corporations, governments, non-governmental organizations, political organizations, international organizations, armed forces, charities, not-for-profit corporations, partnerships, cooperatives, and educational institutions, etc. A hybrid organization is a body that operates in both the public sector and the private sector simultaneously, fulfilling public duties and developing commercial market activities. A voluntary association is an organization consisting of volunteers. Such organizations may be able to operate without legal formalities, depending on jurisdiction, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organizations Established In 1921
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose. The word is derived from the Greek word ''organon'', which means tool or instrument, musical instrument, and organ. Types There are a variety of legal types of organizations, including corporations, governments, non-governmental organizations, political organizations, international organizations, armed forces, charities, not-for-profit corporations, partnerships, cooperatives, and educational institutions, etc. A hybrid organization is a body that operates in both the public sector and the private sector simultaneously, fulfilling public duties and developing commercial market activities. A voluntary association is an organization consisting of volunteers. Such organizations may be able to operate without legal formalities, depending on jurisdiction, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workers Alliance Of America
The Workers Alliance of America (WAA) was a Popular Front era political organization established in March 1935 in the United States which united several efforts to mobilize unemployed workers under a single banner. Founded by the Socialist Party of America (SPA), the Workers Alliance was later joined by the Unemployed Councils of the USA, a mass organization of the Communist Party USA (CPUSA), and by the National Unemployed Leagues originating with A.J. Muste's Conference for Progressive Labor Action (CPLA) and successor organizations. The WAA was initially headed by Socialist David Lasser, but the organization gradually came to be dominated by the CPUSA, which had superior size and organizational discipline compared to its partners. Originally resembling a trade union for relief workers employed by the Works Progress Administration (WPA), in its later incarnation it came to resemble a political pressure group focused upon winning additional funding of the WPA by a budget-conscio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unemployed Councils
The Unemployed Councils of the USA (UC) was a mass organization of the Communist Party, USA established in 1930 in an effort to organize and mobilize unemployed workers to advance party policy goals in preparation for an anticipated final conflict to overthrow capitalism. The UC was the organizational successor of the Unemployment Council of New York, a broad-based organization established by various trade unions in New York City in the spring of 1921, during the economic downturn which followed the termination of the First World War. The organization was dissolved through merger into the Workers Alliance of America, a parallel organization affiliated with the Socialist Party of America, in April 1936. Organizational history Forerunners In March 1921 a conference was held in New York City to address the unemployment question.Franklin Folsom, ''Impatient Armies of the Poor: The Story of Collective Action of the Unemployed, 1808-1942.'' Niwot, CO: University Press of Colorado, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow City Hall
Glasgow's City Halls and Old Fruitmarket is a concert hall and former market located on Candleriggs, in the Merchant City, Glasgow, Scotland. History The City Halls are part of a market complex designed by John Carrick in 1882, but the grand hall itself was designed by George Murray and opened in 1841. It was the first hall suitable for large gatherings and concerts to be built in the City and played host to the likes of Benjamin Disraeli, Charles Dickens, Hungarian patriot Lajos Kossuth and William Ewart Gladstone. From its early days it hosted a wide variety of popular and classical concerts including those by touring groups such as Louis-Antoine Jullien's celebrated London-based orchestra and Charles Halle's orchestra from Manchester. Glasgow's first regular orchestral subscription concert series, played by an orchestra managed by the Glasgow Choral Union, was given in the grand hall from 1874 until the opening of the much larger St Andrew's Hall in 1877. Arthur Sullivan was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Lansbury
George Lansbury (22 February 1859 – 7 May 1940) was a British politician and social reformer who led the Labour Party from 1932 to 1935. Apart from a brief period of ministerial office during the Labour government of 1929–31, he spent his political life campaigning against established authority and vested interests, his main causes being the promotion of social justice, women's rights, and world disarmament. Originally a radical Liberal, Lansbury became a socialist in the early 1890s, and thereafter served his local community in the East End of London in numerous elective offices. His activities were underpinned by his Christian beliefs which, except for a short period of doubt, sustained him through his life. Elected to the UK Parliament in 1910, he resigned his seat in 1912 to campaign for women's suffrage, and was briefly imprisoned after publicly supporting militant action. In 1912, Lansbury helped to establish the '' Daily Herald'' newspaper, and became its edito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poplar High Street
Poplar High Street is a street in Poplar and partly in Blackwall, Tower Hamlets, in the East End of London. Although the street became less used after 1860, it had previously been the principal street in Poplar. Notable buildings on Poplar High Street * New City College - Tower Hamlets * Poplar Hospital * St Matthias Old Church St Matthias Old Church is the modern name given to the Poplar Chapel built by the East India Company in 1654, in Poplar in the East End of London. The church is designated a Grade II* listed building. St Matthias Old Church is one of the ver ... References Streets in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets Poplar, London {{London-road-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1923 United Kingdom Dock Strike
The 1923 United Kingdom dock strike commenced in June 1923 when over 50,000 dockers were unhappy with a proposed pay reduction from 8s to 5s 6d for a four-hour minimum employment period. Ernest Bevin, the general secretary of the recently founded Transport and General Workers' Union had signed an agreement accepting this new rate of pay. The strike began in Hull but soon spread across the UK. Thousands of dockers left the TGWU to joined the Amalgamated Stevedores' Labour Protection League to form the National Amalgamated Stevedores, Lightermen, Watermen and Dockers The National Amalgamated Stevedores and Dockers (NASD), sometimes referred to as the National Amalgamated Stevedores' and Dockers' Society, was a trade union in the United Kingdom. History The union was founded in 1871 as the Labour Protection .... References {{reflist 1923 labor disputes and strikes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
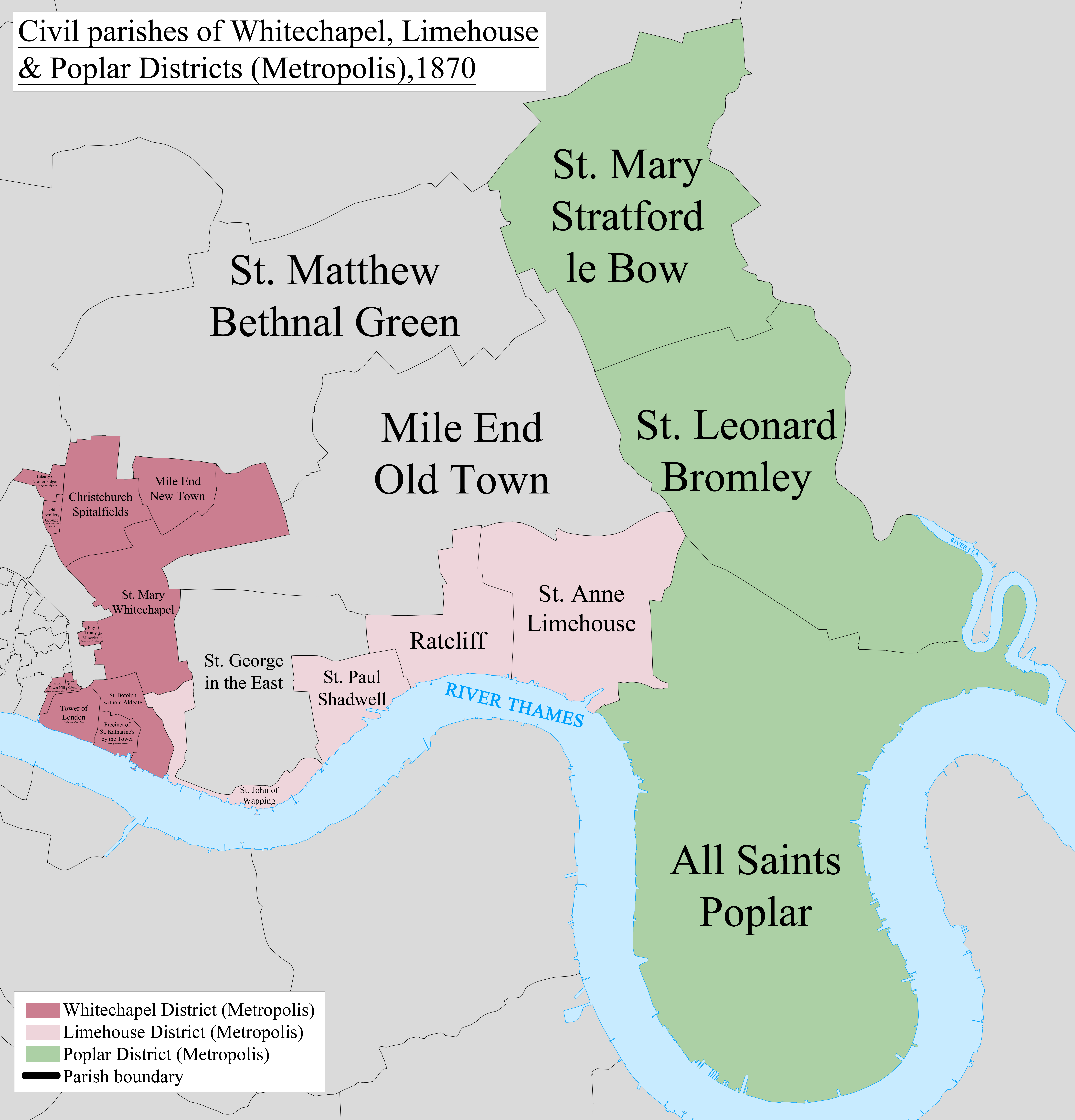
Poplar, London
Poplar is a district in East London, England, the administrative centre of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, borough of Tower Hamlets. Five miles (8 km) east of Charing Cross, it is part of the East End of London, East End. It is identified as a major district centre in the London Plan, with its district centre being Chrisp Street Market, a significant commercial and retail centre surrounded by extensive residential development. Poplar includes Poplar Baths, Blackwall Yard and Trinity Buoy Wharf and the locality of Blackwall, London, Blackwall. Originally part of the Stepney#Manor and Ancient Parish, Manor and Ancient Parish of Stepney, the ''Hamlet of Poplar'' had become an autonomous area of Stepney by the 17th century, and an independent parish in 1817. The Hamlet and Parish of Poplar included Blackwall, London, Blackwall and the Isle of Dogs. After a series of mergers, Poplar became part of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in 1965. History Origin and administrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |