|
National Spiritual Mobilization Movement
The was an organization established in the Empire of Japan as part of the controls on civilian organizations under the National Mobilization Law by Prime Minister Fumimaro Konoe. Representatives from 74 nationalist organizations were assembled at the Prime Minister's residence in October 1937, and were told that their organizations were now part of the "Central League of the Spiritual Mobilization Movement", headed by Admiral Ryokitsu Arima and under the joint supervision of the Ministry of Home Affairs and Ministry of Education. The purpose of the Movement would be to rally the nation for a total war effort against China in the Second Sino-Japanese War. Konoe later ordered another 19 nationalist organizations to join the League. This movement and other policies were part of "New Order" ('' Shintaisei'') which was promulgated on 3 November 1938, a holiday marking emperor Meiji's birthday. Apart from public calls for increased patriotism, the National Spiritual Mobilization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxury Is Our Enemy
Luxury may refer to: *Luxury goods, an economic good or service for which demand increases more than proportionally as income rises *Luxury tax, tax on products not considered essential, such as expensive cars **Luxury tax (sports), surcharge put on the aggregate payroll of a sports team to the extent to which it exceeds a predetermined guideline level set by the league *Luxury car, expensive automobiles *Luxury train, expensive tourist trains *Luxury yacht, expensive privately owned, professionally crewed yacht *Luxury apartment, a type of property that is intended to provide its occupant with higher-than-average levels of comfort, quality and convenience *Luxury hotel, high-quality amenities, full-service accommodations and the highest level of personalized services *Luxury resort, exclusive vacation facilities *Luxury box, term for a special seating section in arenas, stadiums and other sports venues *Luxury magazine, magazines devoted to fine craft and luxury goods Music ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
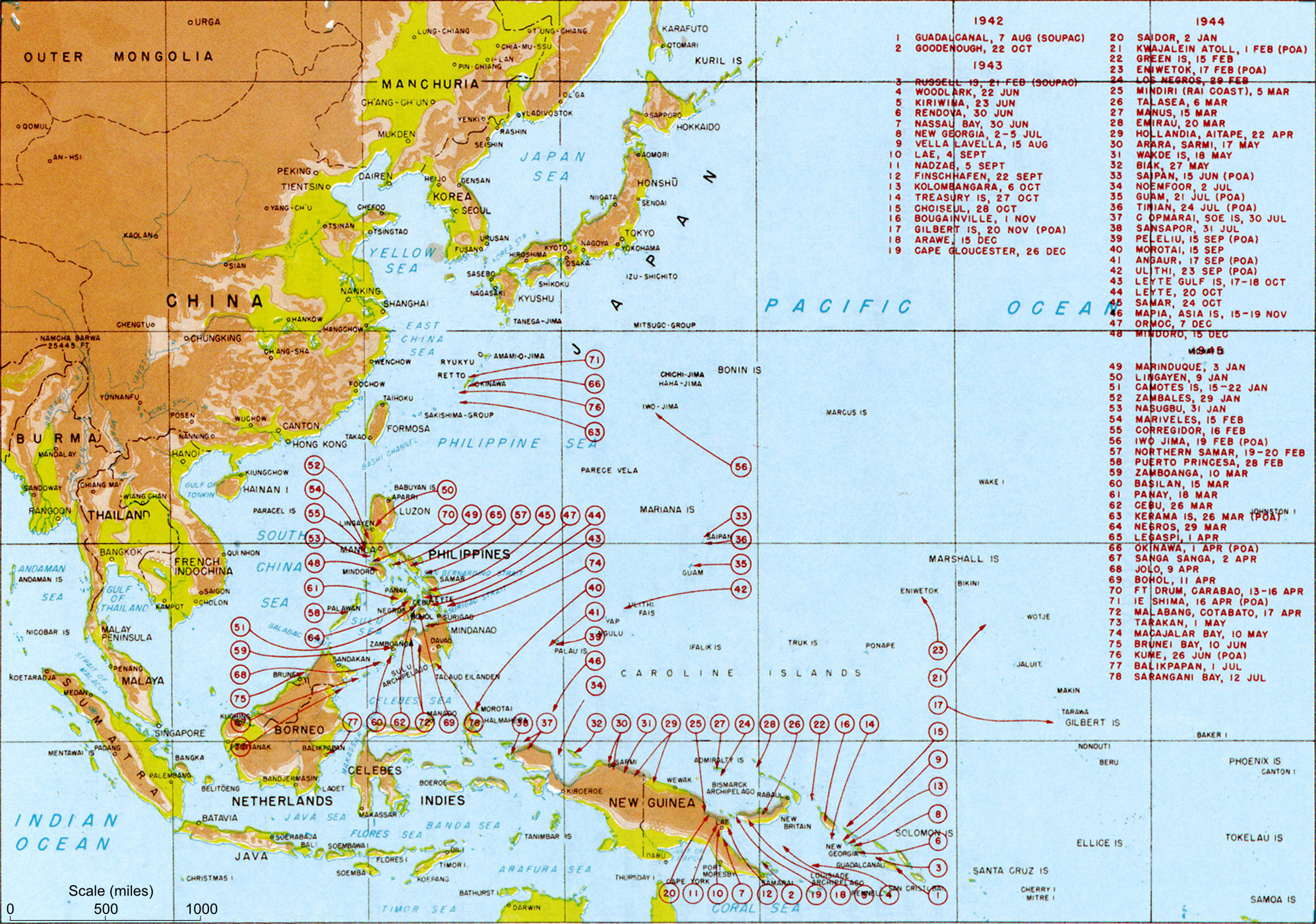
Japan In World War II
Japan during World War II refers to the history of the Empire of Japan during World War II. This includes the invasion of the Republic of China, the annexation of French Indochina and the subsequent invasion of British India, the Pacific War and the Surrender of Japan. Prelude The Empire of Japan had been expanding its territory since before World War I. In 1931, Japan invaded and conquered Manchuria in northeast China. The bordering Chinese territory of Jehol was also taken in 1933, and in 1936, Japan created a similar puppet state in Inner Mongolia. Japanese invasion of China The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Theater of the Second World War. The beginning of the war is conventionally dated to the Marco Polo Bridge Incident on 7 July 1937, when a dispute between Japanese and Chinese troops in Peking esca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taisei Yokusankai
The , or Imperial Aid Association, was the Empire of Japan's ruling organization during much of World War II. It was created by Prime Minister Fumimaro Konoe on 12 October 1940, to promote the goals of his ("New Order") movement. It evolved into a "statist" ruling political party which aimed at removing the sectionalism in the politics and economics in the Empire of Japan to create a totalitarian one-party state, in order to maximize the efficiency of Japan's total war effort in China. When the organization was launched officially, Konoe was hailed as a "political savior" of a nation in chaos; however, internal divisions soon appeared. Origins Based on recommendations by the , Konoe originally conceived of the Imperial Rule Assistance Association as a reformist political party to overcome the deep-rooted differences and political cliques between bureaucrats, politicians and the military. During the summer of 1937, Konoe appointed 37 members chosen from a broad political spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
League Of Diet Members Believing The Objectives Of The Holy War
The was a political party coalition in the lower house of the Diet of Japan formed on March 25, 1940, with the backing of the Imperial Japanese Army as a reaction against a speech made by Saitō Takao, of the ''Rikken Minseitō'' critical of the government’s aggressive policies in the Second Sino-Japanese War. page 139-150 The official establishment took measures, including setting up this group, and attempted to censor public "doubting". The speaker was censured in Parliament, and expelled from the chamber (and from his own party), to make an example. Its membership comprised a total of 250 active members in the lower house, which represented all political parties of the period. This grouping pushed for its members to be considered as "loyal" politicians in the militarists cause, differing from Saitō, who was accused of being a traitor to nation and the real values of the country. The grouping published an open declaration: "We welcome the four years of sacred campaigning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrender Of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) had become incapable of conducting major operations and an Allied invasion of Japan was imminent. Together with the United Kingdom and China, the United States called for the unconditional surrender of the Japanese armed forces in the Potsdam Declaration on 26 July 1945—the alternative being "prompt and utter destruction". While publicly stating their intent to fight on to the bitter end, Japan's leaders (the Supreme Council for the Direction of the War, also known as the "Big Six") were privately making entreaties to the publicly neutral Soviet Union to mediate peace on terms more favorable to the Japanese. While maintaining a sufficient level of diplomatic engagement with the Japanese to give them the impression they might be wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Commander Of The Allied Powers
was the title held by General Douglas MacArthur during the United States-led Allied occupation of Japan following World War II. It issued SCAP Directives (alias SCAPIN, SCAP Index Number) to the Japanese government, aiming to suppress its "militaristic nationalism". The position was created at the start of the occupation of Japan on August 14, 1945. In Japan, the position was generally referred to as GHQ (General Headquarters), as SCAP also referred to the offices of the occupation (which was officially referred by SCAP itself as ), including a staff of several hundred US civil servants as well as military personnel. Some of these personnel effectively wrote a first draft of the Japanese Constitution, which the National Diet then ratified after a few amendments. Australian, British Empire, and New Zealand forces under SCAP were organized into a sub-command known as British Commonwealth Occupation Force. These actions led MacArthur to be viewed as the new Imperial force in Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokutai
is a concept in the Japanese language translatable as "system of government", "sovereignty", "national identity, essence and character", "national polity; body politic; national entity; basis for the Emperor's sovereignty; Japanese constitution" or nation. The word is also a short form of the (unrelated) name for the National Sports Festival of Japan. Etymology ''Kokutai'' originated as a Sino-Japanese loanword from Chinese ''guoti'' (; "state political system; national governmental structure"). The Japanese compound word joins and . According to the ''Hanyu Da Cidian'', the oldest ''guoti'' usages are in two Chinese classic texts. The 2nd century BCE ''Guliang zhuan'' () to the Spring and Autumn Annals glosses ''dafu'' () as ''guoti'' metaphorically meaning "embodiment of the country". The 1st century CE ''Book of Han'' history of Emperor Cheng of Han used ''guoti'' to mean "laws and governance" of Confucianist officials. Pre-1868 The historical origins of ''kokutai'' go b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonarigumi
The was the smallest unit of the national mobilization program established by the Japanese government in World War II. It consisted of units consisting of 10-15 households organized for fire fighting, civil defense and internal security. History and development Neighborhood mutual-aid associations existed in Japan since before the Edo period. The system was formalized on 11 September 1940 by order of the Home Ministry (Japan) under Imperial Rule Assistance Association by the cabinet of Prime Minister Fumimaro Konoe. Participation was mandatory. Each unit was responsible for allocating rationed goods, distributing government bonds, fire fighting, public health, and civil defense. Each unit was also responsible for assisting the National Spiritual Mobilization Movement by distribution of government propaganda and organizing participation in patriotic rallies. The government also found the ''tonarigumi'' useful for the maintenance of public security. A network of informants was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded language to produce an emotional rather than a rational response to the information that is being presented. Propaganda can be found in news and journalism, government, advertising, entertainment, education, and activism and is often associated with material which is prepared by governments as part of war efforts, political campaigns, health campaigns, revolutionaries, big businesses, ultra-religious organizations, the media, and certain individuals such as soapboxers. In the 20th century, the English term ''propaganda'' was often associated with a manipulative approach, but historically, propaganda has been a neutral descriptive term of any material that promotes certain opinions or ideologies. Equivalent non-English terms have also la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Programs
A radio program, radio programme, or radio show is a segment of content intended for broadcast on radio. It may be a one-time production or part of a periodically recurring series. A single program in a series is called an episode. Radio networks International radio In the 1950s, a small but growing cohort of rock and pop music fans, dissatisfied with the BBC's output, would listen to Radio Luxembourg, but to some extent and probably not enough to have any impact on the BBC's monopoly and invariably only at night, when the signal from Luxembourg was stronger. During the post-1964 period, western Europe offshore radio (such as Radio Caroline broadcasting from ships at anchor or abandoned forts) helped to supply the demand for the pop and rock music. The BBC launched its own pop music station, BBC Radio 1, in 1967. The international broadcasts became highly popular in major world languages. Of particular impact were programmes by BBC World Service, Voice of America, Radio Mosco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demonstration (political)
A political demonstration is an action by a mass group or collection of groups of people in favor of a political or other cause or people partaking in a protest against a cause of concern; it often consists of walking in a mass march formation and either beginning with or meeting at a designated endpoint, or rally, in order to hear speakers. It is different from mass meeting. Actions such as blockades and sit-ins may also be referred to as demonstrations. Demonstrations can be nonviolent or violent (usually referred to by participants as "Militant (word), militant"), or can begin as nonviolent and turn violent depending on the circumstances. Sometimes riot police or other forms of Law enforcement agency, law enforcement become involved. In some cases, this may be in order to try to prevent the protest from taking place at all. In other cases, it may be to prevent clashes between rival groups, or to prevent a demonstration from spreading and turning into a riot. History The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |