|
Nanwang Water Division System
Nanwang water division system ( or ) is a historical system for management of the water in the Grand Canal in the Shandong province in China. Nanwang water division system is built in the area around Nanwang in Wenshang County in Jining city that was the highest point of the historical canal Emperor Yongle (r. 1402–1424) moved the Ming dynasty capital from Nanjing to Beijing which increased the need for traffic along the Grand Canal. The passage through Shandong Peninsula (Huitong Canal) was only to be crossed with great difficulties because the water level was often not high enough and sluices were necessary and passage through sluices. Therefore at the year 1411 the emperor ordered Song Li to renovate the problematic section. With help from the local expert Bai Ying a water diversion system which included dozens of sluice gates was built. When the system was completed it could adjust the water flow of the canal so the needed transports could be controlled. The Daicun D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Canal (China)
The Grand Canal, known to the Chinese as the Jing–Hang Grand Canal (, or more commonly, as the「大运河」("Grand Canal")), a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is the longest canal or artificial river in the world. Starting in Beijing, it passes through Tianjin and the provinces of Hebei, Shandong, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang to the city of Hangzhou, linking the Yellow River and Yangtze River. The oldest parts of the canal date back to the 5th century BC, but the various sections were first connected during the Sui dynasty (581–618 AD). Dynasties in 1271–1633 significantly restored and rebuilt the canal and altered its route to supply their capital. The Grand Canal played a major role in reunifying north and south China. The canal was built by conscripted laborers and connected the Yellow River in the north with the Yangtze River in the south, which made it much easier to transport grain from the south to the centers of political and military power in north China. The total length ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
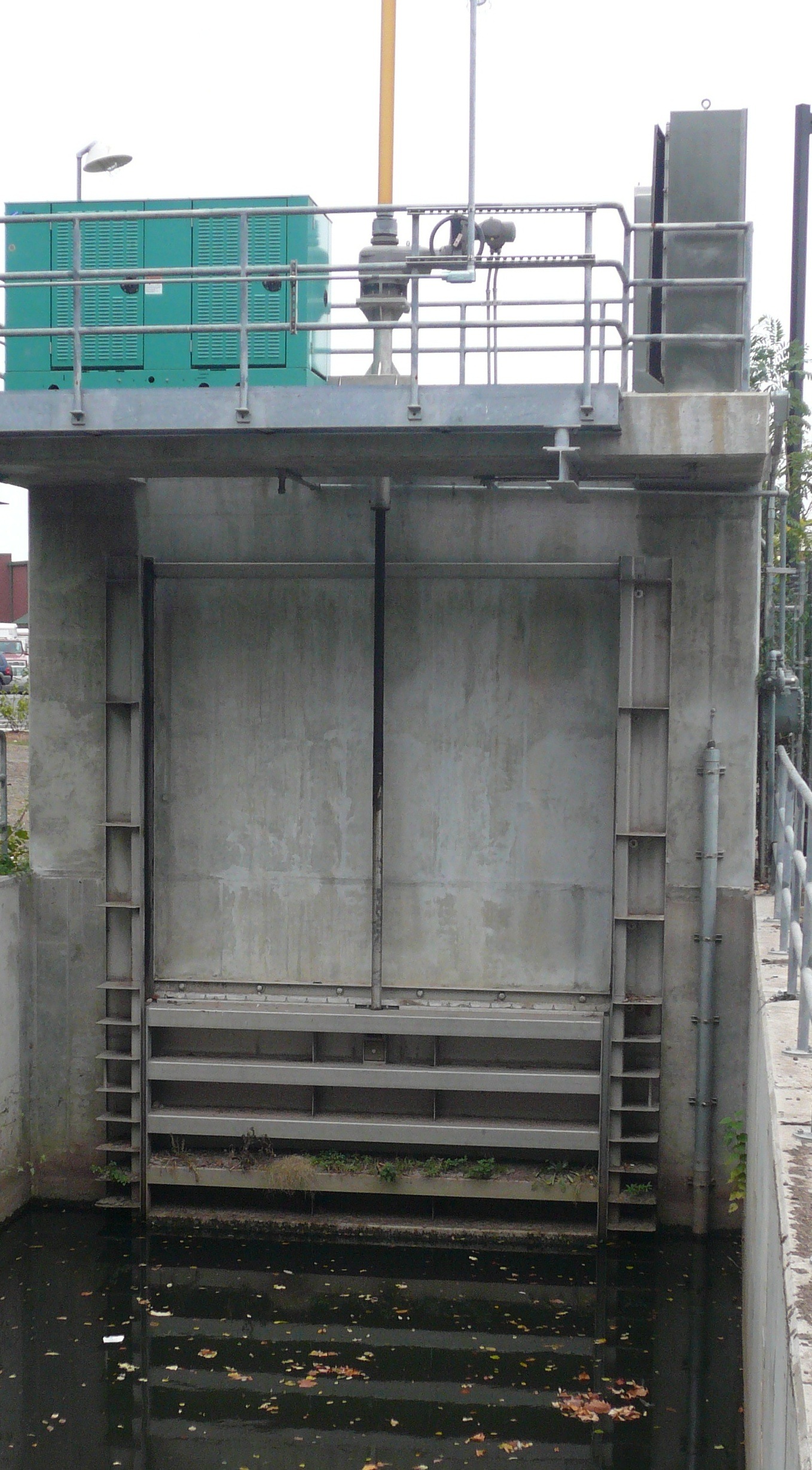
Sluice
Sluice ( ) is a word for a channel controlled at its head by a movable gate which is called a sluice gate. A sluice gate is traditionally a wood or metal barrier sliding in grooves that are set in the sides of the waterway and can be considered as a bottom opening in a wall. Sluice gates are one of the most common hydraulic structures in controlling flow rate and water level in open channels such as rivers and canals. They also could be used to measure the flow. A water channel containing a sluice gate forms a type of lock to manage the water flow and water level. It can also be an open channel which processes material, such as a River Sluice used in gold prospecting or fossicking. A mill race, leet, flume, penstock or lade is a sluice channeling water toward a water mill. The terms sluice, sluice gate, knife gate, and slide gate are used interchangeably in the water and wastewater control industry. They are also used in wastewater treatment plants and to recover minerals in minin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major National Historical And Cultural Sites In Shandong
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators, major is one rank above captain, and one rank below lieutenant colonel. It is considered the most junior of the field officer ranks. Background Majors are typically assigned as specialised executive or operations officers for battalion-sized units of 300 to 1,200 soldiers while in some nations, like Germany, majors are often in command of a company. When used in hyphenated or combined fashion, the term can also imply seniority at other levels of rank, including ''general-major'' or ''major general'', denoting a low-level general officer, and ''sergeant major'', denoting the most senior non-commissioned officer (NCO) of a military unit. The term ''major'' can also be used with a hyphen to denote the leader of a military band such as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
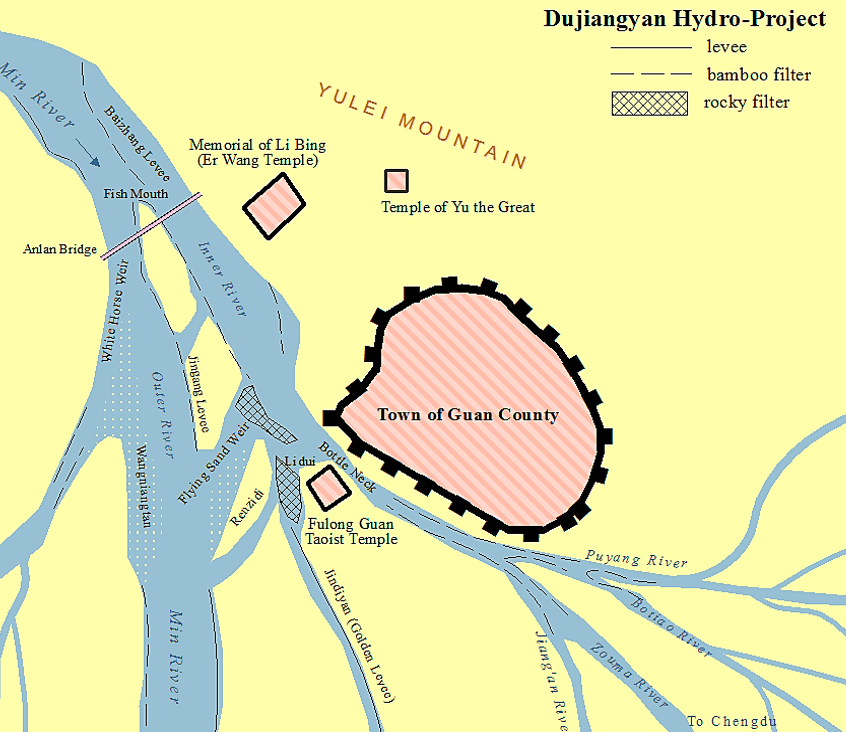
Dujiangyan
The Dujiangyan () is an ancient irrigation system in Dujiangyan City, Sichuan, China. Originally constructed around 256 BC by the State of Qin (state), Qin as an irrigation and flood control project, it is still in use today. The system's infrastructure develops on the Min River (Sichuan), Min River (Minjiang), the longest tributary of the Yangtze. The area is in the west part of the Chengdu Plain, between the Sichuan Basin and the Tibetan Plateau. Originally, the Min would rush down from the Min Mountains and slow down abruptly after reaching the Chengdu Plain, filling the watercourse with silt, thus making the nearby areas extremely prone to floods. King Zhao of Qin commissioned the project, and the construction of the Dujiangyan harnessed the river using a new method of channeling and dividing the water rather than simply damming it. The water management scheme is still in use today to irrigate over of land in the region. The Dujiangyan, the Zhengguo Canal in Shaanxi and the Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology and represents a part of the archaeological record. Sites may range from those with few or no remains visible above ground, to buildings and other structures still in use. Beyond this, the definition and geographical extent of a "site" can vary widely, depending on the period studied and the theoretical approach of the archaeologist. Geographical extent It is almost invariably difficult to delimit a site. It is sometimes taken to indicate a settlement of some sort although the archaeologist must also define the limits of human activity around the settlement. Any episode of deposition such as a hoard or burial can form a site as well. Development-led archaeology undertaken as cultural resources management has the disadvantage (or the ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levee
A levee (), dike (American English), dyke (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is a structure that is usually soil, earthen and that often runs parallel (geometry), parallel to the course of a river in its floodplain or along low-lying coastlines. The purpose of a levee is to keep the course of rivers from changing and to protect against flooding of the area adjoining the river or coast. Levees can be naturally occurring ridge structures that form next to the bank of a river, or be an artificially constructed fill dirt, fill or wall that regulates water levels. Ancient civilizations in the Indus Valley civilisation, Indus Valley, ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia and China all built levees. Today, levees can be found around the world, and failures of levees due to erosion or other causes can be major disasters. Etymology Speakers of American English (notably in the Midwestern United States, Midwest and Deep South) u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
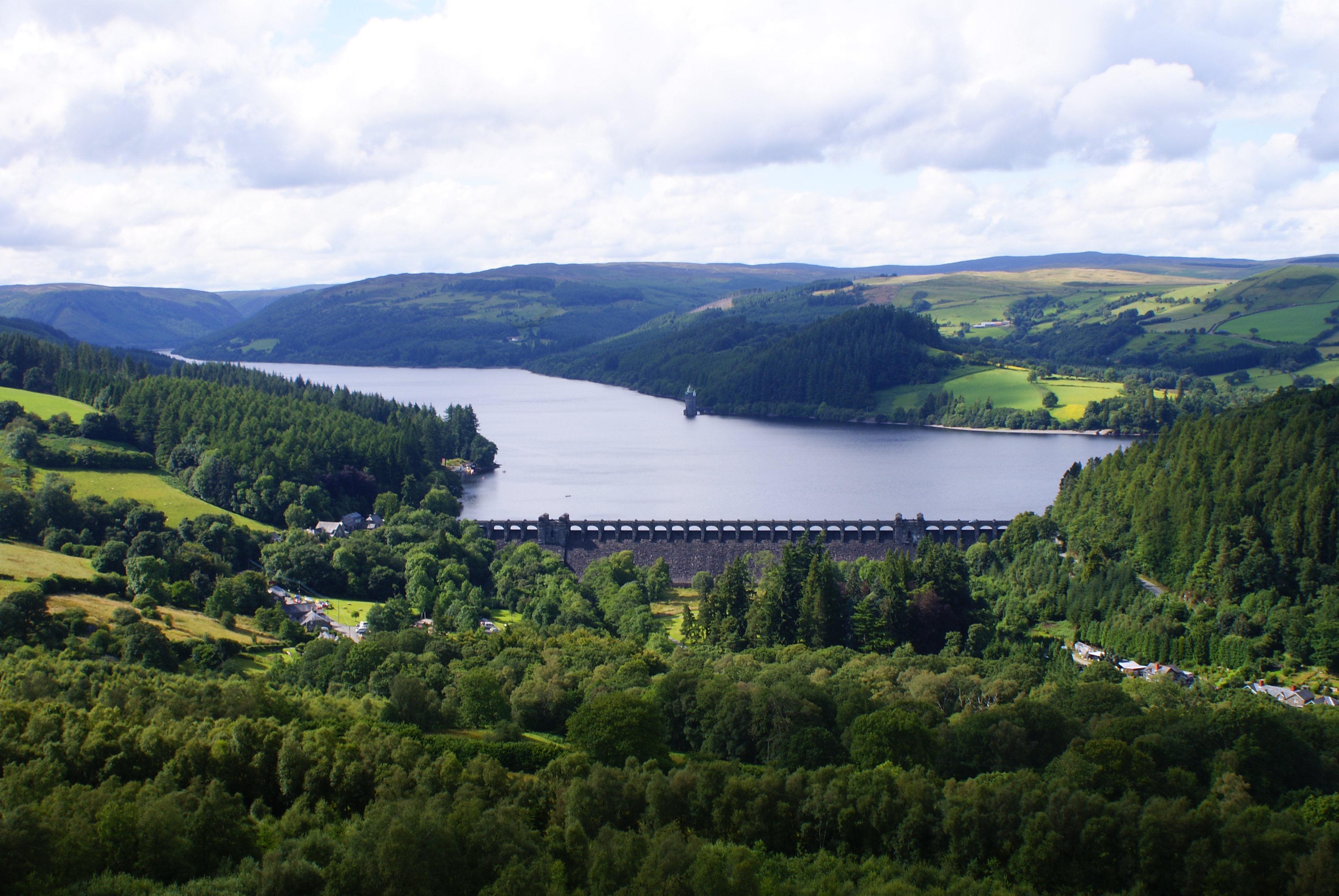
Reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation. Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of water, interrupting a watercourse to form an embayment within it, through excavation, or building any number of retaining walls or levees. In other contexts, "reservoirs" may refer to storage spaces for various fluids; they may hold liquids or gasses, including hydrocarbons. ''Tank reservoirs'' store these in ground-level, elevated, or buried tanks. Tank reservoirs for water are also called cisterns. Most underground reservoirs are used to store liquids, principally either water or petroleum. Types Dammed valleys Dammed reservoirs are artificial lakes created and controlled by a dam A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bai Ying
BAI or Bai may refer to: BAI Organizations *BAI Communications, telecommunications infrastructure company *BAI (organization), professional organization for financial services in the United States *Badminton Association of India, India's governing body for badminton *Banco Angolano de Investimentos, a bank in Angola *Board of Audit and Inspection, supreme audit institution of South Korea *Brittany Ferries, a French shipping company *Broadcasting Authority of Ireland, regulator of broadcasting in Ireland *Bureau of Animal Industry, formerly an agency of the United States Department of Agriculture *WBAI, a listener-supported radio station in New York City Science *Beck Anxiety Inventory, a psychological assessment tool *Body adiposity index, a method of measuring body fat in humans *Brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 Other uses * BAI (file format), file format for performing electronic cash management balance reporting * BA-I, a Soviet armoured car * Battlefield air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Song (minister)
Li Song or Song Li is the name of: ;People surnamed Li *Emperor Shunzong of Tang (761–806), emperor of the Tang dynasty *Li Song (politician) (died 948), politician of Later Tang, Later Jin, Liao and Later Han dynasties during the Five Dynasties period *Li Song (painter) ( 1190–1230), Song dynasty imperial court painter *Song Li (bioengineer) Song Li () is a Chancellor Professor and Department Chair of Bioengineering at University of California, Los Angeles. He received his Ph.D. in bioengineering from University of California, San Diego. Dr. Li was a Bioengineering faculty at Universit ... (born 1965), Chinese-born bioengineering researcher at the University of California Los Angeles, USA * Li Song (minister), (1358-1422) Ming dynasty Minister of Works ;People surnamed Song * Song Li (speed skater) (born 1981), Chinese speed skater {{hndis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shandong Peninsula
The Shandong (Shantung) Peninsula or Jiaodong (Chiaotung) Peninsula is a peninsula in Shandong Province in eastern China, between the Bohai Sea to the north and the Yellow Sea to the south. The latter name refers to the east and Jiaozhou. Geography The waters bordering the peninsula are Laizhou Bay to the northwest, which opens into the Bohai Sea to the north, which in turn passes through the Bohai Strait to the northeast into the Yellow Sea to the east and south. The peninsula's territory comprises three prefecture-level cities of Shandong: Qingdao in the southwest, Yantai in the north and centre, and Weihai at the eastern tip. Shandong Peninsula is the largest peninsula in China. Stretching into the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea, it is 290 kilometers long from east to west, 190 kilometers wide from north to south, and 50 kilometers narrow. The total area of Shandong Peninsula is 73,000 square kilometers. Geologically it was once connected to the Korean Peninsula and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region. Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilization along the lower reaches of the Yellow River. It has served as a pivotal cultural and religious center for Taoism, Chinese Buddhism and Confucianism. Shandong's Mount Tai is the most revered mountain of Taoism and a site with one of the longest histories of continuous religious worship in the world. The Buddhist temples in the mountains to the south of the provincial capital of Jinan were once among the foremost Buddhist sites in China. The city of Qufu is the birthplace of Confucius and was later established as the center of Confucianism. Confucianism developed from what was later called the Hundred Schools of Thought from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius. Shandong's location at the intersection of ancient and modern n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |