|
Nanolaser
A nanolaser is a laser that has nanoscale dimensions and it refers to a micro-/nano- device which can emit light with light or electric excitation of nanowires or other nanomaterials that serve as resonators. A standard feature of nanolasers includes their light confinement on a scale approaching or suppressing the diffraction limit of light. These tiny lasers can be modulated quickly and, combined with their small footprint, this makes them ideal candidates for on-chip optical computing. History Albert Einstein proposed the stimulated emission in 1916, which contributed to the first demonstration of laser in 1961. From then on, people have been pursuing the miniaturization of lasers for more compact size and less energy consumption all the time. Since people noticed that light has different interactions with matter at the nanoscale in the 1990s, significant progress has been made to achieve the miniaturization of lasers and increase power conversion efficiency. Various types of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peidong Yang
Peidong Yang (; born 1971) is a Chinese-American chemist, material scientist, and businessman. He is currently a professor at the University of California, Berkeley (since 1999) and a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. He is a Professor of Chemistry and a Professor of Materials Science. His research group studies the synthesis of nanomaterials and their electronic and optical properties. He is also a Department Head at the Joint Center for Artificial Photosynthesis, Senior Faculty Scientist at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, and Deputy Director of the Center of Integrated Nanomechanical Systems (COINS). He is an associate editor of the ''Journal of the American Chemical Society'', an American Chemical Society Journal. Biography Yang received a B.A. in Chemistry from the University of Science and Technology of China in 1993. For his graduate studies, he worked with Charles M. Lieber at Harvard University, and in 1997, he was awarded a Ph.D. in Chemist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light which is ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers and lidar (light detection and ranging). Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow spectrum. Alternatively, temporal coherence can be used to produce ultrashort pulses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaser
A spaser or plasmonic laser is a type of laser which aims to confine light at a subwavelength scale far below Rayleigh's diffraction limit of light, by storing some of the light energy in electron oscillations called surface plasmon polaritons. The phenomenon was first described by David J. Bergman and Mark Stockman in 2003. The word ''spaser'' is an acronym for " surface plasmon amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first such devices were announced in 2009 by three groups: a 44-nanometer-diameter nanoparticle with a gold core surrounded by a dyed silica gain medium created by researchers from Purdue, Norfolk State and Cornell universities, a nanowire on a silver screen by a Berkeley group, and a semiconductor layer of 90 nm surrounded by silver pumped electrically by groups at the Eindhoven University of Technology and at Arizona State University. While the Purdue-Norfolk State-Cornell team demonstrated the confined plasmonic mode, the Berkeley team and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaser
A spaser or plasmonic laser is a type of laser which aims to confine light at a subwavelength scale far below Rayleigh's diffraction limit of light, by storing some of the light energy in electron oscillations called surface plasmon polaritons. The phenomenon was first described by David J. Bergman and Mark Stockman in 2003. The word ''spaser'' is an acronym for " surface plasmon amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first such devices were announced in 2009 by three groups: a 44-nanometer-diameter nanoparticle with a gold core surrounded by a dyed silica gain medium created by researchers from Purdue, Norfolk State and Cornell universities, a nanowire on a silver screen by a Berkeley group, and a semiconductor layer of 90 nm surrounded by silver pumped electrically by groups at the Eindhoven University of Technology and at Arizona State University. While the Purdue-Norfolk State-Cornell team demonstrated the confined plasmonic mode, the Berkeley team and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanowire Lasers
Semiconductor nanowire lasers are nano-scaled lasers that can be embedded on chips and constitute an advance for computing and information processing applications. Nanowire lasers are coherent light sources (single mode optical waveguides) as any other laser device, with the advantage of operating at the nanoscale. Built by molecular beam epitaxy, nanowire lasers offer the possibility for direct integration on silicon, and the construction of optical interconnects and data communication at the chip scale. Nanowire lasers are built from III–V semiconductor heterostructures. Their unique 1D configuration and high refractive index allow for low optical loss and recirculation in the active nanowire core region. This enables subwavelength laser sizes of only a few hundred nanometers. Nanowires are Fabry–Perot resonator cavities defined by the end facets of the wire, therefore they do not require polishing or cleaving for high-reflectivity facets as in conventional lasers. Properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
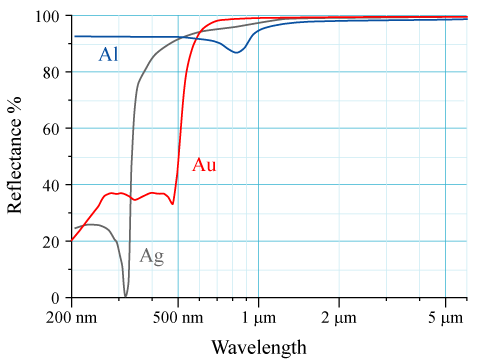
Reflectance
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the response of the electronic structure of the material to the electromagnetic field of light, and is in general a function of the frequency, or wavelength, of the light, its polarization, and the angle of incidence. The dependence of reflectance on the wavelength is called a ''reflectance spectrum'' or ''spectral reflectance curve''. Mathematical definitions Hemispherical reflectance The ''hemispherical reflectance'' of a surface, denoted , is defined as R = \frac, where is the radiant flux ''reflected'' by that surface and is the radiant flux ''received'' by that surface. Spectral hemispherical reflectance The ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in frequency'' and ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in wavelength'' of a surface, denoted and respectively, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Laser Medium
The active laser medium (also called gain medium or lasing medium) is the source of optical gain within a laser. The gain results from the stimulated emission of photons through electronic or molecular transitions to a lower energy state from a higher energy state previously populated by a pump source. Examples of active laser media include: * Certain crystals, typically doped with rare-earth ions (e.g. neodymium, ytterbium, or erbium) or transition metal ions (titanium or chromium); most often yttrium aluminium garnet ( Y3 Al5 O12), yttrium orthovanadate (YVO4), or sapphire (Al2O3); and not often Caesium cadmium bromide ( Cs Cd Br3) (Solid-state lasers) * Glasses, e.g. silicate or phosphate glasses, doped with laser-active ions; * Gases, e.g. mixtures of helium and neon (HeNe), nitrogen, argon, krypton, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, or metal vapors; ( Gas lasers) * Semiconductors, e.g. gallium arsenide (GaAs), indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs), or gallium nitride (GaN). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Properties Of Nanolaser
Property is the ownership of land, resources, improvements or other tangible objects, or intellectual property. Property may also refer to: Mathematics * Property (mathematics) Philosophy and science * Property (philosophy), in philosophy and logic, an abstraction characterizing an object *Material properties, properties by which the benefits of one material versus another can be assessed *Chemical property, a material's properties that becomes evident during a chemical reaction * Physical property, any property that is measurable whose value describes a state of a physical system *Semantic property *Thermodynamic properties, in thermodynamics and materials science, intensive and extensive physical properties of substances *Mental property, a property of the mind studied by many sciences and parasciences Computer science * Property (programming), a type of class member in object-oriented programming * .properties, a Java Properties File to store program settings as name-value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lasing Threshold
The lasing threshold is the lowest excitation level at which a laser's output is dominated by stimulated emission rather than by spontaneous emission. Below the threshold, the laser's output power rises slowly with increasing excitation. Above threshold, the slope of power vs. excitation is orders of magnitude greater. The linewidth of the laser's emission also becomes orders of magnitude smaller above the threshold than it is below. Above the threshold, the laser is said to be ''lasing''. The term "lasing" is a back formation from "laser," which is an acronym, not an agent noun. Theory The lasing threshold is reached when the optical gain of the laser medium is exactly balanced by the sum of all the losses experienced by light in one round trip of the laser's optical cavity. This can be expressed, assuming steady-state operation, as :R_1 R_2\exp(2g_\text\,l) \exp(-2\alpha l) = 1. Here R_1 and R_2 are the mirror (power) reflectivities, l is the length of the gain medium, \ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photonic Topological Insulator
Photonic topological insulators are artificial electromagnetic materials that support topologically non-trivial, unidirectional states of light. Photonic topological phases are classical electromagnetic wave analogues of electronic topological phases studied in condensed matter physics. Similar to their electronic counterparts, they, can provide robust unidirectional channels for light propagation. The field that studies these phases of light is referred to as topological photonics, even though the working frequency of these ''electromagnetic'' topological insulators may fall in other parts of the electromagnetic spectrum such as the microwave range. History Topological order in solid state systems has been studied in condensed matter physics since the discovery of integer quantum Hall effect. But topological matter attracted considerable interest from the physics community after the proposals for possible observation of symmetry-protected topological phases (or the so-called ''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micro Disk Resonator Sem
Micro may refer to: Measurement * micro- (μ), a metric prefix denoting a factor of 10−6 Places * Micro, North Carolina, town in U.S. People * DJ Micro, (born Michael Marsicano) an American trance DJ and producer *Chii Tomiya (都宮 ちい, born 1991), Japanese female professional wrestler, ring name Micro Arts, entertainment, and media * Micro (comics), often known as Micro, a character in Marvel Comics * ''Micro'' (novel), techno-thriller by Michael Crichton, published posthumously in 2011 * Micro (Thai band), a Thai rock band formed in 1983 * ''IEEE Micro'', a peer-reviewed scientific journal Brands and enterprises * Micro Cars, Sri Lankan automobile company, established 1995 * Micro Center, an American computer department store, established 1979 * Micro ISV (mISV or μISV), a term for a small independent software vendor * Micro Mobility Systems, Swiss company producing kickscooters Computing * ''Micro'', a mostly-obsolete term for a microcomputer, e.g.: **BBC Mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Well
A quantum well is a potential well with only discrete energy values. The classic model used to demonstrate a quantum well is to confine particles, which were initially free to move in three dimensions, to two dimensions, by forcing them to occupy a planar region. The effects of quantum confinement take place when the quantum well thickness becomes comparable to the de Broglie wavelength of the carriers (generally electrons and holes), leading to energy levels called "energy subbands", i.e., the carriers can only have discrete energy values. A wide variety of electronic quantum well devices have been developed based on the theory of quantum well systems. These devices have found applications in lasers, photodetectors, modulators, and switches for example. Compared to conventional devices, quantum well devices are much faster and operate much more economically and are a point of incredible importance to the technological and telecommunication industries. These quantum well devic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |