|
Nainativu
Nainativu ( ta, நயினாதீவு ''Nainatheevu'', si, නාගදීපය ''Nagadeepa''), is a small but notable island off the coast of Jaffna Peninsula in the Northern Province, Sri Lanka. The name of the island alludes to the folklore inhabitants, the Naga people. It is home to the Hindu shrine of Nagapooshani Amman Temple; one of the prominent 64 Shakti Peethas, and the Buddhist shrine Nagadeepa Purana Viharaya. Historians note the island is mentioned in the ancient Tamil Sangam literature of nearby Tamil Nadu such as ''Manimekalai'' where it was mentioned as ''Manipallavam'' ( ta, மணிபல்லவம்), and ancient Buddhist legends of Sri Lanka such as '' Mahavamsa''. Ptolemy, a Greek cartographer, describes the islands around the Jaffna peninsula as ''Nagadiba'' ( el, Ναγάδιβα) in the first century CE. History Nāka Tivu / Nāka Nadu was the name of the whole Jaffna peninsula in some historical documents. There are number of Buddhist myth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
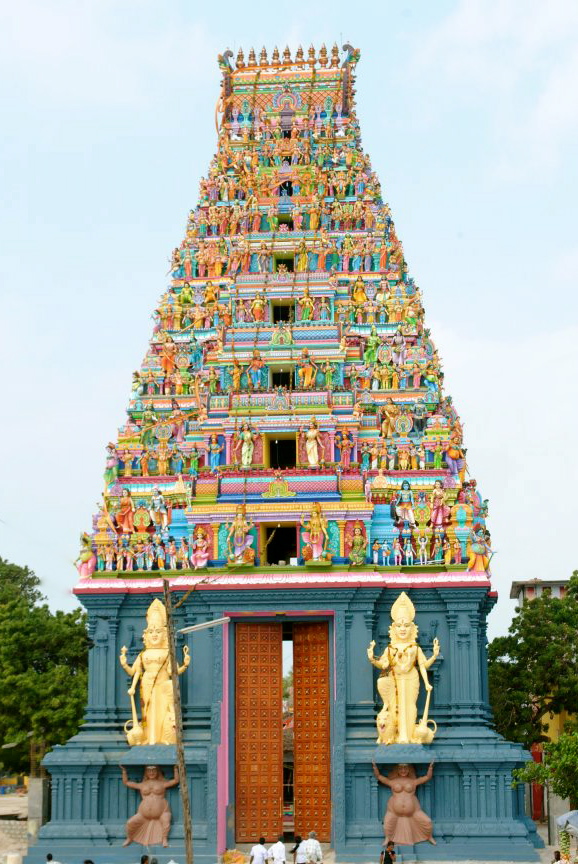
Nainativu Nagapooshani Amman Temple
Nainativu Nagapooshani Amman Temple _ta.html" ;"title="nowiki/> ta">:ta:நயினாதீவு நாகபூசணி அம்மன் கோயில், நயினாதீவு நாகபூசணி அம்மன் கோயில், translit=Nayiṉātīvu Nākapūcaṇi Am'maṉ Kōyil - Meaning: Nainativu (island/city of the temple); Nagapooshani (The Goddess who wears snakes as jewellery); Amman (Goddess)] is an ancient and historic Hindu temple located amidst the Palk Strait on the island of Nainativu, Sri Lanka. It is dedicated to Parvati who is known as Nagapooshani or Bhuvaneswari and her consort, Shiva who is named here as Nayinaar. The temple's fame is accredited to Adi Shankaracharya, a 9th-century Hindu philosopher, for identifying it as one of the prominent 64 Shakti Peethams in ''Shakti Peetha Stotram'' and its mention in the Brahmanda Purana. The temple complex houses four ''gopurams'' (gateway towers) ranging from 20–25 feet in height, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naga People (Lanka)
The Naga people are believed by some to be an ancient tribe who once inhabited Sri Lanka and various parts of Southern India. There are references to Nagas in several ancient texts such as Mahavamsa, Manimekalai, Mahabharata and also in other Sanskrit and Pali literature. They were generally represented as a class of super-humans taking the form of serpents who inhabit a subterranean world. Certain places such as Nagadeepa in Jaffna and Kalyani in Gampaha are mentioned as their abodes. The names of some Naga kings in Sri Lankan legends such as Mani Akkhitha (Mani Naga) and Mahodara are also found in Sanskrit literature among superhuman Nagas, and the cult of Mani Naga prevailed in India up to medieval times. The Jaffna Peninsula was mentioned in Tamil literature as ''Naka Nadu'', in Pali literature as ''Nagadeepa'' and in Greek gazetteer as ''Nagadiba''. The name ''Nagabhumi'' was also found on a Brahmi-inscribed coin from Uduthurai, Jaffna and in a Tamil inscription from Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagadeepa Purana Viharaya
Nagadeepa Purana Vihara ( si, නාගදීප පුරාණ විහාරය, ta, நயினாதீவு நாக விகாரை ) is an ancient Buddhist temple situated in Jaffna district of Northern Province, Sri Lanka. It is among the country's sixteen holiest Buddhist shrines (''Solosmasthana''). According to contemporary history, the Gautama Buddha visited the site after five years of attaining Enlightenment to settle the dispute between two warring Naga kings, Chulodara and Mahodara. Ancient history according to the Mahavamsa chronicles and the Tamil Buddhist epic Manimekalai mentions a gem-studded throne and a stone with the Buddha’s footprint at the island Nainativu, (also known as Nagadeepa) which pilgrims from India visited. History and development The site is known as the place where Lord Buddha came during his second visit to Sri Lanka, after five years of attaining Enlightenment, to intervene and mediate in settling a dispute between two Naga Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kayts
Kayts ( ta, ஊர்காவற்துறை, translit=Ūrkāvaṟtuṟai'','' ), is one of the important villages in Velanai Island which is a small island off the coast of the Jaffna Peninsula in northern Sri Lanka. There are number of other villages within the Velanai Islands such as Allaippiddi, Mankumpan, Velanai, Saravanai, Puliyankoodal, Suruvil, Naranthanai, Karampon and Melinchimunai. Most of the people are Tamils. There are number of Hindu temples as well as churches and a mosque. The island is also served by a dozen schools. Since 1983 Kayts Island has also been the scene of violence as part of the Sri Lankan Civil War, including the Allaipiddy massacre. On 8 August 1992, Major General Denzil Kobbekaduwa and Commodore Mohan Jayamaha were killed along with several senior army and navy officers when their Land Rover hit a land mine off Araly Point in Kayts. Etymology The name Kayts is of colonial origin. The name is derived from the Portuguese "Caes dos Elefant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shakti Peethas
The Shakti Pitha or the Shakti Peethas ( sa, शक्ति पीठ, , ''seat of Shakti'') are significant shrines and pilgrimage destinations in Shaktism, the goddess-centric denomination in Hinduism. The shrines are dedicated to various forms of Adi Shakti. Various Puranas such as Srimad Devi Bhagavatam state the existence of varying number of 51, 64 and 108 Shakti peethas of which 18 are named as Astadasha ''Maha'' (major) in medieval Hindu texts. Various legends explain how the Shakti Peetha came into existence. The most popular is based on the story of the death of the goddess Sati. Out of grief and sorrow, Lord Shiva carried Sati's body, reminiscing about their moments as a couple, and roamed around the universe with it. Lord Vishnu had cut her body into 51 body parts, using his Sudarshana Chakra, which fell on Earth to become sacred sites where all the people can pay homage to the Goddess. To complete this massively long task, Lord Shiva took the form of Bhairava. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the '' Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quadrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
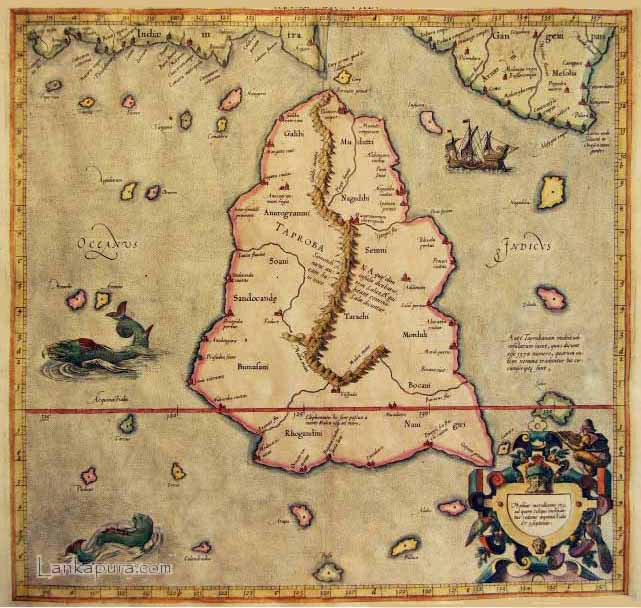
Taprobana
Taprobana ( grc, Ταπροβανᾶ) and Taprobane (, ) was the name by which the Indian Ocean island of Sri Lanka was known to the ancient Greeks. History Reports of the island's existence were known before the time of Alexander the Great as inferred from Pliny. The treatise ''De Mundo'', supposedly by Aristotle (died 322 BC) but according to others by Chrysippus the Stoic (280 to 208 BC), incorrectly states that the island is as large as Great Britain (in fact, it is only about one third as big). The name was first reported to Europeans by the Greek geographer Megasthenes around 290 BC. Herodotus (444 BC) does not mention the island. The first Geography in which it appears is that of Eratosthenes (276 to 196 BC) and was later adopted by Claudius Ptolemy (139 AD) in his geographical treatise to identify a relatively large island south of continental Asia. Writing during the era of Augustus, Greek geographer Strabo makes reference to the island, noting that "Taprobane send ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a śramaṇa, wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in Lumbini, in what is now Nepal, to royal parents of the Shakya clan, but Great Renunciation, renounced his Householder (Buddhism), home life to live as a wandering ascetic ( sa, śramaṇa). After leading a life of begging, asceticism, and meditation, he attained Enlightenment in Buddhism, enlightenment at Bodh Gaya in what is now India. The Buddha thereafter wandered through the lower Indo-Gangetic Plain, teaching and building a Sangha, monastic order. He taught a Middle Way between sensual indulgence and severe asceticism, leading to Nirvana (Buddhism), Nirvana, that is, Vimutti, freedom from Avidyā (Buddhism), ignorance, Upādāna, craving, Saṃsāra (Buddhism), rebirth, and suffering. His teachings are summarized in the Noble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manimekalai
''Maṇimēkalai'' ( ta, மணிமேகலை, ), also spelled ''Manimekhalai'' or ''Manimekalai'', is a Tamil-Buddhist epic composed by Kulavāṇikaṉ Seethalai Sataṉar probably around the 6th century. It is an "anti-love story", a sequel to the "love story" in the earliest Tamil epic ''Silappadikaram'', with some characters from it and their next generation. The epic consists of 4,861 lines in ''akaval'' meter, arranged in 30 cantos. The title ''Manimekalai'' is also the name of the daughter of Kovalan and Madhavi, who follows in her mother's footsteps as a dancer and a Buddhist nun. The epic tells her story. Her physical beauty and artistic achievements seduces the Chola prince Udayakumara. He pursues her. She, a nun of Mahayana Buddhism persuasion, feels a commitment to free herself from human ties. She rejects his advances, yet finds herself drawn to him. She hides, prays and seeks the help of her mother, her Buddhist teacher Aravana Adikal and angels. They teach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kundalakesi
''Kundalakesi'' ( ta, குண்டலகேசி Kuṇṭalakēci, ''lit.'' "woman with curly hair"), also called ''Kuntalakeciviruttam'', is a Tamil Buddhist epic written by Nathakuthanaar, likely sometime in the 10th-century.Aiyangar 2004, p. 360 The epic is a story about love, marriage, getting tired with the married partner, murder and then discovering religion. The ''Kundalakesi'' epic has partially survived into the modern age in fragments, such as in commentaries written centuries later. From these fragments, it appears to be a tragic love story about a Hindu or Jain girl of merchant caste named Kundalakesi who falls in love with Kalan – a Buddhist criminal on a death sentence. The girl's rich merchant father gets the criminal pardoned and freed, the girl marries him. Over time, their love fades and they start irritating each other. During an argument, Kundalakesi reminds him of his criminal past which angers Kalan. A few days later, he invites her to a hike up a hil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemstone
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, or semiprecious stone) is a piece of mineral crystal which, in cut and polished form, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. However, certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, and obsidian) and occasionally organic materials that are not minerals (such as amber, jet, and pearl) are also used for jewelry and are therefore often considered to be gemstones as well. Most gemstones are hard, but some soft minerals are used in jewelry because of their luster or other physical properties that have aesthetic value. Rarity and notoriety are other characteristics that lend value to gemstones. Apart from jewelry, from earliest antiquity engraved gems and hardstone carvings, such as cups, were major luxury art forms. A gem expert is a gemologist, a gem maker is called a lapidarist or gemcutter; a diamond cutter is called a diamantaire. Characteristics and classification The traditional classification in the West, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)
