|
Nahal Snir
The Hasbani River ( ar, الحاصباني / ALA-LC: ''al-Ḥāṣbānī''; he, חצבני ''Ḥatzbaní'') or Snir Stream ( he, נחל שניר / ''Nahal Sənir''), is the major tributary of the Jordan River. Local natives in the mid-19th century knew the river as the Upper Jordan. The Hasbani River derives most of its discharge from two springs in Lebanon, the Wazzani and the Haqzbieh, the latter being a group of springs on the uppermost Hasbani. The Hasbani runs for in Lebanon before crossing the border at Ghajar and shortly after joining with the Banias and Dan Rivers at a point in northern Israel, to form the River Jordan. For about downstream of Ghajar, the Hasbani forms the border between Lebanon and the Golan Heights. The Wazzani's and the Haqzbieh's combined discharge averages 138 million m³ per year. About 20% of the Hasbani flow emerges from the Wazzani Spring at Ghajar, close to the Lebanese-Golan Heights border, about west of the base of Mount Hermon. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordan Valley Unified Water Plan
The Jordan Valley Unified Water Plan, commonly known as the "Johnston Plan", was a plan for the unified water resource development of the Jordan Valley. It was negotiated and developed by US ambassador Eric Johnston between 1953 and 1955, and based on an earlier plan commissioned by United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA). Modeled upon the Tennessee Valley Authority's engineered development plan, it was approved by technical water committees of all the regional riparian countries—Israel, Jordan, Lebanon and Syria.The UNRWA commissioned a plan for the development of the Jordan River; this became widely known as "The Johnston plan". The plan was modelled on the Tennessee Valley Authority development plan for the development of the Jordan River as a single unit. Greg Shapland, (1997''Rivers of Discord: International Water Disputes in the Middle East'' C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, p 14 Though the plan was rejected by the Arab League, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kayaking
Kayaking is the use of a kayak for moving over water. It is distinguished from canoeing by the sitting position of the paddler and the number of blades on the paddle. A kayak is a low-to-the-water, canoe-like boat in which the paddler sits facing forward, legs in front, using a double-bladed paddle to pull front-to-back on one side and then the other in rotation. Most kayaks have closed decks, although sit-on-top and inflatable kayaks are growing in popularity as well. History Kayaks were created thousands of years ago by the Inuit, formerly known as Eskimos, of the northern Arctic regions. They used driftwood and sometimes the skeleton of whale, to construct the frame of the kayak, and animal skin, particularly seal skin was used to create the body. The main purpose for creating the kayak, which literally translates to "hunter's boat" was for hunting and fishing. The kayak's stealth capabilities allowed for the hunter to sneak up behind animals on the shoreline and successf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mekorot
Mekorot ( he, מקורות, lit. "Sources") is the national water company of Israel and the country's top agency for water management. Founded in 1937, it supplies Israel with 90% of its drinking water and operates a cross-country water supply network known as the National Water Carrier. Mekorot and its subsidiaries have partnered with numerous countries around the world in areas including desalination and water management. History Mekorot was established as the "''Ḥevrat ha-Mayim''" ('Water Company') on 15 February 1937 by Levi Shkolnik (later Eshkol, Prime Minister of Israel between 1963-1969), water engineer Simcha Blass, and Pinchas Koslovsky (later Sapir, Minister of Finance between 1963-1968). Water supply system Mekorot supplies 80% of Israel's drinking water and 70% of its water supplies. The company runs 3,000 installations throughout the country for water supply, water quality, infrastructure, sewage purification, desalination, rain enhancement, etc. Mekorot overse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casus Belli
A (; ) is an act or an event that either provokes or is used to justify a war. A ''casus belli'' involves direct offenses or threats against the nation declaring the war, whereas a ' involves offenses or threats against its ally—usually one bound by a mutual defense pact. Either may be considered an A declaration of war usually contains a description of the ''casus belli'' that has led the party in question to declare war on another party. Terminology The term ''casus belli'' came into widespread use in Europe in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries through the writings of Hugo Grotius (1653), Cornelius van Bynkershoek (1707), and Jean-Jacques Burlamaqui (1732), among others, and due to the rise of the political doctrine of ''jus ad bellum'' or "just war theory". The term is also used informally to refer to any "just cause" a nation may claim for entering into a conflict. It is used retrospectively to describe situations that arose before the term came into wide use, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariel Sharon
Ariel Sharon (; ; ; also known by his diminutive Arik, , born Ariel Scheinermann, ; 26 February 1928 – 11 January 2014) was an Israeli general and politician who served as the 11th Prime Minister of Israel from March 2001 until April 2006. Sharon was a commander in the Israeli Army from its creation in 1948. As a soldier and then an officer, he participated prominently in the 1948 Palestine war, becoming a platoon commander in the Alexandroni Brigade and taking part in many battles, including Operation Bin Nun Alef. He was an instrumental figure in the creation of Unit 101 and the reprisal operations, as well as in the 1956 Suez Crisis, the Six-Day War of 1967, the War of Attrition, and the Yom-Kippur War of 1973. Yitzhak Rabin called Sharon "the greatest field commander in our history"."Israel's Man of War", Michael Kramer, ''New York'', pages 19–24, 9 August 1982: "the "greatest field commander in our history," says Yitzak Rabin" Upon retirement from the military, Shar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
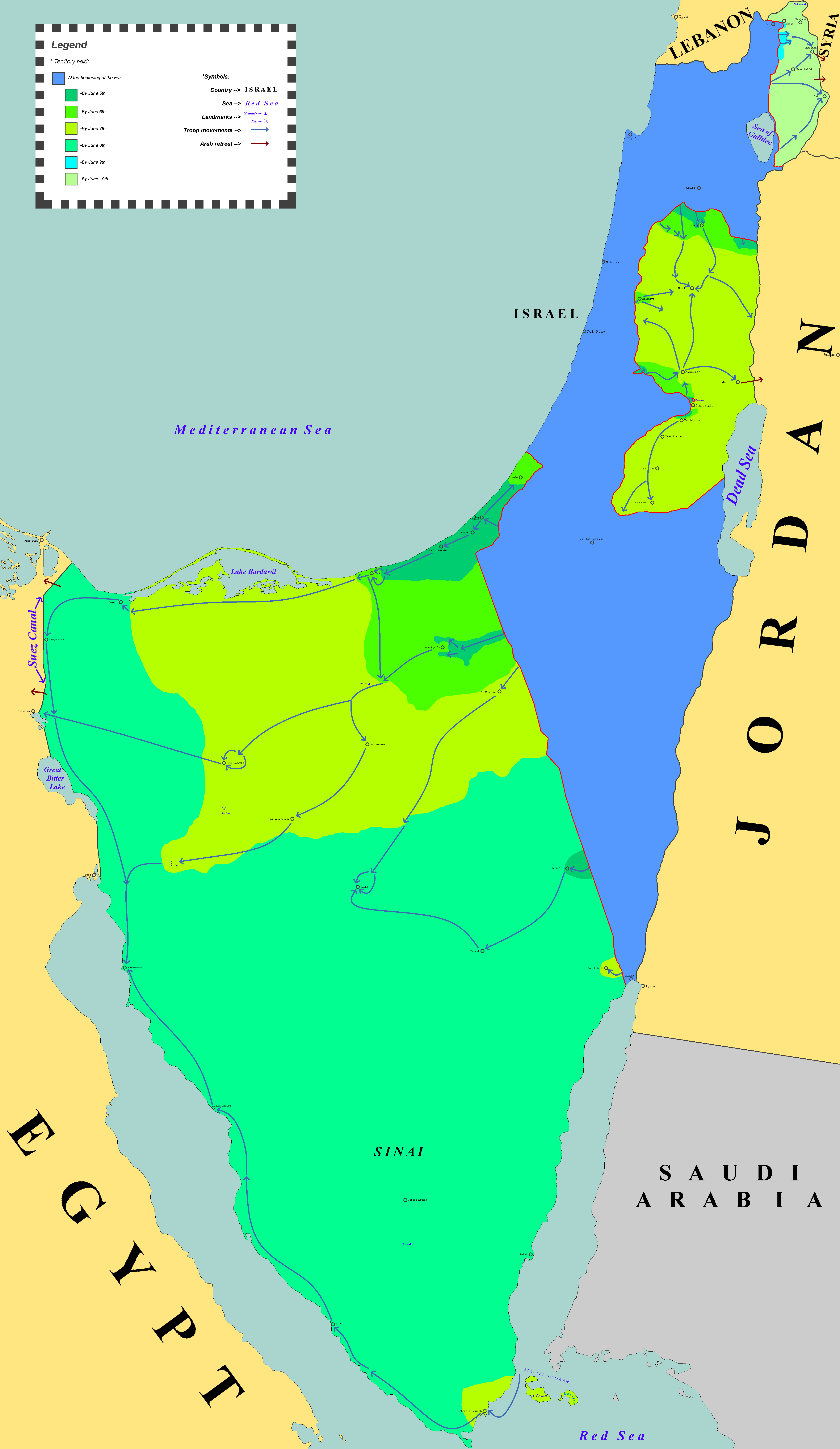
Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 June 1967. Escalated hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbours following the 1949 Armistice Agreements, which were signed at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, First Arab–Israeli War. Earlier, in 1956, regional tensions over the Straits of Tiran escalated in what became known as the Suez Crisis, when Israel invaded Egypt over the Israeli passage through the Suez Canal and Straits of Tiran, Egyptian closure of maritime passageways to Israeli shipping, ultimately resulting in the re-opening of the Straits of Tiran to Israel as well as the deployment of the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) along the Borders of Israel#Border with Egypt, Egypt–Israel border. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Over Water (Jordan River)
The "War over Water", also the Battle over Water, refers to a series of confrontations between Israel and its Arab neighbors from November 1964 to May 1967 over control of water sources in the Jordan River drainage basin. History Early tensions: 1949–64 The 1949 Armistice Agreements which followed the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, created three demilitarized zones on the Israel-Syria border. The southernmost, and also the largest, stretched from the south-eastern part of the Sea of Galilee eastwards to the Yarmuk River where the borders of Israel, Jordan and Syria converge. The issue of water sharing from the Jordan–Yarmuk system turned out to be a major problem between Israel, Syria and Jordan. Small scale water-related skirmishes had occurred following the 1949 agreements. In July 1953, Israel began construction of an intake for its National Water Carrier at the Daughters of Jacob Jordan Bridge in the demilitarized zone north of the Sea of Galilee. Syrian artillery units ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarmouk River
The Yarmuk River ( ar, نهر اليرموك, translit=Nahr al-Yarmūk, ; Greek: Ἱερομύκης, ; la, Hieromyces or ''Heromicas''; sometimes spelled Yarmouk), is the largest tributary of the Jordan River. It runs in Jordan, Syria and Israel, and drains much of the Hauran plateau. Its main tributaries are the wadis of 'Allan and Ruqqad from the north, Ehreir and Zeizun from the east. Although it is narrow and shallow throughout its course, at its mouth it is nearly as wide as the Jordan, measuring thirty feet in breadth and five in depth. The once celebrated Matthew Bridge used to cross the Yarmuk at its confluence with the Jordan. History Yarmuk forms a natural border between the plains to the north - Hauran, Bashan and Golan - and the Gilead mountains to the south. Thus it has often served as boundary line between political entities. Neolithic The Yarmukian is a Pottery Neolithic culture that inhabited parts of Palestine and Jordan. Its type site is at Sha'ar HaGolan, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banias
Banias or Banyas ( ar, بانياس الحولة; he, בניאס, label=Modern Hebrew; Judeo-Aramaic, Medieval Hebrew: פמייס, etc.; grc, Πανεάς) is a site in the Golan Heights near a natural spring, once associated with the Greek god Pan. It had been inhabited for 2,000 years, until it was abandoned and destroyed following the Six Day War.How modern disputes have reshaped the ancient city of Banias : "In June 1967, the penultimate day of the Six Day War saw Israeli tanks storm into Banias in breach of a UN ceasefire accepted by Syria hours earlier. The Israeli general Moshe Dayan had decided to act u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headwater Diversion Plan (Jordan River)
The Headwater Diversion Plan was an Arab League plan to divert two of the three sources of the Jordan River, and prevent them from flowing into the Sea of Galilee, in order to thwart Israel's plans to use the water of the Hasbani and Banias in its National Water Carrier of Israel, National Water Carrier project for out-of-Basin irrigation. The plan was approved by the Arab League in 1964 but Israel prevented the project's development by conducting airstrikes in Syrian territory in April 1967. Background In 1955 the Jordan Valley Unified Water Plan, Unified (Johnston) Plan for the multinational development of Jordan River basin between the Water riparian rights holders was finalized. The Plan was accepted by the technical committees from both Israel and the Arab League. A discussion in the Knesset in July 1955 ended without a vote. The Arab Experts Committee approved the plan in September 1955 and referred it for final approval to the Arab League Council. On 11 October 1955, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It is a unitary republic that consists of 14 governorates (subdivisions), and is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east and southeast, Jordan to the south, and Israel and Lebanon to the southwest. Cyprus lies to the west across the Mediterranean Sea. A country of fertile plains, high mountains, and deserts, Syria is home to diverse ethnic and religious groups, including the majority Syrian Arabs, Kurds, Turkmens, Assyrians, Armenians, Circassians, Albanians, and Greeks. Religious groups include Muslims, Christians, Alawites, Druze, and Yazidis. The capital and largest city of Syria is Damascus. Arabs are the largest ethnic group, and Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)