|
NLRC4
NLR family CARD domain-containing protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NLRC4'' gene. Structure The NLRC4 protein is highly conserved across mammalian species. It bears homology to the ''C. elegans'' Ced4 protein. It contains an N-terminal CARD domain, a central nucleotide binding/ NACHT domain, and a C-terminal leucine rich repeat ( LRR) domain. It belongs to a family of NLR proteins that includes the transcriptional co-activator CIITA and the canonical inflammasome protein NLRP3. A truncated murine NLRC4 was the first member of this family whose crystal structure was solved. Function NLRC4 is best associated with triggering formation of the inflammasome. Unlike NLRP3, certain inflammasome-dependent functions of NLRC4 may be carried out independently of the inflammasome scaffold ASC. Human Ced4 homologs include APAF1, NOD1 (CARD4), and NOD2 (CARD15). These proteins have at least 1 N-terminal CARD domain followed by a centrally located nucleotide-bindi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
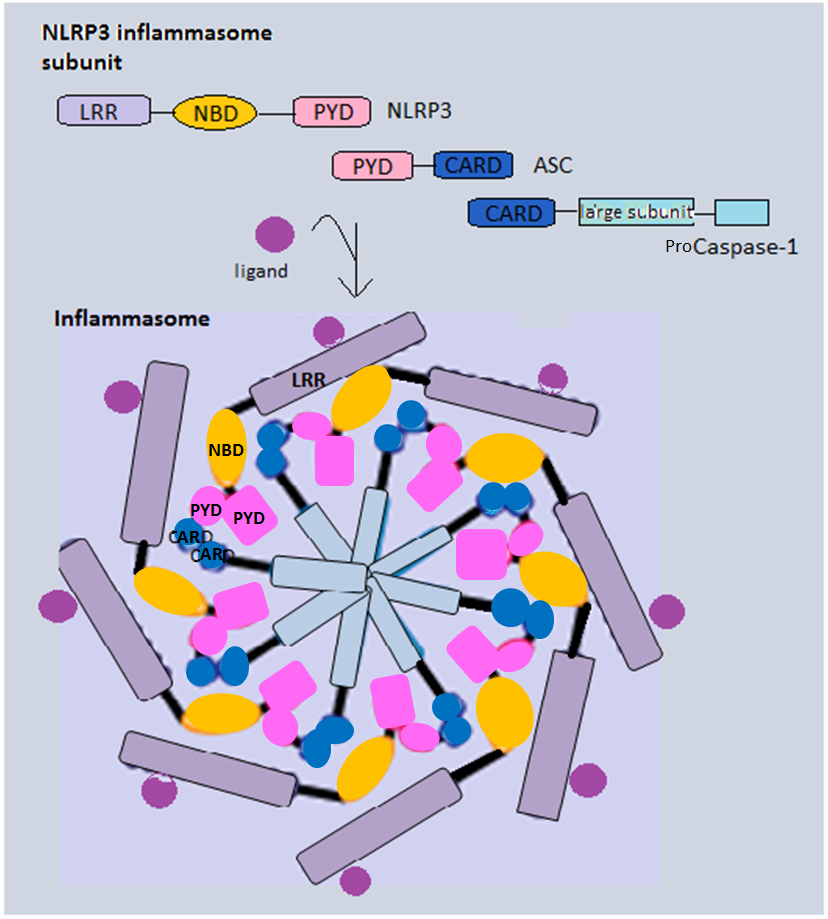
Inflammasome
Inflammasomes are cytosolic multiprotein oligomers of the innate immune system responsible for the activation of inflammatory responses. Activation and assembly of the inflammasome promotes proteolytic cleavage, maturation and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and interleukin 18 (IL-18), as well as cleavage of Gasdermin-D. The N-terminal fragment resulting from this cleavage induces a pro-inflammatory form of programmed cell death distinct from apoptosis, referred to as pyroptosis, and is responsible for secretion of the mature cytokines, presumably through the formation of pores in the plasma membrane. Inflammasome activation is initiated by different kinds of cytosolic pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that respond to either microbe-derived pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) generated by the host cell. Pattern recognition receptors involved in inflammasomes comprise NLRs (nucleoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspase 1
Caspase-1/Interleukin-1 converting enzyme (ICE) is an evolutionarily conserved enzyme that proteolytically cleaves other proteins, such as the precursors of the inflammatory cytokines interleukin 1β and interleukin 18 as well as the pyroptosis inducer Gasdermin D, into active mature peptides. It plays a central role in cell immunity as an inflammatory response initiator. Once activated through formation of an inflammasome complex, it initiates a proinflammatory response through the cleavage and thus activation of the two inflammatory cytokines, interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and interleukin 18 (IL-18) as well as pyroptosis, a programmed lytic cell death pathway, through cleavage of Gasdermin D. The two inflammatory cytokines activated by Caspase-1 are excreted from the cell to further induce the inflammatory response in neighboring cells. Cellular expression Caspase-1 is evolutionarily conserved in many eukaryotes of the Kingdom Animalia. Due to its role in the inflammatory immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOD2
Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 2 (NOD2), also known as caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 15 (CARD15) or inflammatory bowel disease protein 1 (IBD1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NOD2'' gene located on chromosome 16. NOD2 plays an important role in the immune system. It recognizes bacterial molecules ( peptidoglycans) and stimulates an immune reaction. NOD2 is an intracellular pattern recognition receptor, which is similar in structure to resistant proteins of plants and recognizes molecules containing the specific structure called muramyl dipeptide (MDP) that is found in certain bacteria. Structure The C-terminal portion of the protein contains a leucine-rich repeat domain that is known to play a role in protein–protein interactions. The middle part of the protein is characterized by a NOD domain involved in protein self-oligomerization. The N-terminal portion contains two CARD domains known to play a role in apo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CARD Domain
Caspase recruitment domains, or caspase activation and recruitment domains (CARDs), are interaction motifs found in a wide array of proteins, typically those involved in processes relating to inflammation and apoptosis. These domains mediate the formation of larger protein complexes via direct interactions between individual CARDs. CARD domains are found on a strikingly wide range of proteins, including helicases, kinases, mitochondrial proteins, caspases, and other cytoplasmic factors. Basic features CARD domains are a subclass of protein motif known as the death fold, which features an arrangement of six to seven antiparallel alpha helices with a hydrophobic core and an outer face composed of charged residues. Other motifs in this class include the pyrin domain (PYD), death domain (DD), and death effector domain (DED), all of which also function primarily in regulation of apoptosis and inflammatory responses. In apoptosis CARD domains were originally characterized based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NACHT Domain
The NACHT domain is an evolutionarily conserved protein domain. This NTPase domain is found in apoptosis proteins as well as those involved in MHC transcription. Its name reflects some of the proteins that contain it: NAIP (NLP family apoptosis inhibitor protein), CIITA (that is, C2TA or MHC class II transcription activator), HET-E (incompatibility locus protein from ''Podospora anserina'') and TEP1 (that is, TP1 or telomerase-associated protein). The NACHT domain contains 300 to 400 amino acids. It is a predicted nucleoside-triphosphatase (NTPase) domain, which is found in animal, fungal and bacterial proteins. It is found in association with other domains, such as the CARD domain (), the pyrin domain (), the HEAT repeat domain (), the WD40 repeat (), the leucine-rich repeat (LRR) or the BIR repeat (). The NACHT domain consists of seven distinct conserved motifs, including the ATP/GTPase specific P-loop, the Mg2+-binding site ( Walker A and B motifs, respectively) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WD40 Repeat
The WD40 repeat (also known as the WD or beta-transducin repeat) is a short structural motif of approximately 40 amino acids, often terminating in a tryptophan-aspartic acid (W-D) dipeptide. Tandem copies of these repeats typically fold together to form a type of circular solenoid protein domain called the WD40 domain. Structure WD40 domain-containing proteins have 4 to 16 repeating units, all of which are thought to form a circularised beta-propeller structure (see figure to the right). The WD40 domain is composed of several repeats, a variable region of around 20 residues at the beginning followed by a more common repeated set of residues. These repeats typically form a four stranded anti-parallel beta sheet or blade. These blades come together to form a propeller with the most common being a 7 bladed beta propeller. The blades interlock so that the last beta strand of one repeat forms with the first three of the next repeat to form the 3D blade structure. Function WD40-repe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neonatal Onset Multisystem Inflammatory Disease
Neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease is a rare genetic periodic fever syndrome which causes uncontrolled inflammation in multiple parts of the body starting in the newborn period. Symptoms include skin rashes, severe arthritis, and chronic meningitis leading to neurologic damage. It is one of the cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes. NOMID can result from a mutation in the ''CIAS1'' gene (also known as ''NLRP3'' gene), which helps control inflammation. Mutations in this gene also cause familial cold urticaria and Muckle–Wells syndrome. NOMID has been successfully treated with the drug anakinra. This syndrome is also known as the Prieur–Griscelli syndrome as it was first described by these authors in 1981.Prieur AM, Griscelli C (1981) Arthropathy with rash, chronic meningitis, eye lesions, and mental retardation. J. Pediat 99:79-83 Signs and symptoms The age of onset is almost always before 3 months of age. Many infants are born preterm (1/3 cases) and dysmature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 18
Interleukin-18 (IL-18), also known as interferon-gamma inducing factor) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''IL18'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a proinflammatory cytokine. Many cell types, both hematopoietic cells and non-hematopoietic cells, have the potential to produce IL-18. It was first described in 1989 as a factor that induced interferon-γ (IFN-γ) production in mouse spleen cells. Originally, IL-18 production was recognized in Kupffer cells, liver-resident macrophages. However, IL-18 is constitutively expressed in non-hematopoietic cells, such as intestinal epithelial cells, keratinocytes, and endothelial cells. IL-18 can modulate both innate and adaptive immunity and its dysregulation can cause autoimmune or inflammatory diseases. Processing Cytokines usually contain the signal peptide which is necessary for their extracellular release. In this case, ''IL18'' gene, similar to other IL-1 family members, lacks this signal peptide. Furthermore, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage Activation Syndrome
Macrophage activation syndrome is a severe, potentially life-threatening, complication of several chronic rheumatic diseases of childhood. It occurs most commonly with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SoJIA). In addition, MAS has been described in association with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Kawasaki disease, and adult-onset Still's disease. It is thought to be closely related and pathophysiologically very similar to reactive (secondary) hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). The incidence of MAS is unknown as there is a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations, and episodes may remain unrecognized. Signs and symptoms The hallmark clinical and laboratory features include high fever, hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, pancytopenia, liver dysfunction, disseminated intravascular coagulation, hypofibrinogenemia, hyperferritinemia, and hypertriglyceridemia. Despite marked systemic inflammation, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is paradoxically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodic Fever Syndrome
Periodic fever syndromes are a set of disorders characterized by recurrent episodes of systemic and organ-specific inflammation. Unlike autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus, in which the disease is caused by abnormalities of the adaptive immune system, people with autoinflammatory diseases do not produce autoantibodies or antigen-specific T or B cells. Instead, the autoinflammatory diseases are characterized by errors in the innate immune system. The syndromes are diverse, but tend to cause episodes of fever, joint pains, skin rashes, abdominal pains and may lead to chronic complications such as amyloidosis. Most autoinflammatory diseases are genetic and present during childhood. The most common genetic autoinflammatory syndrome is familial Mediterranean fever, which causes short episodes of fever, abdominal pain, serositis, lasting less than 72 hours. It is caused by mutations in the MEFV gene, which codes for the protein pyrin. Pyrin is a protein norma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |