|
NEOSTEL
The Near Earth Object Survey TELescope (NEOSTEL - also known as "Flyeye") is an astronomical survey and early-warning system for detecting near-Earth objects sized and above a few weeks before they impact Earth. NEOSTEL is a project founded by the European Space Agency (ESA), starting with an initial prototype currently under construction at OHB in Milan, Italy. The telescope is of a new "fly-eye" design inspired by the wide field of vision from a fly's eye. The design combines a single objective reflector with multiple sets of optics and CCDs, giving a very wide field of view (around , or 220 times the area of the full moon). When complete it will have one of the widest fields of view of any telescope and be able to survey the majority of the visible sky in a single night. If the initial prototype is successful, three more telescopes are planned, in complementary positions around the globe close to the equator. In terms of light gathering power, the size of the primary mirr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid Impact Prediction
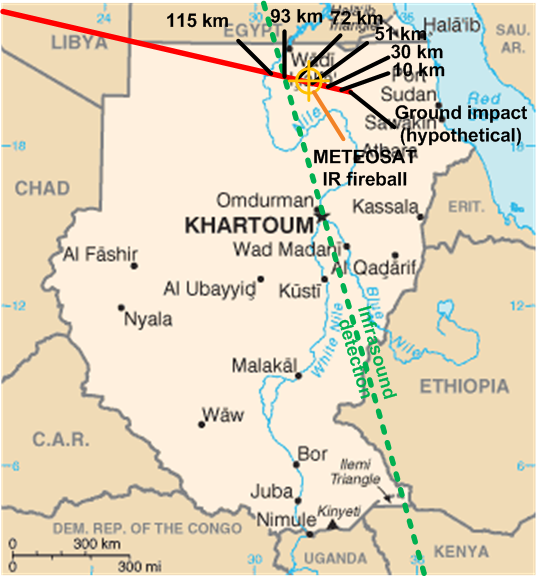
Asteroid impact prediction is the prediction of the dates and times of asteroids impacting Earth, along with the locations and severities of the impacts. The process of impact prediction follows three major steps: # Discovery of an asteroid and initial assessment of its orbit which is generally based on a short observation arc of less than 2 weeks. # Follow up observations to improve the orbit determination # Calculating if, when and where the orbit may intersect with Earth at some point in the future. In addition, although not strictly part of the prediction process, once an impact has been predicted, an appropriate response needs to be made. Most asteroids are discovered by a camera on a telescope with a wide field of view. Image differencing software compares a recent image with earlier ones of the same part of the sky, detecting objects that have moved, brightened, or appeared. Those systems usually obtain a few observations per night, which can be linked up into a very pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid Impact Prediction
Asteroid impact prediction is the prediction of the dates and times of asteroids impacting Earth, along with the locations and severities of the impacts. The process of impact prediction follows three major steps: # Discovery of an asteroid and initial assessment of its orbit which is generally based on a short observation arc of less than 2 weeks. # Follow up observations to improve the orbit determination # Calculating if, when and where the orbit may intersect with Earth at some point in the future. In addition, although not strictly part of the prediction process, once an impact has been predicted, an appropriate response needs to be made. Most asteroids are discovered by a camera on a telescope with a wide field of view. Image differencing software compares a recent image with earlier ones of the same part of the sky, detecting objects that have moved, brightened, or appeared. Those systems usually obtain a few observations per night, which can be linked up into a very pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Near-Earth Object Observation Projects
List of near-Earth object observation projects is a list of projects that observe Near-Earth objects. Most are astronomical surveys intended to find undiscovered asteroids. They sometimes find comets. Neo-chart.png, Annual NEA discoveries by survey: (all NEAs) NEA 1 km or more.png, Annual NEA discoveries by survey: (NEAs > 1 km) Telescope at the Catalina Sky Survey.jpg, A telescope used by the Catalina Sky Survey WISE artist concept (PIA17254, crop).jpg, '' WISE'', used for NEOWISE See also *List of asteroid close approaches to Earth *Asteroid impact prediction * :Asteroid surveys *Space debris *Astronomical survey *Timeline of astronomical maps, catalogs, and surveys *List of asteroid-discovering observatories The list of asteroid-discovering observatories contains a section for each observatory which has discovered one or more asteroids, along with a list of those asteroids. For each numbered asteroid, the Minor Planet Center lists one or more dis ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System
The Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) is a robotic astronomical survey and early warning system optimized for detecting smaller near-Earth objects a few weeks to days before they impact Earth. Funded by NASA, and developed and operated by the University of Hawaii's Institute for Astronomy, the system currently has four 0.5-meter telescopes, two located apart in the Hawaiian islands, at Haleakala (ATLAS-HKO, Observatory code T05) and Mauna Loa (ATLAS-MLO, Observatory code T08) observatories, one located at the Sutherland Observatory (ATLAS–SAAO, Observatory code M22) in South Africa, and one at the El Sauce Observatory in Rio Hurtado (Chile) (Observatory code W68). ATLAS began observations in 2015 with one telescope at Haleakala, and a two-telescopes version became operational in 2017. The project then obtained NASA funding for two additional telescopes in the Southern hemisphere, which became operational in early 2022. Each telescope surveys one q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Situational Awareness Programme
The Space Safety Programme, formerly the Space Situational Awareness (SSA) programme, is the European Space Agency's (ESA) initiative to monitor hazards from space, determine their risk, make this data available to the appropriate authorities and where possible, mitigate the threat. The SSA Programme was designed to support Europe's independent space access and utilization through the timely and accurate information delivery regarding the space environment, particularly hazards to both in-orbit and ground infrastructure. In 2019 it evolved into the present Space Safety Programme with an expanded focus, also including missions and activities to mitigate and prevent dangers from space. The programme is split into four main segments: * Space weather: monitoring the Sun, the solar wind, and in Earth's magnetosphere, ionosphere and thermosphere, that can affect spaceborne and ground-based infrastructure or endanger human life or health. This data is processed by thSpace Weather Service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAU Code
This is a list of observatory codes (IAU codes or MPC codes) published by the Minor Planet Center. For a detailed description, ''see observations of small Solar System bodies Observations of minor planets as well as comets and natural satellites of the Solar System are made by astronomical observatories all over the world and reported to the Minor Planet Center (MPC), a service of the International Astronomical Unio ...''. List References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Observatory codes * Astronomy-related lists Technology-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aperture
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture and focal length of an optical system determine the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane. An optical system typically has many openings or structures that limit the ray bundles (ray bundles are also known as ''pencils'' of light). These structures may be the edge of a lens or mirror, or a ring or other fixture that holds an optical element in place, or may be a special element such as a diaphragm placed in the optical path to limit the light admitted by the system. In general, these structures are called stops, and the aperture stop is the stop that primarily determines the ray cone angle and brightness at the image point. In some contexts, especially in photography and astronomy, ''aperture'' refers to the diameter of the aperture stop rather than the physical stop or the opening itself. For example, in a telescope, the aperture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Plate
Photographic plates preceded photographic film as a capture medium in photography, and were still used in some communities up until the late 20th century. The light-sensitive emulsion of silver salts was coated on a glass plate, typically thinner than common window glass. History Glass plates were far superior to film for research-quality imaging because they were stable and less likely to bend or distort, especially in large-format frames for wide-field imaging. Early plates used the wet collodion process. The wet plate process was replaced late in the 19th century by gelatin dry plates. A view camera nicknamed "The Mammoth" weighing was built by George R. Lawrence in 1899, specifically to photograph "The Alton Limited" train owned by the Chicago & Alton Railway. It took photographs on glass plates measuring × . Glass plate photographic material largely faded from the consumer market in the early years of the 20th century, as more convenient and less fragile fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid (geometry)
In geometry, a pyramid () is a polyhedron formed by connecting a polygonal base and a point, called the apex. Each base edge and apex form a triangle, called a ''lateral face''. It is a conic solid with polygonal base. A pyramid with an base has vertices, faces, and edges. All pyramids are self-dual. A right pyramid has its apex directly above the centroid of its base. Nonright pyramids are called oblique pyramids. A regular pyramid has a regular polygon base and is usually implied to be a ''right pyramid''. When unspecified, a pyramid is usually assumed to be a ''regular'' square pyramid, like the physical pyramid structures. A triangle-based pyramid is more often called a tetrahedron. Among oblique pyramids, like acute and obtuse triangles, a pyramid can be called ''acute'' if its apex is above the interior of the base and ''obtuse'' if its apex is above the exterior of the base. A right-angled pyramid has its apex above an edge or vertex of the base. In a tetrahedro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexadecagon
In mathematics, a hexadecagon (sometimes called a hexakaidecagon or 16-gon) is a sixteen-sided polygon. Regular hexadecagon A '' regular hexadecagon'' is a hexadecagon in which all angles are equal and all sides are congruent. Its Schläfli symbol is and can be constructed as a truncated octagon, t, and a twice-truncated square tt. A truncated hexadecagon, t, is a triacontadigon, . Construction As 16 = 24 (a power of two), a regular hexadecagon is constructible using compass and straightedge: this was already known to ancient Greek mathematicians. Measurements Each angle of a regular hexadecagon is 157.5 degrees, and the total angle measure of any hexadecagon is 2520 degrees. The area of a regular hexadecagon with edge length ''t'' is :\begin A = 4t^2 \cot \frac =& 4t^2 \left(1+\sqrt+\sqrt\right)\\ =& 4t^2 (\sqrt+1)(\sqrt+1) .\end Because the hexadecagon has a number of sides that is a power of two, its area can be computed in terms of the circumradius ''R'' by truncatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Piece
An eyepiece, or ocular lens, is a type of lens that is attached to a variety of optical devices such as telescopes and microscopes. It is named because it is usually the lens that is closest to the eye when someone looks through the device. The objective lens or mirror collects light and brings it to focus creating an image. The eyepiece is placed near the focal point of the objective to magnify this image. The amount of magnification depends on the focal length of the eyepiece. An eyepiece consists of several "lens elements" in a housing, with a "barrel" on one end. The barrel is shaped to fit in a special opening of the instrument to which it is attached. The image can be focused by moving the eyepiece nearer and further from the objective. Most instruments have a focusing mechanism to allow movement of the shaft in which the eyepiece is mounted, without needing to manipulate the eyepiece directly. The eyepieces of binoculars are usually permanently mounted in the binocular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspheric Lens
An aspheric lens or asphere (often labeled ''ASPH'' on eye pieces) is a lens whose surface profiles are not portions of a sphere or cylinder. In photography, a lens assembly that includes an aspheric element is often called an aspherical lens. The asphere's more complex surface profile can reduce or eliminate spherical aberration and also reduce other optical aberrations such as astigmatism, compared to a simple lens. A single aspheric lens can often replace a much more complex multi-lens system. The resulting device is smaller and lighter, and sometimes cheaper than the multi-lens design. Aspheric elements are used in the design of multi-element wide-angle and fast normal lenses to reduce aberrations. They are also used in combination with reflective elements (catadioptric systems) such as the aspherical Schmidt corrector plate used in the Schmidt cameras and the Schmidt–Cassegrain telescopes. Small molded aspheres are often used for collimating diode lasers. Aspheric lenses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |