|
NATO Reporting Name
NATO reporting names are code names for military equipment from Russia, China, and historically, the Eastern Bloc (Soviet Union and other nations of the Warsaw Pact). They provide unambiguous and easily understood English words in a uniform manner in place of the original designations, which either may have been unknown to the Western world at the time or easily confused codes. For example, the Russian bomber jet Tupolev Tu-160 is simply called "Blackjack". NATO maintains lists of the names. The assignment of the names for the Russian and Chinese aircraft was once managed by the five-nation Air Standardization Coordinating Committee (ASCC), but that is no longer the case. American variations The United States Department of Defense (DOD) expands on the NATO reporting names in some cases. NATO refers to surface-to-air missile systems mounted on ships or submarines with the same names as the corresponding land-based systems, but the US DoD assigns a different series of numbers with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Code Name
A code name, call sign or cryptonym is a code word or name used, sometimes clandestinely, to refer to another name, word, project, or person. Code names are often used for military purposes, or in espionage. They may also be used in industrial counter-espionage to protect secret projects and the like from business rivals, or to give names to projects whose marketing name has not yet been determined. Another reason for the use of names and phrases in the military is that they transmit with a lower level of cumulative errors over a walkie-talkie or radio link than actual names. Military origins During World War I, names common to the Allies referring to nations, cities, geographical features, military units, military operations, diplomatic meetings, places, and individual persons were agreed upon, adapting pre-war naming procedures in use by the governments concerned. In the British case names were administered and controlled by the Inter Services Security Board (ISSB) staffed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
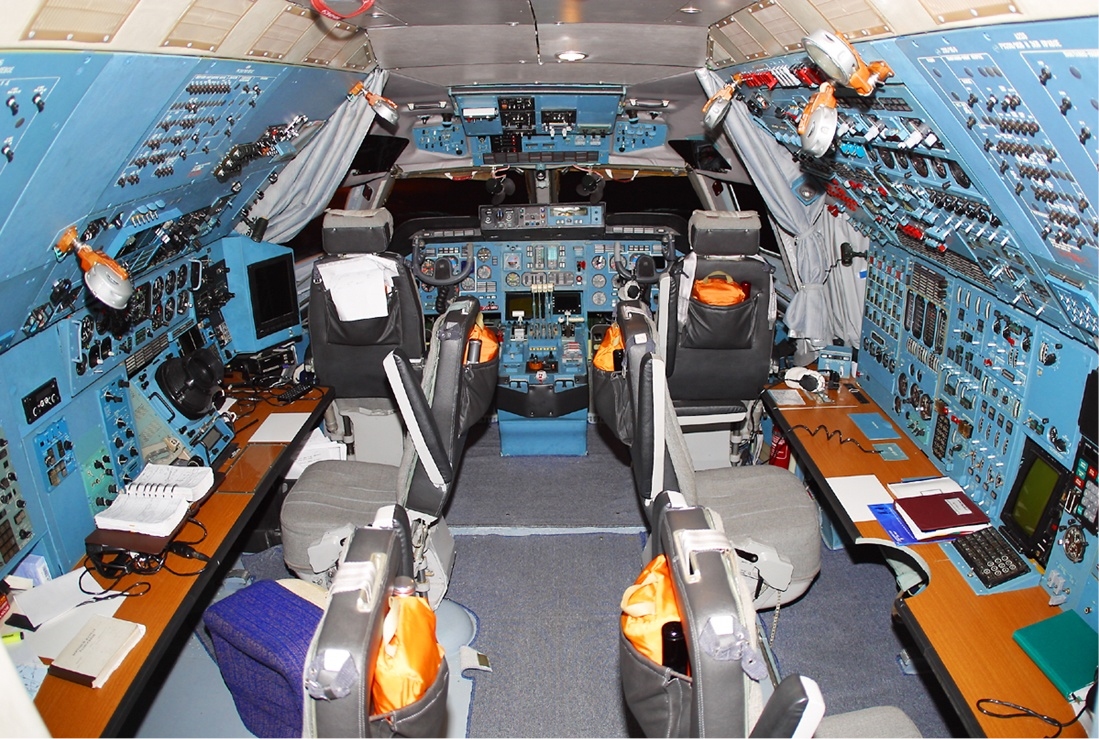
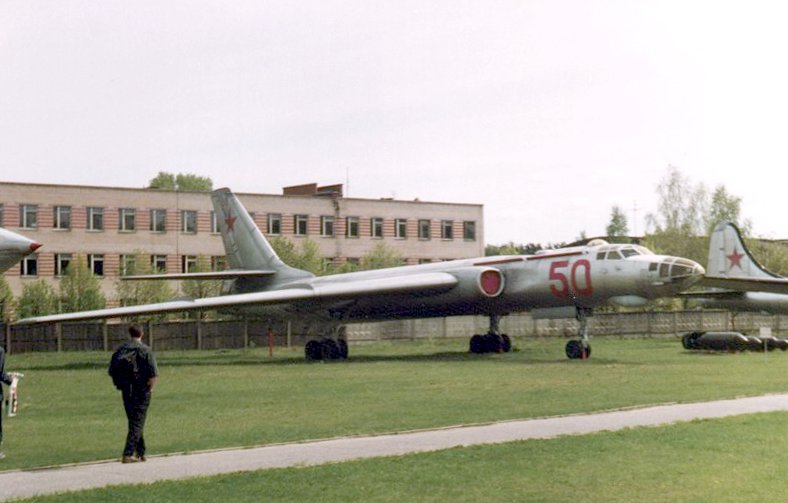
Tupolev Tu-16
The Tupolev Tu-16 ( NATO reporting name: Badger) is a twin-engined jet strategic heavy bomber used by the Soviet Union. It has been flown for almost 70 years, and the Chinese license-built Xian H-6 remains in service with the People's Liberation Army Air Force. Development In the late 1940s, the Soviet Union was strongly committed to matching the United States in strategic bombing capability. The Soviets' only long-range bomber at the time was Tupolev's Tu-4 'Bull', a reverse-engineered copy of the American B-29 Superfortress. The development of the notably powerful Mikulin AM-3 turbojet led to the possibility of a large, jet-powered bomber. The Tupolev design bureau began work on the Tu-88 ("Aircraft N") prototypes in 1950. The Tu-88 first flew on 27 April 1952. After winning a competition against the Ilyushin Il-46, it was approved for production in December 1952. The first production bombers entered service with Frontal Aviation in 1954, receiving the service designation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
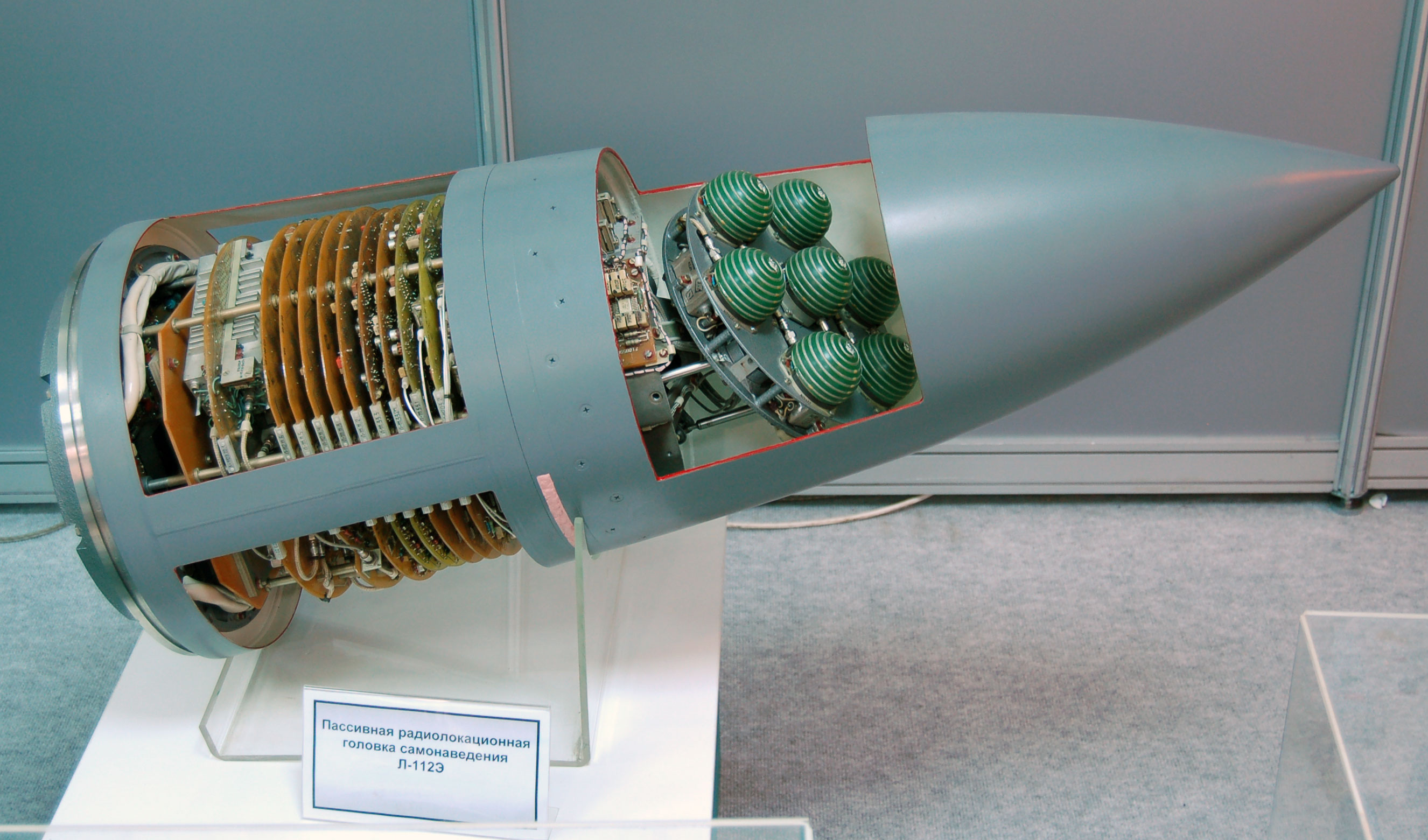
SS-N-2 Styx
The P-15 ''Termit'' (russian: П-15 "Термит"; en, termite) is an anti-ship missile developed by the Soviet Union's Raduga design bureau in the 1950s. Its GRAU designation was 4K40, its NATO reporting name was ''Styx'' or SS-N-2. China acquired the design in 1958 and created at least four versions: the CSS-N-1 ''Scrubbrush'' and CSS-N-2 versions were developed for ship-launched operation, while the CSS-C-2 ''Silkworm'' and CSS-C-3 ''Seersucker'' were used for coastal defence. Other names for this basic type of missile include: HY-1, SY-1, and FL-1 ''Flying Dragon'' (Chinese designations typically differ for export and domestic use, even for otherwise identical equipment), North Korean local produced KN-1 or KN-01, derived from both Silkworm variants and Russian & USSR P-15, Rubezh, P-20 P-22 . Despite its large size, thousands of P-15s were built and installed on many classes of ships from torpedo boats to destroyers, and coastal batteries and bomber aircraft (Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS-1 Scud
A Scud missile is one of a series of tactical ballistic missiles developed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. It was exported widely to both Second and Third World countries. The term comes from the NATO reporting name attached to the missile by Western intelligence agencies. The Russian names for the missile are the R-11 (the first version), and the R-17 (later R-300) Elbrus (later developments). The name Scud has been widely used to refer to these missiles and the wide variety of derivative variants developed in other countries based on the Soviet design. Scud missiles have been used in combat since the 1970s, mostly in wars in the Middle East. They became familiar to the Western public during the 1991 Persian Gulf War, when Iraq fired dozens at Israel and Saudi Arabia. In Russian service it is being replaced by the 9K720 Iskander. Development The first use of the term ''Scud'' was in the NATO name SS-1b Scud-A, applied to the R-11 Zemlya ballistic missile. The earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of NATO Reporting Names For Surface-to-air Missiles
NATO reporting name for SA series surface-to-air missiles, with Soviet designations: * SA-1 "Guild" (S-25 ''Berkut'') * SA-2 "Guideline" (S-75 ''Dvina''/''Volkhov''/''Desna'') * SA-3 "Goa" (S-125 ''Nyeva'') * SA-4 " Ganef" (9M8 ''Krug'') * SA-5 " Gammon" (S-200 ''Volga'') * SA-6 " Gainful" (2K12 ''Kub''/''Kvadrat'') * SA-7 "Galosh" and "Grail" (9K32 ''Strela-2'') * SA-8 "Gecko" (9K33 ''Osa'') * SA-9 "Gaskin" (9K31 ''Strela-1'') * SA-10 " Grumble" (S-300P/PS/PT) * SA-11 " Gadfly" (9K37 ''Buk'') * SA-12 " Gladiator/Giant" (S-300V) * SA-13 "Gopher" (9K35 ''Strela-10'') * SA-14 "Gremlin" (9K36 ''Strela-3'') * SA-15 " Gauntlet" (9K330/9K331/9K332 ''Tor'') * SA-16 " Gimlet" (9K310 ''Igla-1'') * SA-17 "Grizzly" (9K37 ''Buk-M1-2'') * SA-18 "Grouse" (9K38 ''Igla'') * SA-19 "Grison" (2K22 ''Tunguska'') * SA-20 "Gargoyle" (S-300PM/PMU ''Favorit'') * SA-21 " Growler" (S-400 ''Triumf'') * SA-22 "Greyhound" (Pantsir-S1) * SA-23 " Gladiator/Giant" (S-300VM "Antey-2500") * SA-24 "Grin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SA-2 Guideline
The S-75 (Russian: С-75; NATO reporting name SA-2 Guideline) is a Soviet-designed, high-altitude air defence system, built around a surface-to-air missile with command guidance. Following its first deployment in 1957 it became one of the most widely deployed air defence systems in history. It scored the first destruction of an enemy aircraft by a surface-to-air missile, with the shooting down of a Taiwanese Martin RB-57D Canberra over China on 7 October 1959 that was hit by a salvo of three V-750 (1D) missiles at an altitude of 20 km (65,600 ft). This success was credited to Chinese fighter aircraft at the time to keep the S-75 program secret. This system first gained international fame when an S-75 battery, using the newer, longer-range, higher-altitude V-750VN (13D) missile was deployed in the 1960 U-2 incident, when it shot down the U-2 of Francis Gary Powers overflying the Soviet Union on May 1, 1960. The system was also deployed in Cuba during the Cuban Missile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of NATO Reporting Names For Air-to-surface Missiles
NATO reporting name for AS series air-to-surface missiles, with Soviet designations: Note: The Soviet / Russian designation is a Cyrillic letter " Х", which is translated as "Kh" or "H". Also, sometimes a combination ("complex") of a missile with its aircraft is marked with a letter "K" (for example, a missile Kh-22 with an aircraft is a "complex K-22"). The Cyrillic "X" (read "Kh") in the designation of Soviet ASMs is in fact a Latin " X" ("ecks") for Xperimental, as used by the design bureau. With passing time, however, this was ignored and used in Soviet/Russian as well as foreign literature as the Cyrillic Kh. * AS-1 "Kennel" (KS-1 ''Kometa'') * AS-2 "Kipper" (K-10S ''Yen'') * AS-3 "Kangaroo" (Kh-20) * AS-4 "Kitchen" (Kh-22 Burya) * AS-5 "Kelt" (Kh-11/KSR-2) * AS-6 "Kingfish" (Kh-26/KSR-5) * AS-7 "Kerry" (Kh-66, Kh-23 ''Grom'') * AS-8 (9M114V ''Shturm-V'') * AS-9 "Kyle" (Kh-28) * AS-10 "Karen" (Kh-25) * AS-11 "Kilter" (Kh-58 ''Izdeliye D-7'') * AS-12 "Kegler" (Kh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AS-17 Krypton
The Kh-31 (russian: Х-31; AS-17 'Krypton') is a Russian air-to-surface missile carried by aircraft such as the MiG-29 or Su-27. It is capable of Mach 3.5 and was the first supersonic anti-ship missile that could be launched by tactical aircraft. There are several variants; the Kh-31 is best known as an anti-radiation missile (ARM) but there are also anti-shipping and target drone versions. There has been talk of adapting it to make an " AWACS killer", a long-range air-to-air missile. Development The proliferation of surface-to-air missiles (SAMs) has made the Suppression of Enemy Air Defences (SEAD) a priority for any modern air force intending offensive action. Knocking out air search radars and fire control radars is an essential part of this mission. ARMs must have sufficient range that the launch platform is out of range of the SAMs, high speed to reduce the risk of being shot down and a seeker that can detect a range of radar types, but they do not need a particularly b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of NATO Reporting Names For Air-to-air Missiles
NATO reporting name for AA series air-to-air missiles, with Soviet designations: * AA-1 "Alkali" (Kaliningrad K-5) * AA-2 "Atoll" (Vympel K-13) * AA-3 "Anab" (Kaliningrad K-8) * AA-4 "Awl" (Raduga K-9) * AA-5 "Ash" (Bisnovat R-4) * AA-6 "Acrid" (Bisnovat R-40) * AA-7 "Apex" (Vympel R-23) * AA-8 "Aphid" (Molniya R-60) * AA-9 "Amos" (Vympel R-33) * AA-10 "Alamo" (Vympel R-27) * AA-11 "Archer" (Vympel R-73) * AA-12 "Adder" (Vympel R-77) * AA-X-13 "Axehead" (Vympel R-37) * - none - Novator K-100 (was KS-172, R-172 etc.) * CH-AA-7 * CH-AA-9 * CH-AA-10A ''See also'': NATO reporting name References {{Russian and Soviet missiles, AAM air-to-air missiles file:Python5-missile001.jpg, The newest and the oldest member of Rafael Advanced Defense Systems, Rafael's Python (missile), Python family of AAM for comparisons, Python-5 (displayed lower-front) and Shafrir-1 (upper-back) An air-to-air miss ... Cold War air-to-air missiles of the Soviet Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AA-2 Atoll
The Vympel K-13 (NATO reporting name: AA-2 "Atoll") is a short-range, infrared homing air-to-air missile developed by the Soviet Union. It is similar in appearance and function to the American AIM-9B Sidewinder from which it was reverse-engineered. Although it since has been replaced by more modern missiles in frontline service, it saw widespread service in many nations. Background - the Sidewinder missile During the Second Taiwan Strait Crisis in 1958, Taiwan's F-86 Sabres faced the much higher performance mainland Chinese PLAAF MiG-17s. The MiG-17s had speed, maneuverability, and altitude advantages over the Sabres, allowing them to engage only when they desired, normally at advantageous times. In response, the US Navy rushed to modify 100 ROCAF Sabres to carry the newly introduced AIM-9 Sidewinder missile. These were introduced into combat on 24 September 1958, when a group of MiG-17s cruised past a flight of Sabres, only to find themselves under attack by missile fire. This w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilyushin Il-76
The Ilyushin Il-76 (russian: Илью́шин Ил-76; NATO reporting name: Candid) is a multi-purpose, fixed-wing, four-engine turbofan strategic airlifter designed by the Soviet Union's Ilyushin design bureau. It was first planned as a commercial freighter in 1967, as a replacement for the Antonov An-12. It was designed to deliver heavy machinery to remote, poorly served areas. Military versions of the Il-76 have been widely used in Europe, Asia and Africa, including use as an aerial refueling tanker or command center. The Il-76 has seen extensive service as a commercial freighter for ramp-delivered cargo, especially for outsized or heavy items unable to be otherwise carried. It has also been used as an emergency response transport for civilian evacuations as well as for humanitarian aid and disaster relief around the world. Due to its ability to operate from unpaved runways, it has been useful in undeveloped areas. Specialized models have also been produced for aerial fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonov An-124
The Antonov An-124 Ruslan (; russian: Антонов Ан-124 Руслан, , Ruslan; NATO reporting name: Condor) is a large, strategic airlift, four-engined aircraft that was designed in the 1980s by the Antonov design bureau in the Ukrainian SSR, then part of the Soviet Union (USSR). The An-124 is the world's 2nd heaviest gross weight production cargo airplane and heaviest operating cargo aircraft, behind the destroyed one-off Antonov An-225 Mriya (a greatly enlarged design based on the An-124) and the Boeing 747-8. The An-124 remains the largest military transport aircraft in service. In 1971, design work commenced on the project, which was initially referred to as ''Izdeliye 400'' (''Product #400''), at the Antonov Design Bureau in response to a shortage in heavy airlift capability within the Military Transport Aviation Command (''Komandovaniye voyenno-transportnoy aviatsii'' or VTA) arm of the Soviet Air Forces. Two separate final assembly lines plants setup for the ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_fires_a_P-15_Termit_missile.jpg)

_(2).jpg)
