|
Nzime
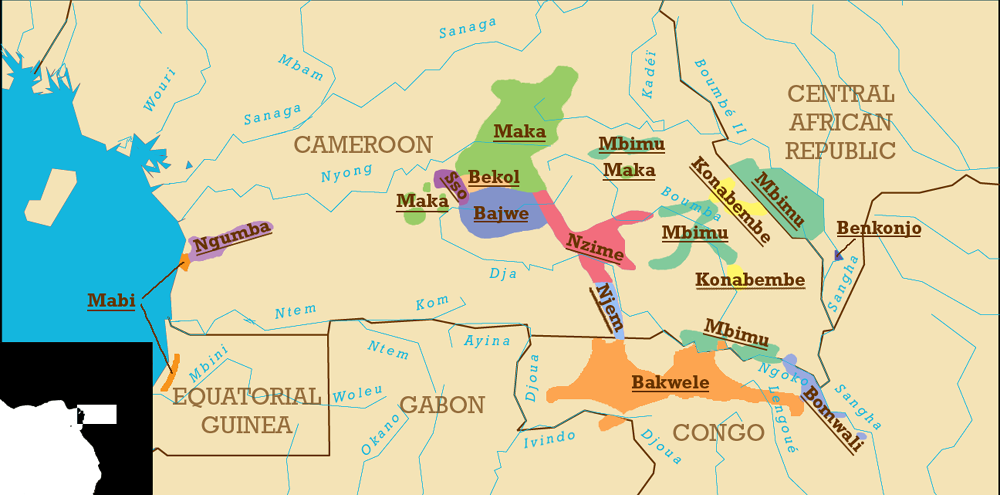
The Nzime are a Bantu ethnic group inhabiting the rain forest zone of southeastern Cameroon. The Nzime live along the road running south of Abong-Mbang, through Mindourou and Lomié, and forking to Zoulabot and Zwadiba. Their territory lies south of the Koonzime in Djaposten, east of the Badwe'e, north of the Njyem, and west of the Konabembe people, all related groups. The Nzime speak the Nzime dialect of Koonzime ("OZM"), one of the Makaa–Njyem Bantu languages. History The Makaa–Njyem-speaking peoples entered present-day Cameroon from the Congo River basin or modern Chad between the 14th and 17th centuries. By the 19th century, they inhabited the lands north of the Lom River in the border region between the present-day East and Adamawa Provinces. Not long thereafter, however, the Beti-Pahuin peoples invaded these areas under pressure from the Vute and Mbum, themselves fleeing Fulani (Fula) warriors. The Makaa–Njyem speakers were forced south. Nzime groups continue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwe'e People
The Badwe'e (also ''Bajwe'e''; French ''Badjoué'') are an ethnic group inhabiting the rain forest zone of southeastern Cameroon. They recognize themselves as the descendants of Edwe'e, the youngest son of Koo and the brother of Njeme and Nzime. The Badwe'e live south of Messaména in the East Province in a region south of the Bekol and both north and west of the Nzime. Their territory includes much of the northern and western border of the Dja Biosphere Reserve. They speak a dialect of Koozime, together with the Nzime. History The ancestors of the Badwe'e lived in the Congo River basin or the present territory of Chad before moving into the present territory of Cameroon between the 14th and 17th centuries. Along with the other speakers of Makaa–Njyem languages, they lived along the northern Lom River near the present-day border between the Adamawa and East provinces. Under pressure from migrating Beti-Pahuin groups (themselves fleeing the Vute and Mbum), the Makaa– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koonzime
Nzime (''Koonzime'') is a Bantu language of Cameroon, spoken by the Nzime and Dwe'e (''Bajwe'e'') people. Maho (2009) lists these as two languages. It is closely related to Mpo. Demographics Koonzime is spoken in most of the southern part of the Haut-Nyong region (Eastern Region). The Nzime are located mainly around and east of Lomié, and the closely related Njem in Ngoïla Ngoila, also spelled Ngoyla and Ngoida, is a village in the East Province of Cameroon, located at 2.617° N, 14.017° E. The primary ethnic group is the Njem. Ngoila is the capital of the Ngoila subdivision of the Haut-Nyong division. See also ... commune. Koonzime is spoken by about 30,000 speakers. References Makaa-Njem languages Languages of Cameroon {{Bantu-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bekwel
Bekwel (Bekwil) is a Bantu language of the Republic of the Congo. There are some 10,000 speakers there, with a quarter that number across the border in Gabon, and perhaps a similar on the opposite side in Cameroon. It is rather close to Nzime The Nzime are a Bantu ethnic group inhabiting the rain forest zone of southeastern Cameroon. The Nzime live along the road running south of Abong-Mbang, through Mindourou and Lomié, and forking to Zoulabot and Zwadiba. Their territory lies sou ... (Koonzime). Maho (2009) considers Nkonabeeb (Konabembe) to be a dialect of Bekwil rather than of Mpumpong. References Languages of the Republic of the Congo Makaa-Njem languages {{Bantu-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maka People
The Maka or Makaa are a Bantu ethnic group inhabiting the southern rain forest zone of Cameroon. They live primarily in the northern portions of the Upper Nyong division of Cameroon's East Province. Major Maka settlements include Abong-Mbang, Doumé, and Nguélémendouka. Some Maka villages lie over the border into the Centre Province, as well. Most Maka speak a language known as Maka or South Maka, which had an estimated 80,000 speakers in 1987. In the north of Maka territory, speakers use a related language known as Byep, or North Maka. Byep had an estimated 9,500 speakers in 1988. Though they consider themselves a single people, Maka dialects serve as a form of identity as well. The main dialects are Maka are Bebent (Bebende, Biken, Bewil, Bemina), Mbwaanz, and Sekunda. Byep has two dialects, Byep and Besep (Besha, Bindafum). History The Maka and related speakers of Makaa–Njem languages entered present-day Cameroon from the Congo River basin or modern Chad between th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lomié
Lomié is a town in the Lomié District in the Upper Nyong division of the East Province of Cameroon. An article in the ''Mail & Guardian Online'' describes it as having "no telephone connection to the outside world, and a single access road that is little more than a forest trail". In fact Lomié has been connected to the cellular phone network since 2006 and the town has had several 'boom' periods. While previous employment came from the logging industry currently the town is near an important cobalt and zinc mining project. The GEOVIC mining company uses Lomié as a base. Lomié has a number of interesting historical buildings, dating from the German and French era. Among these building are the house of the senior civil administrator, a jail, a courthouse and a post-office. The town used to be center of the Upper Nyong Division until it was replaced by Abong-Mbang. Roads from Lomié lead north to Abong-Mbang via Mindourou, east to Messok and Yokadouma and south to Ngoila. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west- central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Its coastline lies on the Bight of Biafra, part of the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean. Due to its strategic position at the crossroads between West Africa and Central Africa, it has been categorized as being in both camps. Its nearly 27 million people speak 250 native languages. Early inhabitants of the territory included the Sao civilisation around Lake Chad, and the Baka hunter-gatherers in the southeastern rainforest. Portuguese explorers reached the coast in the 15th century and named the area ''Rio dos Camarões'' (''Shrimp River''), which became ''Cameroon'' in English. Fulani soldiers founded the Adamawa E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantu Languages
The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀) are a large family of languages spoken by the Bantu people of Central, Southern, Eastern africa and Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages. The total number of Bantu languages ranges in the hundreds, depending on the definition of "language" versus "dialect", and is estimated at between 440 and 680 distinct languages."Guthrie (1967-71) names some 440 Bantu 'varieties', Grimes (2000) has 501 (minus a few 'extinct' or 'almost extinct'), Bastin ''et al.'' (1999) have 542, Maho (this volume) has some 660, and Mann ''et al.'' (1987) have ''c.'' 680." Derek Nurse, 2006, "Bantu Languages", in the ''Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics'', p. 2:Ethnologue report for Southern Bantoid" lists a total of 535 languages. The count includes 13 Mbam languages, which are not always included under "Narrow Bantu". For Bantuic, Linguasphere has 260 outer languages (which are equivalent to lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |