|
Nutgrove, Queensland
Nutgrove is a rural Suburbs and localities (Australia), locality in the Toowoomba Region, Queensland, Australia. In the Nutgrove had a population of 32 people. History The Cooyar railway line opened to Nutgrove on 28 April 1913 with the locality served by the Nutgrove railway station, located immediately to the north of Douglas Nutgrove Road (), now in Wutul, Queensland, Wutul. Nutgrove State School opened on 20 June 1923 and closed on 1947. It was located at 5779 Dalby Cooyar Road (). In the Nutgrove had a population of 32 people. Road infrastructure The Oakey–Cooyar Road runs through from south to north-east. The Dalby–Cooyar Road enters from the west and joins Oakey–Cooyar Road. Heritage listings Nutgrove has a number of heritage-listed sites, including: * Narko-Nutgrove Road from Highgrove, Queensland, Highgrove to Nutgrove (): Muntapa Tunnel Economy There are a number of homesteads in the locality: * Bowriver () * Highgrove () Education There are no sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
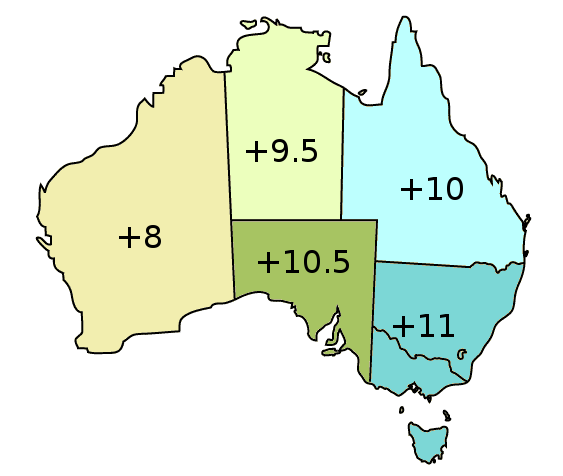
AEST
Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Western Standard Time (AWST; UTC+08:00), Australian Central Standard Time (ACST; UTC+09:30), and Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST; UTC+10:00). Time is regulated by the individual state governments, some of which observe daylight saving time (DST). Australia's external territories observe different time zones. Standard time was introduced in the 1890s when all of the Australian colonies adopted it. Before the switch to standard time zones, each local city or town was free to determine its local time, called local mean time. Now, Western Australia uses Western Standard Time; South Australia and the Northern Territory use Central Standard Time; while New South Wales, Queensland, Tasmania, Victoria (Australia), Victoria, Jervis Bay Territory, and the Australian Capital Territory use Eastern Standard Time. Daylight saving time (+1 hour) is used in jurisdictions in the south and south-east: South Australia, New South Wales, Vict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maclagan, Queensland
Maclagan is a rural town and locality in the Toowoomba Region, Queensland, Australia. In the the locality of Maclagan had a population of 195 people. Geography Maclagan is a small town on the Darling Downs, 80 km (49.7 mi) north-west of Toowoomba and 45 km (28 mi) east of Dalby. The Dalby–Cooyar Road runs through from south to east. Bunya Mountains-Maclagan Road exits to the north. The Pechey-Maclagan Road ends at the southern boundary where it meets Dalby-Cooyar Road. History The township of Maclagan was surveyed on 17 May 1889. The town was originally named Bismarck after Otto von Bismarck until 1916 when it was renamed Maclagan due to the anti-German sentiment during World War I. The township was renamed Maclagan in honour of Brigadier Ewen George Sinclair-Maclagan (1868-1948). Bismarck Street is still a street in the town. Moola Road Provisional School opened on 5 September 1904. On 1 January 1909, it became Moola Road State School. In 1916 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muntapa Tunnel
Muntapa Tunnel is a heritage-listed tunnel from Narko-Nutgrove Road, Highgrove through to Nutgrove, both in the Toowoomba Region, Queensland, Australia. It was designed by Queensland Railways and built from 1910 to 1913 by Queensland Railways. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 3 May 2007. History The Muntapa Tunnel is a concrete railway tunnel located on the Cooyar railway line, a former branch line linking Oakey to Cooyar in the eastern Darling Downs. The tunnel is one of a small number built on a branch line and it is the only tunnel in Queensland that crosses between the inland and coastal sides of the Great Dividing Range. It was opened in 1913. Branch lines were secondary railway lines designed to connect rural districts with the main rail routes. They were constructed with the aim of supporting small-scale agriculturalists, dairy farmers and the timber industry. Branch lines were generally of cheaper construction than main lines, more frequent sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heritage-listed
This list is of heritage registers, inventories of cultural properties, natural and man-made, tangible and intangible, movable and immovable, that are deemed to be of sufficient heritage value to be separately identified and recorded. In many instances the pages linked below have as their primary focus the registered assets rather than the registers themselves. Where a particular article or set of articles on a foreign-language Wikipedia provides fuller coverage, a link is provided. International *World Heritage Sites (see Lists of World Heritage Sites) – UNESCO, advised by the International Council on Monuments and Sites *Representative list of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity (UNESCO) *Memory of the World Programme (UNESCO) *Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) – Food and Agriculture Organization *UNESCO Biosphere Reserve * European Heritage Label (EHL) are European sites which are considered milestones in the creation of Europe. At th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalby–Cooyar Road
The roads that join the towns of , and form a triangle that encloses some of the most fertile land on the Darling Downs in Queensland, Australia. These roads are the Warrego Highway, Oakey–Cooyar Road and Dalby–Cooyar Road. Several of the more significant internal roads intersect with Dalby–Cooyar Road, and these are briefly described in this article, along with some significant external roads. Dalby–Cooyar Road is a continuous road route in the Western Downs and Toowoomba regions of Queensland. It is a regional road (number 416). It is part of the shortest route from the Sunshine Coast and to Dalby. Route description The Dalby–Cooyar Road commences at an intersection with the Bunya Highway (State Route 49) in . It leaves Dalby as Irvingdale Road and runs east, soon becoming Dalby–Cooyar Road. It turns north-east and reaches the eastern boundary of Dalby, where it passes the exit to Dalby–Nungil Road and turns north, passing between Dalby and before turni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oakey–Cooyar Road
Oakey–Cooyar Road is a continuous road route in the Darling Downs and Toowoomba regions of Queensland, Australia. The entire route is signed as State Route 68. It is a state-controlled part regional and part district road (number 417). It provides an alternate route between the Warrego Highway and the New England Highway, bypassing . Route description The Department of Transport and Main Roads (TMR) defines a single point in at which all of its local roads start and end, or pass through to other end points. The former route of the Warrego Highway through the town, now known as Oakey Connection Road (see below) is the basis from which other roads emanate. Thus the Oakey–Cooyar Road starts at its junction with Oakey Connection Road, which is the TMR designated point. State Route 68 does not end at that point, but follows Oakey Connection Road and Oakey–Pittsworth Road until it meets the Warrego Highway. For convenience this article describes the full length of State Rou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland Government
The Queensland Government is the democratic administrative authority of the Australian state of Queensland. The Government of Queensland, a parliamentary constitutional monarchy was formed in 1859 as prescribed in its Constitution, as amended from time to time. Since the Federation of Australia in 1901, Queensland has been a State of Australia, with the Constitution of Australia regulating the relationships between all state and territory governments and the Australian Government. Under the Australian Constitution, all states and territories (including Queensland) ceded powers relating to certain matters to the federal government. The government is influenced by the Westminster system and Australia's federal system of government. The Governor of Queensland, as the representative of Charles III, King of Australia, holds nominal executive power, although in practice only performs ceremonial duties. In practice executive power lies with the Premier and Cabinet. The Cabinet of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland Family History Society
The Queensland Family History Society (QFHS) is an incorporated association formed in Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. History The society was established in 1979 as a non-profit, non-sectarian, non-political organisation. They aim to promote the study of family history local history, genealogy, and heraldry, and encourage the collection and preservation of records relating to the history of Queensland families. At the end of 2022, the society relocated from 58 Bellevue Avenue, Gaythorne Gaythorne is a suburb in the City of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. In the , Gaythorne had a population of 3,023 people. Geography Gaythorne is located seven kilometres north-west of the Brisbane central business district. It is bounded to ... () to its new QFHS Family History Research Centre at 46 Delaware Street, Chermside (). References External links * Non-profit organisations based in Queensland Historical societies of Australia Libraries in Brisbane Family hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Railway History
''Australian Railway History'' is a monthly magazine covering railway history in Australia, published by the New South Wales Division of the Australian Railway Historical Society on behalf of its state and territory Divisions. Australian Railway Historical Society History and profile It was first published in 1937 as the ''Australasian Railway and Locomotive Historical Society Bulletin'', being renamed ''ARHS Bulletin'' in 1952. In January 2004, the magazine was re-branded as ''Australian Railway History''. Historically, the magazine had a mix of articles dealing with historical material and items on current events drawn from its affiliate publications. Today, it contains only historical articles, two or three of them being in-depth.Parameters * Size : A4; ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooyar Railway Line
The Cooyar railway line was a branch line in the Darling Downs region of Queensland, Australia. The small town of Cooyar is about halfway to Kingaroy in the South Burnett Region. A plan to connect Kingaroy to the south via Cooyar did not eventuate and left Cooyar at the terminus of a branch line running from Oakey west of Toowoomba. It was opened on 28 April 1913 after previous stages to Kulpi and Peranga opened on 29 April 1912 and 4 November 1912 respectively. The line was partially closed beyond Acland on 1 May 1964, with the last segment closed on 8 December 1969.''The Cooyar Branch Line'' Milne, Rod Australian Railway Historical Society Bulletin, July, 1996 pp195-205 Services Mixed trains initially ran four times a week and were replaced in 1929 by a daily rail motor service to Toowoomba. The line connected the small towns of Acland, Kulpi, Peranga, Narko, Nutgrove, Wutul and Cooyar to the Queensland Rail western line at Oakey until 1964. This provided passenger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland
) , nickname = Sunshine State , image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Queensland , established_title2 = Separation from New South Wales , established_date2 = 6 June 1859 , established_title3 = Federation , established_date3 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Queen Victoria , demonym = , capital = Brisbane , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center_type = Administration , admin_center = 77 local government areas , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 = Jeannette Young , leader_title3 = Premier , leader_name3 = Annastacia Palaszczuk ( ALP) , legislature = Parliament of Queensland , judiciary = Supreme Court of Queensland , national_representation = Parliament of Australia , national_representation_type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toowoomba Region
The Toowoomba Region is a local government area located in the Darling Downs part of Queensland, Australia. Established in 2008, it was preceded by several previous local government areas with histories extending back to the early 1900s and beyond. In 2018-2019, it had a A$491 million budget, of which A$316 million is for service delivery and A$175.13 million capital (infrastructure) budget. History Prior to the 2008 amalgamation, the Toowoomba Region existed as eight distinct local government areas: the City of Toowoomba and the Shires of Cambooya, Clifton, Crows Nest, Jondaryan, Millmerran, Pittsworth, and Rosalie. The City had its beginning in the Toowoomba Municipality which was proclaimed on 24 November 1860 under the ''Municipalities Act 1858'', a piece of New South Wales legislation inherited by Queensland when it became a separate colony in 1859. William Henry Groom, sometimes described as the "father of Toowoomba", was elected its first mayor. It achieved a measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |