|
Nuda
Beroidae is a family of ctenophores or comb jellies more commonly referred to as the beroids. It is the only family within the monotypic order Beroida and the class Nuda. They are distinguished from other comb jellies by the complete absence of tentacles, in both juvenile and adult stages. Species of the family Beroidae are found in all the world's oceans and seas and are free-swimmers that form part of the plankton. Anatomy Some members of the diverse genus ''Beroe'' may occasionally attain a length of up to , though most species and individuals are less than about 10 cm; ''Neis cordigera'' is among the largest species in the class, often exceeding in length. The body is melon or cone-shaped with a wide mouth and pharynx and a capacious gastrovascular cavity. Many meridional canals branch off this and form a network of diverticulae in the mesogloea. There are no tentacles but there are a row of branched papillae, forming a figure of eight around the aboral tip. The sack-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuda
Beroidae is a family of ctenophores or comb jellies more commonly referred to as the beroids. It is the only family within the monotypic order Beroida and the class Nuda. They are distinguished from other comb jellies by the complete absence of tentacles, in both juvenile and adult stages. Species of the family Beroidae are found in all the world's oceans and seas and are free-swimmers that form part of the plankton. Anatomy Some members of the diverse genus ''Beroe'' may occasionally attain a length of up to , though most species and individuals are less than about 10 cm; ''Neis cordigera'' is among the largest species in the class, often exceeding in length. The body is melon or cone-shaped with a wide mouth and pharynx and a capacious gastrovascular cavity. Many meridional canals branch off this and form a network of diverticulae in the mesogloea. There are no tentacles but there are a row of branched papillae, forming a figure of eight around the aboral tip. The sack-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenophore2
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia. Depending on the species, adult ctenophores range from a few millimeters to in size. Only 100 to 150 species have been validated, and possibly another 25 have not been fully described and named. The textbook examples are cydippids with egg-shaped bodies and a pair of retractable tentacles fringed with tentilla ("little tentacles") that are covered with colloblasts, sticky cells that capture prey. Their bodies consist of a mass of jelly, with a layer two cells thick on the outside, and another lining the internal cavity. The phylum has a wide range of body forms, including the egg-shaped cydippids with retractable tentacles that capture prey, the flat generally combless platyct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenophores
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia. Depending on the species, adult ctenophores range from a few millimeters to in size. Only 100 to 150 species have been validated, and possibly another 25 have not been fully described and named. The textbook examples are cydippids with egg-shaped bodies and a pair of retractable tentacles fringed with tentilla ("little tentacles") that are covered with colloblasts, sticky cells that capture prey. Their bodies consist of a mass of jelly, with a layer two cells thick on the outside, and another lining the internal cavity. The phylum has a wide range of body forms, including the egg-shaped cydippids with retractable tentacles that capture prey, the flat generally combless pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comb Jelly
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia. Depending on the species, adult ctenophores range from a few millimeters to in size. Only 100 to 150 species have been validated, and possibly another 25 have not been fully described and named. The textbook examples are cydippids with egg-shaped bodies and a pair of retractable tentacles fringed with tentilla ("little tentacles") that are covered with colloblasts, sticky cells that capture prey. Their bodies consist of a mass of jelly, with a layer two cells thick on the outside, and another lining the internal cavity. The phylum has a wide range of body forms, including the egg-shaped cydippids with retractable tentacles that capture prey, the flat generally combless pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
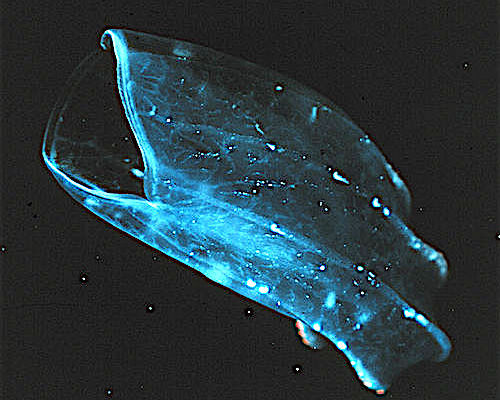
Neis
''Neis'' is a genus of nudan ctenophores. It is a monotypic genus containing the single species ''Neis cordigera''. It occurs only near Australia. As all beroids, it is a free-swimmer that form part of the plankton. ''Neis cordigera'' is among the largest species in the class, often exceeding in length. It is somewhat flattened and characterized by a pair of trailing gelatinous "wings" that extend beyond the aboral tip. Like other comb jellies, the body wall of nudans consists of an outer epidermis and an inner gastrodermis, separated by a jelly-like mesoglea Mesoglea refers to the extracellular matrix found in cnidarians like coral or jellyfish that functions as a hydrostatic skeleton. It is related to but distinct from mesohyl, which generally refers to extracellular material found in sponges. Desc .... The mesoglea has pigments that give many nudan species a slightly pink color; ''Neis cordigera'' may be yellowish or a deep orange-red. The aboral end is extended into tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beroe Gracilis
''Beroe gracilis'' is a species of comb jelly in the family Beroidae. It is a free-swimming species found in the North Sea, the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. Description ''Beroe gracilis'' is a translucent, elongated, hollow, cylindrical animal with a maximum length of about . Like the other members of the family Beroidae, it has no tentacles. The anterior end, with the gaping mouth at its tip, is slightly broader than the closed, posterior end. At the posterior end there is a statocyst, a flattened structure shaped like a figure-of-eight. From this, eight rows of combs with cilia radiate and extend three-quarters of the way along the body wall; it is the beating of these cilia that drive the animal forward, and their movement creates characteristic multicoloured sparkles. The general colour of the body wall is slightly milky, sometimes bluish or pinkish. The gut and its diverticula can be seen through the body wall. Distribution and habitat ''Beroe gracilis'' occurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beroe (ctenophore)
''Beroe'', commonly known as the cigar comb jellies, is a genus of comb jellies in the family Beroidae. Beroe exhibits bioluminescence. Species According to the World Register of Marine Species, the following species are members of this genus: *'' Beroe abyssicola'' Mortensen, 1927 *'' Beroe australis'' Agassiz & Mayer, 1899 *'' Beroe baffini'' Kramp, 1942 *'' Beroe basteri'' Lesson, 1830 *'' Beroe campana'' Komai, 1918 *'' Beroe compacta'' Moser, 1909 *'' Beroe constricta'' Chamisso & Eysenhardt, 1821 *'' Beroe cucumis'' Fabricius, 1780 *'' Beroe culcullus'' Martens, 1829 *'' Beroe cyathina'' A. Agassiz, 1860 *'' Beroe flemingii'' (Eschscholtz, 1829) *''Beroe forskalii'' Milne Edwards, 1841 *'' Beroe gilva'' Eschscholtz, 1829 *''Beroe gracilis'' Künne, 1939 *'' Beroe hyalina'' Moser, 1907 *''Beroe macrostoma'' Péron & Lesueur, 1808 *''Beroe mitraeformis'' Lesson, 1830 *''Beroe mitrata'' (Moser, 1907) *''Beroe ovale'' Bosc, 1802 *''Beroe ovata'' Bruguière, 1789 *''Beroe pand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neis Cordigera
''Neis'' is a genus of nudan ctenophores. It is a monotypic genus containing the single species ''Neis cordigera''. It occurs only near Australia. As all beroids, it is a free-swimmer that form part of the plankton. ''Neis cordigera'' is among the largest species in the class, often exceeding in length. It is somewhat flattened and characterized by a pair of trailing gelatinous "wings" that extend beyond the aboral tip. Like other comb jellies, the body wall of nudans consists of an outer epidermis and an inner gastrodermis, separated by a jelly-like mesoglea Mesoglea refers to the extracellular matrix found in cnidarians like coral or jellyfish that functions as a hydrostatic skeleton. It is related to but distinct from mesohyl, which generally refers to extracellular material found in sponges. Descr .... The mesoglea has pigments that give many nudan species a slightly pink color; ''Neis cordigera'' may be yellowish or a deep orange-red. The aboral end is extended into two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis (zoology)
In zoology, the epidermis is an epithelium (sheet of cells) that covers the body of a eumetazoan (animal more complex than a sponge). Eumetazoa have a cavity lined with a similar epithelium, the gastrodermis, which forms a boundary with the epidermis at the mouth. Sponges have no epithelium, and therefore no epidermis or gastrodermis. The epidermis of a more complex invertebrate is just one layer deep, and may be protected by a non-cellular cuticle. The epidermis of a higher vertebrate has many layers, and the outer layers are reinforced with keratin Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ... and then die. References Animal anatomy Epithelium {{animal-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia, south of the fertile plains of Southern Russia in Eastern Europe, and north of the mountainous Iranian Plateau of Western Asia. It covers a surface area of (excluding the highly saline lagoon of Garabogazköl to its east) and a volume of . It has a salinity of approximately 1.2% (12 g/L), about a third of the salinity of average seawater. It is bounded by Kazakhstan to the northeast, Russia to the northwest, Azerbaijan to the southwest, Iran to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southeast. The sea stretches nearly from north to south, with an average width of . Its gross coverage is and the surface is about below sea level. Its main freshwater inflow, Europe's longest river, the Volga, enters at the shallow north end. Two deep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish and whales. Marine plankton include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries. Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in the freshwaters of lakes and rivers. Plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, but there are also airborne versions, the aeroplankton, that live part of their lives drifting in the atmosphere. These include plant spores, pollen and wind-scattered seeds, as well as microorganisms swept into the air from terrestrial dust storms and oceanic plankton swept into the air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Friedrich Von Eschscholtz
Johann Friedrich Gustav von Eschscholtz (1 November 1793 – 7 May 1831)Sterling (1997) was a Baltic German physician, naturalist, and entomologist. He was one of the earliest scientific explorers of the Pacific region, making significant collections of flora and fauna in Alaska, California, and Hawaii. Biography Eschscholtz was born in the Livonian city of Dorpat, then part of the Russian Empire. His parents, Johann Gottfried and Katherine Hedwig Ziegler Eschscholtz were ethnic Baltic Germans. He studied medicine and zoology at the University of Dorpat and served as an assistant to Carl Friedrich von Ledebour, a professor of botany.McKelvey Eschscholtz received a medical degree in 1815. First voyage On the recommendation of Ledebour, Eschscholtz served as surgeon and naturalist on the Russian expeditionary ship ''Rurik'' under the command of Otto von Kotzebue.Daum (2019) From 1815 to 1818 the expedition circumnavigated the globe for the purposes of seeking a Northwest Passage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |