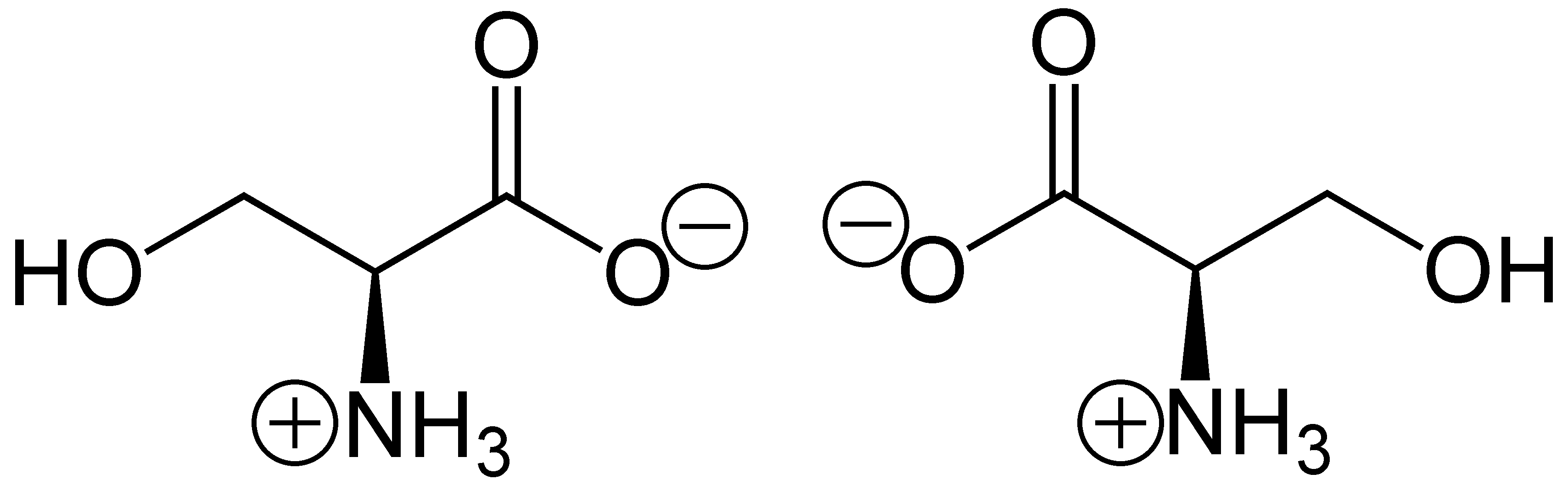|
Nucleic Acid Inhibitor
A nucleic acid inhibitor is a type of antibacterial that acts by inhibiting the production of nucleic acids. There are two major classes: DNA inhibitors and RNA inhibitors. The antifungal flucytosine acts in a similar manner. DNA inhibitors Classic DNA inhibitors such as the quinolones act upon DNA gyrase as a topoisomerase inhibitor. Another group of DNA inhibitors, including nitrofurantoin and metronidazole, act upon anaerobic bacteria. These act by generating metabolites that are incorporated into DNA strands, which then are more prone to breakage. These drugs are selectively toxic to anaerobic organisms, but can affect human cells. RNA inhibitors RNA inhibitors such as rifampin, act upon DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Antifolates (DNA, RNA, and protein) Antifolates act primarily as inhibitors of both RNA and DNA, and are often grouped with nucleic acid inhibitors in textbooks. However, they also act indirectly as protein synthesis inhibitors (because tetrahydrofolate is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rifampin
Rifampicin, also known as rifampin, is an ansamycin antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis (TB), ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, leprosy, and Legionnaires’ disease. It is almost always used together with other antibiotics with two notable exceptions: when given as a "preferred treatment that is strongly recommended" for latent TB infection; and when used as post-exposure prophylaxis to prevent ''Haemophilus influenzae'' type b and meningococcal disease in people who have been exposed to those bacteria. Before treating a person for a long period of time, measurements of liver enzymes and blood counts are recommended. Rifampicin may be given either by mouth or intravenously. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and loss of appetite. It often turns urine, sweat, and tears a red or orange color. Liver problems or allergic reactions may occur. It is part of the recommended treatment of active tuberculosis during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical role in the metabolism and health of many species, including humans. It is encoded by the codon AUG. Methionine is also an important part of angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels. Supplementation may benefit those suffering from copper poisoning. Overconsumption of methionine, the methyl group donor in DNA methylation, is related to cancer growth in a number of studies. Methionine was first isolated in 1921 by John Howard Mueller. Biochemical details Methionine (abbreviated as Met or M; encoded by the codon AUG) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological pH conditions), an amino group (which is in the protonated fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the naturally occurring proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L-stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, ''sericum''. Serine's structure was estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrofolate
Tetrahydrofolic acid (THFA), or tetrahydrofolate, is a folic acid derivative. Metabolism Human synthesis Tetrahydrofolic acid is produced from dihydrofolic acid by dihydrofolate reductase. This reaction is inhibited by methotrexate. It is converted into 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate by serine hydroxymethyltransferase. Bacterial synthesis Many bacteria use dihydropteroate synthetase to produce dihydropteroate, a molecule without function in humans. This makes it a useful target for sulfonamide antibiotics, which compete with the PABA precursor. Functions Tetrahydrofolic acid is a cofactor in many reactions, especially in the synthesis (or anabolism) of amino acids and nucleic acids. In addition, it serves as a carrier molecule for single-carbon moieties, that is, groups containing one carbon atom e.g. methyl, methylene, methenyl, formyl, or formimino. When combined with one such single-carbon moiety as in 10-formyltetrahydrofolate, it acts as a donor of a group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Synthesis Inhibitor
A protein synthesis inhibitor is a compound that stops or slows the growth or proliferation of cells by disrupting the processes that lead directly to the generation of new proteins. While a broad interpretation of this definition could be used to describe nearly any compound depending on concentration, in practice, it usually refers to compounds that act at the molecular level on translational machinery (either the ribosome itself or the translation factor), taking advantages of the major differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosome structures. Mechanism In general, protein synthesis inhibitors work at different stages of bacterial mRNA translation into proteins, like initiation, elongation (including aminoacyl tRNA entry, proofreading, peptidyl transfer, and bacterial translocation) and termination: Earlier stages * Rifamycin inhibits bacterial DNA transcription into mRNA by inhibiting DNA-dependent RNA polymerase by binding its beta-subunit. * alpha-Amanitin is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifolate
Antifolates are a class of antimetabolite medications that antagonise (that is, block) the actions of folic acid (vitamin B9). Folic acid's primary function in the body is as a cofactor to various methyltransferases involved in serine, methionine, thymidine and purine biosynthesis. Consequently, antifolates inhibit cell division, DNA/RNA synthesis and repair and protein synthesis. Some such as proguanil, pyrimethamine and trimethoprim selectively inhibit folate's actions in microbial organisms such as bacteria, protozoa and fungi. The majority of antifolates work by inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR). Comparison of available agents Mechanism Many are primarily DHFR inhibitors, but raltitrexed is an inhibitor of thymidylate synthase, and pemetrexed inhibits both and a third enzyme. Antifolates act specifically during DNA and RNA synthesis, and thus are cytotoxic during the S-phase of the cell cycle. Thus, they have a greater toxic effect on rapidly dividing cells (such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA-dependent RNA Polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template. Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the double-stranded DNA so that one strand of the exposed nucleotides can be used as a template for the synthesis of RNA, a process called transcription. A transcription factor and its associated transcription mediator complex must be attached to a DNA binding site called a promoter region before RNAP can initiate the DNA unwinding at that position. RNAP not only initiates RNA transcription, it also guides the nucleotides into position, facilitates attachment and elongation, has intrinsic proofreading and replacement capabilities, and termination recognition capability. In eukaryotes, RNAP can build chains as long as 2.4 million nucleotides. RNAP produces RNA that, functionally, is either for protein coding, i.e. messenger RNA (mRNA); or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metronidazole
Metronidazole, sold under the brand name Flagyl among others, is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication. It is used either alone or with other antibiotics to treat pelvic inflammatory disease, endocarditis, and bacterial vaginosis. It is effective for dracunculiasis, giardiasis, trichomoniasis, and amebiasis. It is an option for a first episode of mild-to-moderate ''Clostridium difficile'' colitis if vancomycin or fidaxomicin is unavailable. Metronidazole is available by mouth, as a cream, and by injection into a vein. Common side effects include nausea, a metallic taste, loss of appetite, and headaches. Occasionally seizures or allergies to the medication may occur. Some state that metronidazole should not be used in early pregnancy, while others state doses for trichomoniasis are safe. Metronidazole is generally considered compatible with breastfeeding. Metronidazole began to be commercially used in 1960 in France. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Esse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibacterial
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antiseptics) ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrofurantoin
Nitrofurantoin is an antibacterial medication used to treat urinary tract infections, but it is not as effective for kidney infections. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include nausea, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and headaches. Rarely numbness, lung problems, or liver problems may occur. It should not be used in people with kidney problems. While it appears to be generally safe during pregnancy it should not be used near delivery. While it usually works by slowing bacterial growth, it may result in bacterial death at the high concentrations found in urine. Nitrofurantoin was first sold in 1953. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 167th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 3million prescriptions. Medical uses Current uses include the treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs) and prophylaxis against UTIs in people prone to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topoisomerase Inhibitor
Topoisomerase inhibitors are chemical compounds that block the action of topoisomerases, which are broken into two broad subtypes: type I topoisomerases (TopI) and type II topoisomerases (TopII). Topoisomerase plays important roles in cellular reproduction and DNA organization, as they mediate the cleavage of single and double stranded DNA to relax supercoils, untangle catenanes, and condense chromosomes in eukaryotic cells. Topoisomerase inhibitors influence these essential cellular processes. Some topoisomerase inhibitors prevent topoisomerases from performing DNA strand breaks while others, deemed topoisomerase poisons, associate with topoisomerase-DNA complexes and prevent the re-ligation step of the topoisomerase mechanism. These topoisomerase-DNA-inhibitor complexes are cytotoxic agents, as the un-repaired single- and double stranded DNA breaks they cause can lead to apoptosis and cell death. Because of this ability to induce apoptosis, topoisomerase inhibitors have gained int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |