|
Nuclear Safety Systems
:''This article covers the technical aspects of active nuclear safety systems in the United States. For a general approach to nuclear safety, see nuclear safety.'' The three primary objectives of nuclear reactor safety systems as defined by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission are to shut down the reactor, maintain it in a shutdown condition and prevent the release of radioactive material. Reactor protection system (RPS) A reactor protection system is designed to immediately terminate the nuclear reaction. By breaking the nuclear chain reaction, the source of heat is eliminated. Other systems can then be used to remove decay heat from the core. All nuclear plants have some form of reactor protection system. Control rods Control rods are a series of rods that can be quickly inserted into the reactor core to absorb neutrons and rapidly terminate the nuclear reaction. They are typically composed of actinides, lanthanides, transition metals, and boron, in various alloys wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Safety
Nuclear safety is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The achievement of proper operating conditions, prevention of accidents or mitigation of accident consequences, resulting in protection of workers, the public and the environment from undue radiation hazards". The IAEA defines nuclear security as "The prevention and detection of and response to, theft, sabotage, unauthorized access, illegal transfer or other malicious acts involving nuclear materials, other radioactive substances or their associated facilities". This covers nuclear power plants and all other nuclear facilities, the transportation of nuclear materials, and the use and storage of nuclear materials for medical, power, industry, and military uses. The nuclear power industry has improved the safety and performance of reactors, and has proposed new and safer reactor designs. However, a perfect safety cannot be guaranteed. Potential sources of problems include human errors and external even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
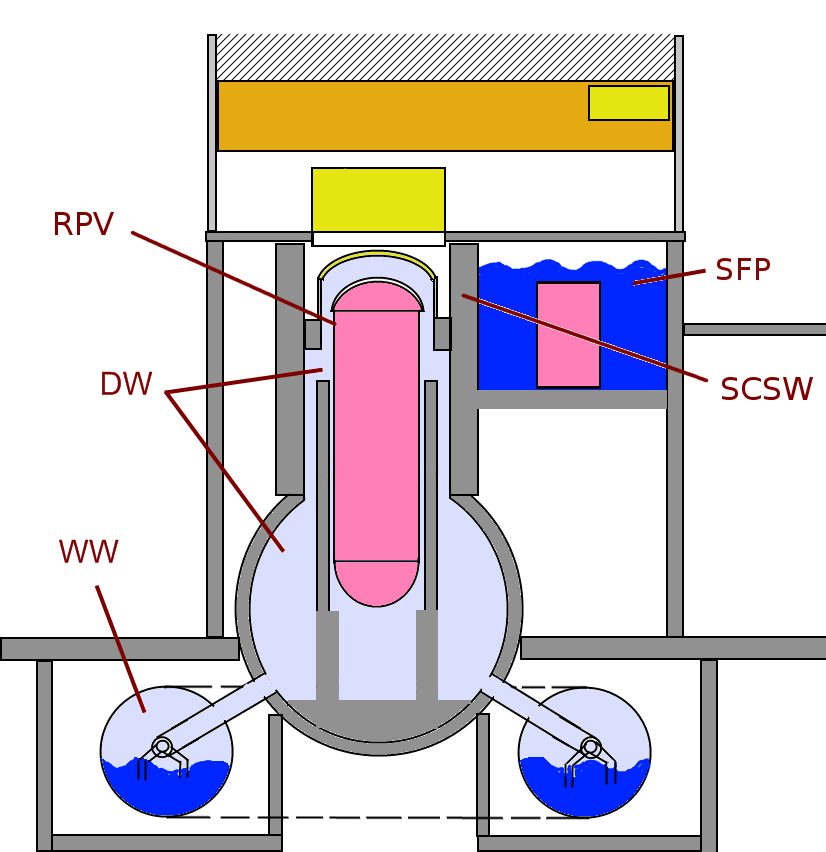
KKP Auslauf
KKP may refer to: * Communist Party of Kurdistan (Turkish: ''Kürdistan Komünist Partisi'', KKP) * Confederation of the Polish Crown (Polish: ''Konfederacja Korony Polskiej'', KKP) * Christian Conservative Party (Norwegian: ''Kristent Konservativt Parti'', KKP) * National Coordinating Commission (Polish: ''Krajowa Komisja Porozumiewawcza'', KKP), the executive branch of the Solidarity trade union * Philippsburg Nuclear Power Plant (German: ''Kernkraftwerk Philippsburg'', KKP) * Ministry of Marine Affairs and Fisheries (Indonesia) (Indonesian: ''Kementerian Kelautan dan Perikanan'', KKP) * Koko-Bera language (ISO 639:kkp) * Kouassi Kouamé Patrice, a politician from Ivory Coast * Kung Kao Po, a Chinese language newspaper in Hong Kong * Kiatnakin Bank, a Thai bank (Stock symbol: KKP) * Kamgar Kisan Paksha, now defunct political party of India See also * Kappa Kappa Psi, a fraternity for college and university band members in the United States, akso known as KKPsi * KK thesis The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Rod
Nuclear fuel is material used in nuclear power stations to produce heat to power turbines. Heat is created when nuclear fuel undergoes nuclear fission. Most nuclear fuels contain heavy fissile actinide elements that are capable of undergoing and sustaining nuclear fission. The three most relevant fissile isotopes are uranium-233, uranium-235 and plutonium-239. When the unstable nuclei of these atoms are hit by a slow-moving neutron, they frequently split, creating two daughter nuclei and two or three more neutrons. In that case, the neutrons released go on to split more nuclei. This creates a self-sustaining chain reaction that is controlled in a nuclear reactor, or uncontrolled in a nuclear weapon. Alternatively, if the nucleus absorbs the neutron without splitting, it creates a heavier nucleus with one additional neutron. The processes involved in mining, refining, purifying, using, and disposing of nuclear fuel are collectively known as the nuclear fuel cycle. Not all ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flywheels
A flywheel is a mechanical device which uses the conservation of angular momentum to store rotational energy; a form of kinetic energy proportional to the product of its moment of inertia and the square of its rotational speed. In particular, assuming the flywheel's moment of inertia is constant (i.e., a flywheel with fixed mass and second moment of area revolving about some fixed axis) then the stored (rotational) energy is directly associated with the square of its rotational speed. Since a flywheel serves to store mechanical energy for later use, it is natural to consider it as a kinetic energy analogue of an electrical inductor. Once suitably abstracted, this shared principle of energy storage is described in the generalized concept of an accumulator. As with other types of accumulators, a flywheel inherently smooths sufficiently small deviations in the power output of a system, thereby effectively playing the role of a low-pass filter with respect to the mechanical velocity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery (electricity)
An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices. When a battery is supplying power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negative terminal is the anode. The terminal marked negative is the source of electrons that will flow through an external electric circuit to the positive terminal. When a battery is connected to an external electric load, a redox reaction converts high-energy reactants to lower-energy products, and the free-energy difference is delivered to the external circuit as electrical energy. Historically the term "battery" specifically referred to a device composed of multiple cells; however, the usage has evolved to include devices composed of a single cell. Primary (single-use or "disposable") batteries are used once and discarded, as the electrode materials are irreversibly changed during discharge; a common example is the alkaline battery us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Generators
A diesel generator (DG) (also known as a diesel Genset) is the combination of a diesel engine with an electric generator (often an alternator) to generate electrical energy. This is a specific case of engine generator. A diesel compression-ignition engine is usually designed to run on diesel fuel, but some types are adapted for other liquid fuels or natural gas. Diesel generating sets are used in places without connection to a power grid, or as an emergency power supply if the grid fails, as well as for more complex applications such as peak-lopping, grid support, and export to the power grid. Diesel generator size is crucial to minimize low load or power shortages. Sizing is complicated by the characteristics of modern electronics, specifically non-linear loads. In size ranges around 50 MW and above, an open cycle gas turbine is more efficient at full load than an array of diesel engines, and far more compact, with comparable capital costs; but for regular part-loading, eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Emergency Core Coolling System
Passive may refer to: * Passive voice, a grammatical voice common in many languages, see also Pseudopassive * Passive language, a language from which an interpreter works * Passivity (behavior), the condition of submitting to the influence of one's superior * Passive-aggressive behavior, resistance to following through with expectations in interpersonal or occupational situations * Passive income, income resulting from cash flow received on a regular basis * Passive immunity, the transfer of active humoral immunity * Passive experience, observation lacking recipricol interaction; and wrought with delusion of control. Science and technology * Passivation (chemistry), process of making a material "passive" in relation to another material prior to using the materials together * Passivity (engineering) a property of engineering systems, particularly in analog electronics and control systems * Passive solar building design, which uses (or avoids) sunlight as an energy source without ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loss Of Coolant Accident
A loss-of-coolant accident (LOCA) is a mode of failure for a nuclear reactor; if not managed effectively, the results of a LOCA could result in reactor core damage. Each nuclear plant's emergency core cooling system (ECCS) exists specifically to deal with a LOCA. Nuclear reactors generate heat internally; to remove this heat and convert it into useful electrical power, a coolant system is used. If this coolant flow is reduced, or lost altogether, the nuclear reactor's emergency shutdown system is designed to stop the fission chain reaction. However, due to radioactive decay, the nuclear fuel will continue to generate a significant amount of heat. The decay heat produced by a reactor shutdown from full power is initially equivalent to about 5 to 6% of the thermal rating of the reactor. If all of the independent cooling trains of the ECCS fail to operate as designed, this heat can increase the fuel temperature to the point of damaging the reactor. *If water is present, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Emergency Core Cooling System
Active may refer to: Music * ''Active'' (album), a 1992 album by Casiopea * Active Records, a record label Ships * ''Active'' (ship), several commercial ships by that name * HMS ''Active'', the name of various ships of the British Royal Navy * USCS ''Active'', a US Coast Survey ship in commission from 1852 to 1861 * USCGC ''Active'', the name of various ships of the US Coast Guard * USRC ''Active'', the name of various ships of the US Revenue Cutter Service * USS ''Active'', the name of various ships of the US Navy Computers and electronics * Active Enterprises, a defunct video game developer * Sky Active, the brand name for interactive features on Sky Digital available in the UK and Ireland * Active (software), software used for open publishing by Indymedia; see Independent Media Center Sciences * Thermodynamic activity, measure of an effective concentration of a species in a mixture. * Activation, in chemistry the process whereby something is prepared for a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Nuclear News
World Nuclear Association is the international organization that promotes nuclear power and supports the companies that comprise the global nuclear industry. Its members come from all parts of the nuclear fuel cycle, including uranium mining, uranium conversion, uranium enrichment, nuclear fuel fabrication, plant manufacture, transport, and the disposition of used nuclear fuel as well as electricity generation itself. Together, World Nuclear Association members are responsible for 70% of the world's nuclear power as well as the vast majority of world uranium, conversion and enrichment production. The Association says it aims to fulfill a dual role for its members: Facilitating their interaction on technical, commercial and policy matters and promoting wider public understanding of nuclear technology. It has a secretariat of around 30 staff. The Association was founded in 2001 on the basis of the Uranium Institute, itself founded in 1975. Membership World Nuclear Associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fukushima II Nuclear Power Plant
The is a nuclear power plant located on a site in the town of Naraha and Tomioka in the Futaba District of Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. The Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) runs the plant. After the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, the four reactors at Fukushima Daini automatically shut down. While the sister plant Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, approximately to the north, suffered extensive damage, the Daini Plant was back under control within two days, reaching cold shutdown. The plant has not been operating since, and in July 2019 a decision to decommission the plant was made. Description All reactors in the Fukushima II Nuclear Power Plant are BWR-5 type with electric power of 1,100 MW each (net output: 1,067 MW each). The reactors for units 1 and 3 were supplied by Toshiba, and for units 2 and 4 by Hitachi. Units 1–3 were built by Kajima while the unit 4 was built by Shimizu and Takenaka. Electrical connections The Fukushima Dain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fukushima I Nuclear Accidents
The was a nuclear accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Fukushima, Japan. The proximate cause of the disaster was the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, which occurred on the afternoon of 11 March 2011 and remains the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Japan. The earthquake triggered a powerful tsunami, with 13–14-meter-high waves damaging the nuclear power plant's emergency diesel generators, leading to a loss of electric power. The result was the most severe nuclear accident since the Chernobyl disaster in 1986, classified as level seven on the International Nuclear Event Scale (INES) after initially being classified as level five, and thus joining Chernobyl as the only other accident to receive such classification. While the 1957 explosion at the Mayak facility was the second worst by radioactivity released, the INES ranks incidents by impact on population, so Chernobyl (335,000 people evacuated) and Fukushima (154,000 evacu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
_Generator_Set.jpg)