|
Nuclear Dimorphism
Nuclear dimorphism is a term referred to the special characteristic of having two different kinds of nuclei in a cell. There are many differences between the types of nuclei. This feature is observed in protozoan ciliates, like ''Tetrahymena'', and some foraminifera. Ciliates contain two nucleus types: a macronucleus that is primarily used to control metabolism, and a micronucleus which performs reproductive functions and generates the macronucleus. The compositions of the nuclear pore complexes help determine the properties of the macronucleus and micronucleus. Nuclear dimorphism is subject to complex epigenetic controls. Nuclear dimorphism is continuously being studied to understand exactly how the mechanism works and how it is beneficial to cells. Learning about nuclear dimorphism is beneficial to understanding old eukaryotic mechanisms that have been preserved within these unicellular organisms but did not evolve into multicellular eukaryotes. Key components The ciliated p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote that develops into an organism composed of cells with two sets of chromosomes ( diploid). This is typical in animals, though the number of chromosome sets and how that number changes in sexual reproduction varies, especially among plants, fungi, and other eukaryotes. Sexual reproduction is the most common life cycle in multicellular eukaryotes, such as animals, fungi and plants. Sexual reproduction also occurs in some unicellular eukaryotes. Sexual reproduction does not occur in prokaryotes, unicellular organisms without cell nuclei, such bacteria and archaea. However, some process in bacteria may be considered analogous to sexual reproduction in that they incorporate new genetic information, including bacterial conjugation, transf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Fission
Binary may refer to: Science and technology Mathematics * Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1) * Binary function, a function that takes two arguments * Binary operation, a mathematical operation that takes two arguments * Binary relation, a relation involving two elements * Binary-coded decimal, a method for encoding for decimal digits in binary sequences * Finger binary, a system for counting in binary numbers on the fingers of human hands Computing * Binary code, the digital representation of text and data * Bit, or binary digit, the basic unit of information in computers * Binary file, composed of something other than human-readable text ** Executable, a type of binary file that contains machine code for the computer to execute * Binary tree, a computer tree data structure in which each node has at most two children Astronomy * Binary star, a star system with two stars in it * Binary planet, two planetary bodies of comparabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
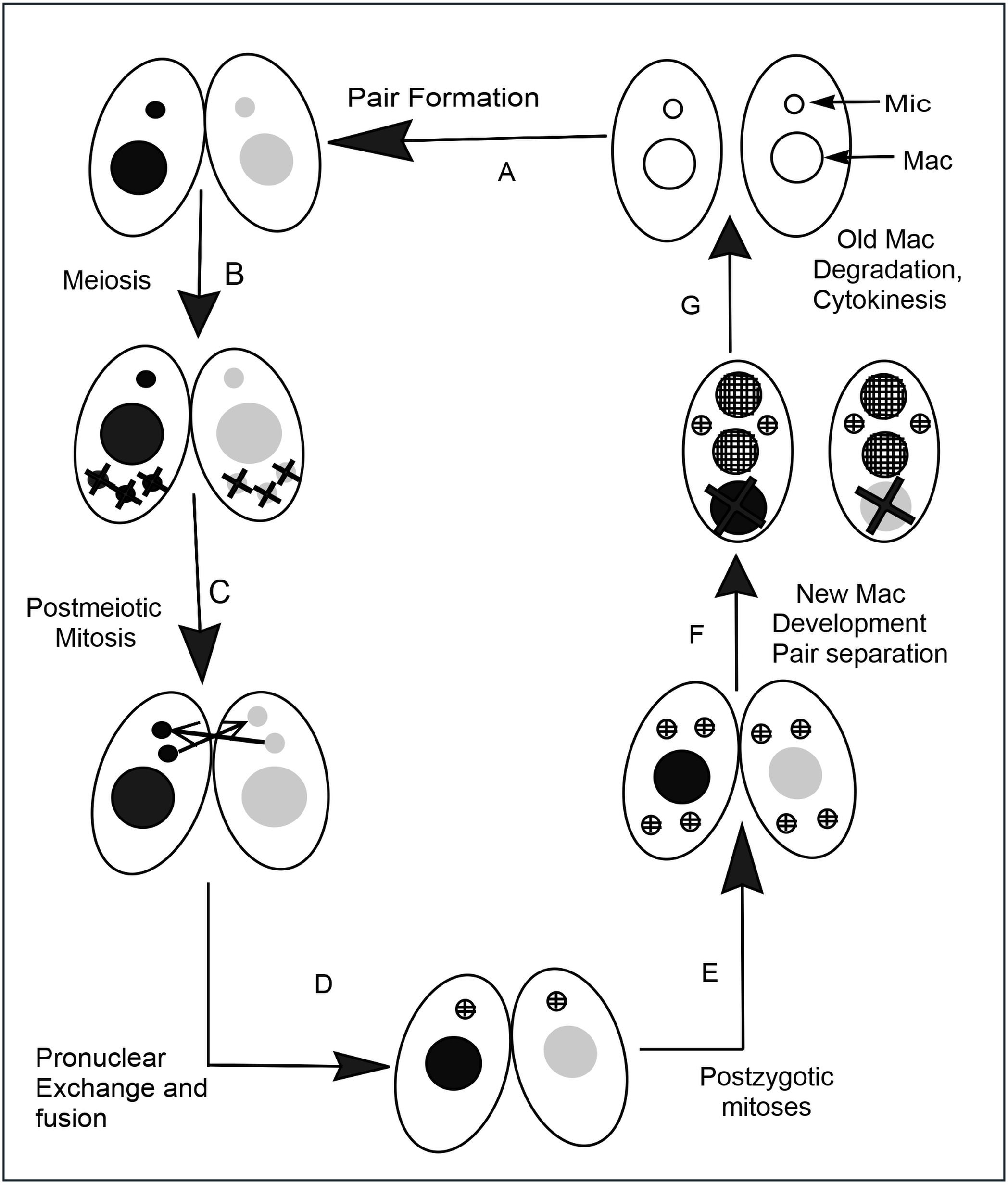
Tetrahymena Conjugation
''Tetrahymena'', a unicellular eukaryote, is a genus of free-living ciliates. The genus Tetrahymena is the most widely studied member of its phylum. It can produce, store and react with different types of hormones. Tetrahymena cells can recognize both related and hostile cells. They can also switch from commensalistic to pathogenic modes of survival. They are common in freshwater lakes, ponds, and streams. ''Tetrahymena'' species used as model organisms in biomedical research are ''T. thermophila'' and '' T. pyriformis''. ''T. thermophila'': a model organism in experimental biology As a ciliated protozoan, ''Tetrahymena thermophila'' exhibits nuclear dimorphism: two types of cell nuclei. They have a bigger, non-germline macronucleus and a small, germline micronucleus in each cell at the same time and these two carry out different functions with distinct cytological and biological properties. This unique versatility allows scientists to use ''Tetrahymena'' to identify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
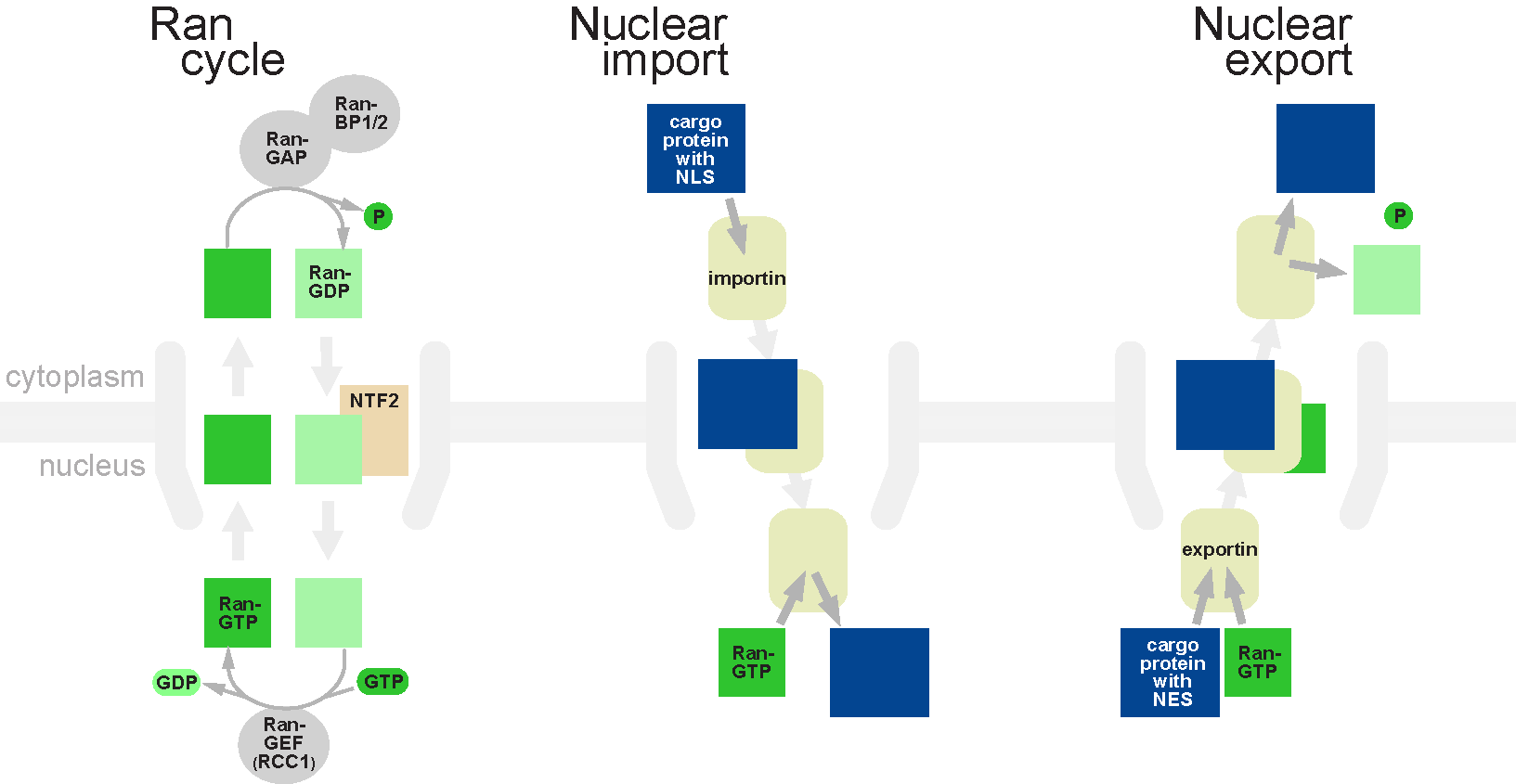
Nuclear Transport
Nuclear transport refers to the mechanisms by which molecules move across the nuclear membrane of a cell. The entry and exit of large molecules from the cell nucleus is tightly controlled by the nuclear pore complexes (NPCs). Although small molecules can enter the nucleus without regulation, macromolecules such as RNA and proteins require association with transport factors known as nuclear transport receptors, like karyopherins called importins to enter the nucleus and exportins to exit. Nuclear import Protein that must be imported to the nucleus from the cytoplasm carry nuclear localization signals (NLS) that are bound by importins. An NLS is a sequence of amino acids that acts as a tag. They are most commonly hydrophilic proteins containing lysine and arginine residues, although diverse NLS sequences have been documented. Proteins, transfer RNA, and assembled ribosomal subunits are exported from the nucleus due to association with exportins, which bind signaling sequences cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Envelope
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material. The nuclear envelope consists of two lipid bilayer membranes: an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. The space between the membranes is called the perinuclear space. It is usually about 10–50 nm wide. The outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. The nuclear envelope has many nuclear pores that allow materials to move between the cytosol and the nucleus. Intermediate filament proteins called lamins form a structure called the nuclear lamina on the inner aspect of the inner nuclear membrane and give structural support to the nucleus. Structure The nuclear envelope is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes, an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. These membranes are connected to each other by nuclear pores. Two sets of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleoporin
Nucleoporins are a family of proteins which are the constituent building blocks of the nuclear pore complex (NPC). The nuclear pore complex is a massive structure embedded in the nuclear envelope at sites where the inner and outer nuclear membranes fuse, forming a gateway that regulates the flow of macromolecules between the cell nucleus and the cytoplasm. Nuclear pores enable the passive and facilitated transport of molecules across the nuclear envelope. Nucleoporins, a family of around 30 proteins, are the main components of the nuclear pore complex in eukaryotic cells. Nucleoporin 62 is the most abundant member of this family. Nucleoporins are able to transport molecules across the nuclear envelope at a very high rate. A single NPC is able to transport 60,000 protein molecules across the nuclear envelope every minute. Structure Nucleoporins aggregate to form a nuclear pore complex, an octagonal ring that traverses the nuclear envelope. The ring consists of eight scaf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism. In multicellular organisms, the zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In humans and most other anisogamous organisms, a zygote is formed when an egg cell and sperm cell come together to create a new unique organism. In single-celled organisms, the zygote can divide asexually by mitosis to produce identical offspring. German zoologists Oscar and Richard Hertwig made some of the first discoveries on animal zygote formation in the late 19th century. Humans In human fertilization, a released ovum (a haploid secondary oocyte with replicate chromosome copies) and a haploid sperm cell (male gamete) combine to form a single diploid cell called the zygote. Once the single sperm fuses with the oocyte, the latter completes the division of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleolus
The nucleolus (, plural: nucleoli ) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis, which is the synthesis of ribosomes. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of signal recognition particles and plays a role in the cell's response to stress. Nucleoli are made of proteins, DNA and RNA, and form around specific chromosomal regions called nucleolar organizing regions. Malfunction of nucleoli can be the cause of several human conditions called "nucleolopathies" and the nucleolus is being investigated as a target for cancer chemotherapy. History The nucleolus was identified by bright-field microscopy during the 1830s. Little was known about the function of the nucleolus until 1964, when a study of nucleoli by John Gurdon and Donald Brown in the African clawed frog '' Xenopus laevis'' generated increasing interest in the function and detailed structure of the nucleolus. They found that 25% of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatic (biology)
The term somatic - etymologically from the Ancient Greek words of "σωματικός" (sōmatikós, “bodily”) and σῶμα (sôma, “body”) - is often used in biology to refer to the cells of the body in contrast to the reproductive (germline) cells, which usually give rise to the egg or sperm (or other gametes in other organisms). These somatic cells are diploid, containing two copies of each chromosome, whereas germ cells are haploid, as they only contain one copy of each chromosome (in preparation for fertilisation). Although under normal circumstances all somatic cells in an organism contain identical DNA, they develop a variety of tissue-specific characteristics. This process is called differentiation, through epigenetic and regulatory alterations. The grouping of similar cells and tissues creates the foundation for organs. Somatic mutations are changes to the genetics of a multicellular organism that are not passed on to its offspring through the germline. Most ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyploid
Polyploidy is a condition in which the cells of an organism have more than one pair of (homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes, where each set contains one or more chromosomes and comes from each of two parents, resulting in pairs of homologous chromosomes between sets. However, some organisms are polyploid. Polyploidy is especially common in plants. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Males of bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germline
In biology and genetics, the germline is the population of a multicellular organism's cells that pass on their genetic material to the progeny (offspring). In other words, they are the cells that form the egg, sperm and the fertilised egg. They are usually differentiated to perform this function and segregated in a specific place away from other bodily cells. As a rule, this passing-on happens via a process of sexual reproduction; typically it is a process that includes systematic changes to the genetic material, changes that arise during recombination, meiosis and fertilization for example. However, there are many exceptions across multicellular organisms, including processes and concepts such as various forms of apomixis, autogamy, automixis, cloning or parthenogenesis. The cells of the germline are called germ cells. For example, gametes such as a sperm and an egg are germ cells. So are the cells that divide to produce gametes, called gametocytes, the cells that produce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |