|
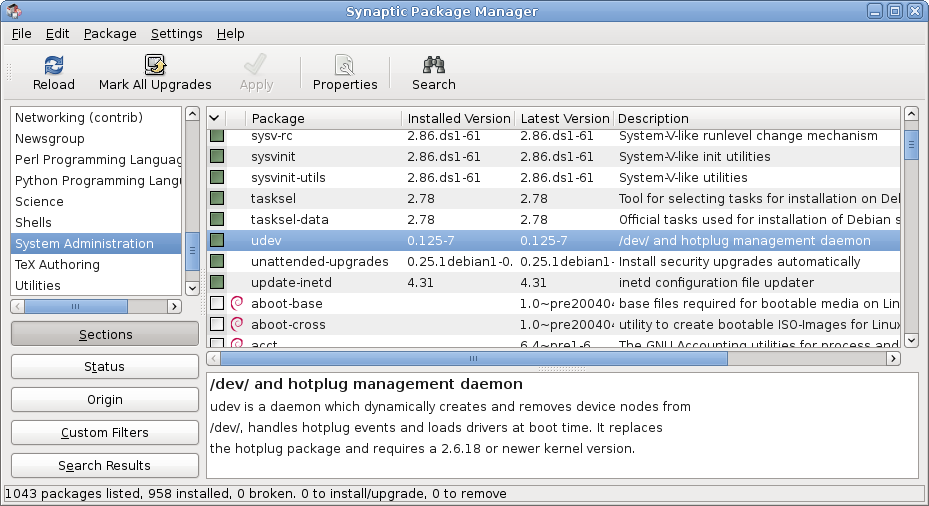
Npackd
This is a list of notable software package management systems, categorized first by package format (binary, source code, hybrid) and then by operating system family. Binary packages The following package management systems distribute apps in binary package form; i.e., all apps are compiled and ready to be installed and use. Unix-like Linux * dpkg: Originally used by Debian and now by Ubuntu. Uses the .deb format and was the first to have a widely known dependency resolution tool, APT. The ncurses-based front-end for APT, aptitude, is also a popular package manager for Debian-based systems; * Entropy: Used by and created for Sabayon Linux. It works with binary packages that are bzip2-compressed tar archives (file extension: .tbz2), that are created using Entropy itself, from tbz2 binaries produced by Portage: From ebuilds, a type of specialized shell script; * Flatpak: A containerized/sandboxed packaging format previously known as xdg-app; * GNU Guix: Used by the GNU System. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Package Management System
A package manager or package-management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner. A package manager deals with ''packages'', distributions of software and data in archive files. Packages contain metadata, such as the software's name, description of its purpose, version number, vendor, checksum (preferably a cryptographic hash function), and a list of dependencies necessary for the software to run properly. Upon installation, metadata is stored in a local package database. Package managers typically maintain a database of software dependencies and version information to prevent software mismatches and missing prerequisites. They work closely with software repositories, binary repository managers, and app stores. Package managers are designed to eliminate the need for manual installs and updates. This can be particularly useful for large ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipkg
ipkg, or the Itsy Package Management System, is a discontinued lightweight package management system designed for embedded devices that resembles Debian's dpkg. It was used in the Unslung operating system for the Linksys NSLU2 ( Optware), in OpenWrt, Openmoko, webOS, Gumstix, the iPAQ, QNAP NAS appliances and elsewhere; as of early 2017 it can still be used for the Synology NAS appliances and in the LuneOS operating system (although opkg is an increasingly common replacement). As usual for package management systems, ipkg's command-line utility allows installation of new packages, upgrading or removal of existing packages, querying package repositories for available packages, and listing already installed packages. The development for this project has been discontinued. Many projects which formerly used ipkg have adopted the ipkg fork opkg opkg (''open package management'') is a lightweight package management system based upon ipkg. It is written in C and resemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
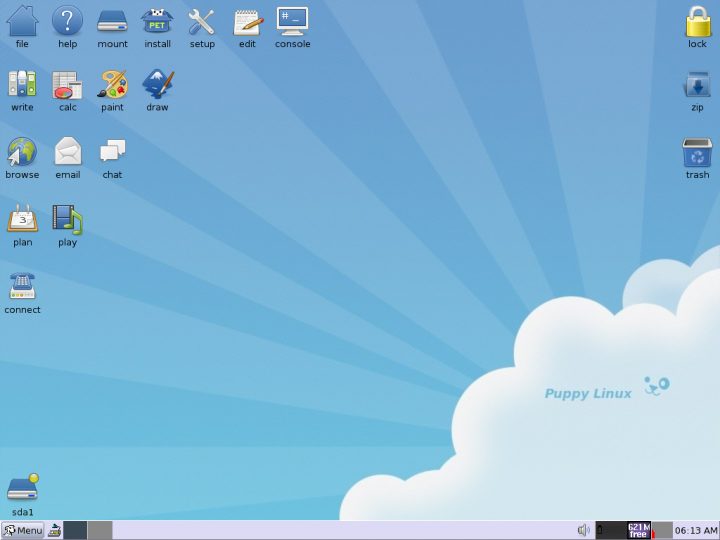
PETget
Puppy Linux is an operating system and family of light-weight Linux distributions that focus on ease of use and minimal memory footprint. The entire system can be run from random-access memory (RAM) with current versions generally taking up about 600 MB (64-bit), 300 MB (32-bit), allowing the boot medium to be removed after the operating system has started. Applications such as AbiWord, Gnumeric and MPlayer are included, along with a choice of lightweight web browsers and a utility for downloading other packages. The distribution was originally developed by Barry Kauler and other members of the community, until Kauler retired in 2013. The tool Woof can build a Puppy Linux distribution from the binary packages of other Linux distributions. History Barry Kauler started Puppy Linux in response to a trend of other distributions becoming stricter on system requirements over time. His own distribution, with an emphasis on speed and efficiency and being lightweight, started from "Boot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DeLi Linux
Deli may refer to: * Delicatessen, a shop selling specially prepared food, or food prepared by such a shop * Sultanate of Deli, a former sultanate in North Sumatra, Indonesia Places * Deli, Boyer-Ahmad, a village in Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province, Iran * Deli, Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari, a village in Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari Province, Iran * Deli, Isfahan, a village in Isfahan Province, Iran * Deli, Izeh, a village in Khuzestan Province, Iran * Deli, Kohgiluyeh, a village in Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province, Iran * Deli Serdang Regency, a regency in the province of North Sumatra, Indonesia * Deli Zal Beyg, a village in Lorestan Province, Iran * Deli, a town in Sumatra developed for tobacco commerce that became Medan Other uses * Deli (company), a global office supply company based in China * Deli (Ottoman troops) A Deli (from Turkish ''deli'', meaning "mad, wild, daring") was a member of a light cavalry unit within the Ottoman Empire. Their main role was to act as fron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frugalware
Frugalware Linux has been a general-purpose Linux distribution designed for intermediate users who are familiar with command-line operations. Early versions were based on Slackware, but it later became an independently developed distribution. Frugalware made use of the Pacman package management system from Arch Linux. History Frugalware was founded in 2004 by Miklós Vajna. He considered Slackware's package manager ''pkgtools'' too slow, and wanted to rewrite it in C. He was told that it would never be accepted by Slackware, so Vajna started to think about founding a separate Linux distribution. He replaced Slackware's original init scripts and build system, and added Pacman, the package manager from Arch Linux. As a result, Frugalware was born. Package management Since version 0.6 Frugalware has used the Pacman-G2 package manager. It is a fork of a CVS version of the complete rewrite of Pacman by Aurelien Foret, which was not officially released at the time. Previously Fruga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch Linux
Arch Linux () is an independently developed, x86-64 general-purpose Linux distribution that strives to provide the latest stable versions of most software by following a rolling-release model. The default installation is a minimal base system, configured by the user to only add what is purposely required. Pacman, a package manager written specifically for Arch Linux, is used to install, remove and update software packages. Arch Linux uses a rolling release model, meaning there are no "major releases" of completely new versions of the system; a regular system update is all that is needed to obtain the latest Arch software; the installation images released every month by the Arch team are simply up-to-date snapshots of the main system components. Arch Linux has comprehensive documentation, consisting of a community-run wiki known as the ArchWiki. History Inspired by CRUX, another minimalist distribution, Judd Vinet started the Arch Linux project in March 2002. The name w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacman (Arch Linux)
Arch Linux () is an independently developed, x86-64 general-purpose Linux distribution that strives to provide the latest stable versions of most software by following a rolling-release model. The default installation is a minimal base system, configured by the user to only add what is purposely required. Pacman, a package manager written specifically for Arch Linux, is used to install, remove and update software packages. Arch Linux uses a rolling release model, meaning there are no "major releases" of completely new versions of the system; a regular system update is all that is needed to obtain the latest Arch software; the installation images released every month by the Arch team are simply up-to-date snapshots of the main system components. Arch Linux has comprehensive documentation, consisting of a community-run wiki known as the ArchWiki. History Inspired by CRUX, another minimalist distribution, Judd Vinet started the Arch Linux project in March 2002. The name was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opkg
opkg (''open package management'') is a lightweight package management system based upon ipkg. It is written in C and resembles Advanced Package Tool (APT)/dpkg in operation. It is intended for use on embedded Linux devices and is used in this capacity in the OpenEmbedded and OpenWrt projects. Opkg was originally forked from ipkg by the Openmoko project. More recently, development of opkg has moved from its old Google Code repository to Yocto Project The Yocto Project is a Linux Foundation collaborative open source project whose goal is to produce tools and processes that enable the creation of Linux distributions for embedded and IoT software that are independent of the underlying architectu ... where it is actively maintained again. Opkg packages usually use either .ipk or .opk extension. References External links * Free package management systems Free software programmed in C Linux package management-related software Linux-only free software {{Linux-stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RPM Package Manager
RPM Package Manager (RPM) (originally Red Hat Package Manager, now a recursive acronym) is a free and open-source package management system. The name RPM refers to the file format and the package manager program itself. RPM was intended primarily for Linux distributions; the file format is the baseline package format of the Linux Standard Base. Although it was created for use in Red Hat Linux, RPM is now used in many Linux distributions such as PCLinuxOS, Fedora, AlmaLinux, CentOS, openSUSE, OpenMandriva and Oracle Linux. It has also been ported to some other operating systems, such as Novell NetWare (as of version 6.5 SP3), IBM's AIX (as of version 4), IBM i, and ArcaOS. An RPM package can contain an arbitrary set of files. Most RPM files are “binary RPMs” (or BRPMs) containing the compiled version of some software. There are also “source RPMs” (or SRPMs) containing the source code used to build a binary package. These have an appropriate tag in the file he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenPKG
OpenPKG is an open source package management system for Unix. It is based on the well known RPM-system and allows easy and unified installation of packages onto common Unix-platforms ( Solaris, Linux and FreeBSD FreeBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), which was based on Research Unix. The first version of FreeBSD was released in 1993. In 2005, FreeBSD was the most popular ...). The project was launched bRalf S. Engelschallin November 2000 and in June 2005 it offered more than 880 freely available packages. External links The OpenPKG Project [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nix Package Manager
Nix is a cross-platform package manager that utilizes a purely functional deployment model where software is installed into unique directories generated through cryptographic hashes. It is also the name of the tool's programming language. A package's hash takes into account the dependencies, which is claimed to eliminate dependency hell, as an alternative to the typical solution of installing multiple versions of dependencies at the same time. This package management model advertises more reliable, reproducible, and portable packages. Nix packages are defined through a lazy functional programming language specifically designed for package management. Dependencies are tracked directly in this language through an intermediate format called "derivations". A Nix environment keeps track of references automatically, which allows unused packages to be garbage collected when no other package depends on them. At the cost of greater storage requirements, all upgrades in Nix are guaran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slackware
Slackware is a Linux distribution created by Patrick Volkerding in 1993. Originally based on Softlanding Linux System, Slackware has been the basis for many other Linux distributions, most notably the first versions of SUSE Linux distributions, and is the oldest distribution that is still maintained. Slackware aims for design stability and simplicity and to be the most "Unix-like" Linux distribution. It makes as few modifications as possible to software packages from upstream and tries not to anticipate use cases or preclude user decisions. In contrast to most modern Linux distributions, Slackware provides no graphical installation procedure and no automatic dependency resolution of software packages. It uses plain text files and only a small set of shell scripts for configuration and administration. Without further modification it boots into a command-line interface environment. Because of its many conservative and simplistic features, Slackware is often considered to be mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |