|
Nowe Miasto, Wałbrzych
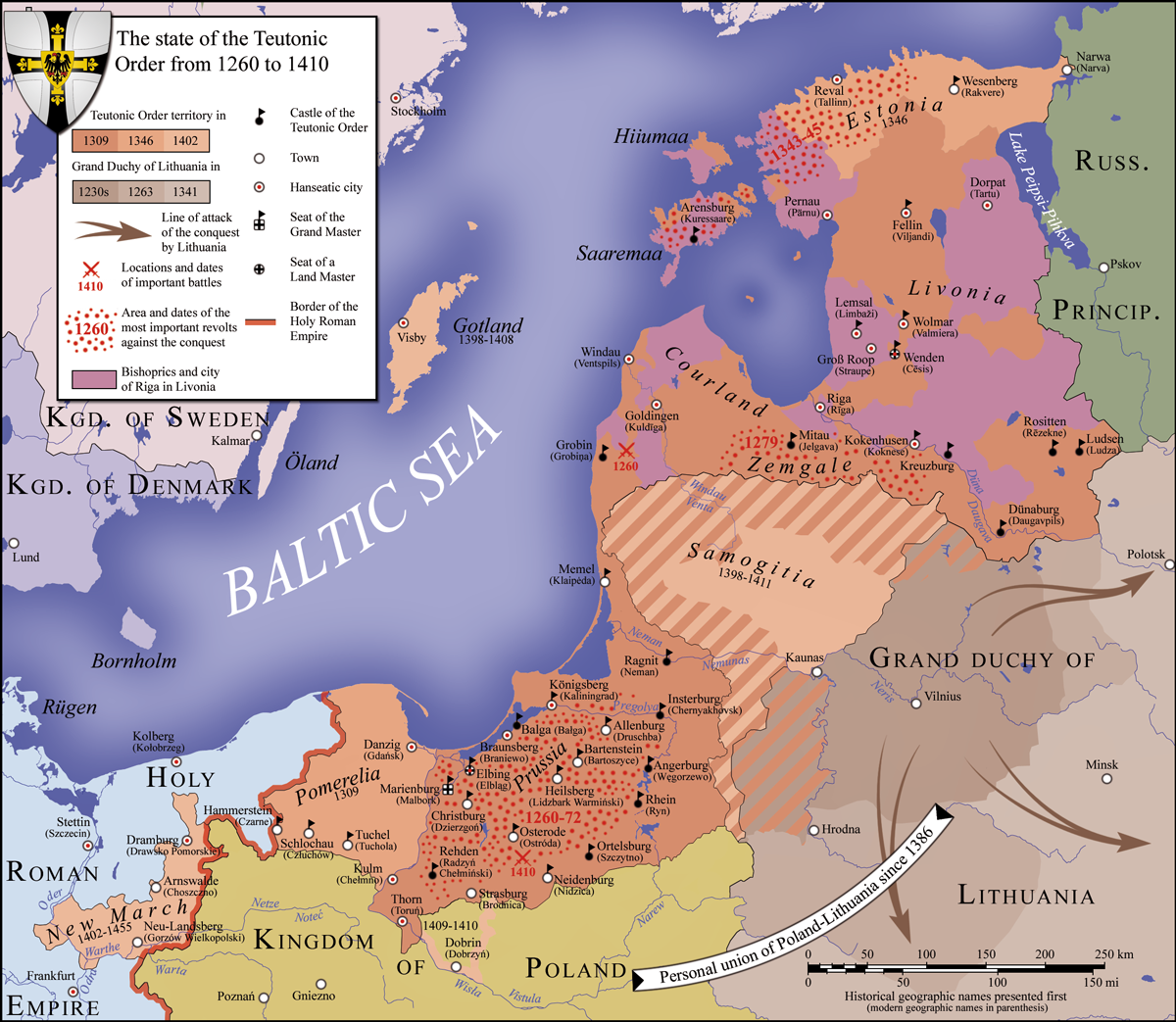
Nowe (german: Neuenburg in Westpreußen, 1942-1945: ''Neuenburg (Weichsel)'') is a town in Świecie County, Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland, with 6,270 inhabitants (2004). Geographical location Nowe is located approximately 75 kilometers north-east of Bydgoszcz and 80 kilometers south of Gdańsk in an elevated position on the river Vistula. It is located in the historic region of Gdańsk Pomerania. History The medieval name of the town was Novo Castro, or Nowy Gród in Polish. The town was founded in 1185 by Sobieslaw I, Duke of Pomerania. In 1266 the settlement is mentioned as a fortess place. In 1282 the Franciscan friars settled down here. It was part of the medieval Kingdom of Poland. In 1301 King Wenceslaus II of Poland granted the town to Piotr Swienca. In 1308 the town was invaded, destroyed and later annexed by the Teutonic Knights. In 1350 it was granted new privileges, later confirmed by King Sigismund I the Old in 1528.''Słownik geograficzny Królest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivodeships Of Poland
A voivodeship (; pl, województwo ; plural: ) is the highest-level administrative division of Poland, corresponding to a province in many other countries. The term has been in use since the 14th century and is commonly translated into English as "province". The Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998, which went into effect on 1 January 1999, created sixteen new voivodeships. These replaced the 49 former voivodeships that had existed from 1 July 1975, and bear a greater resemblance (in territory, but not in name) to the voivodeships that existed between 1950 and 1975. Today's voivodeships are mostly named after historical and geographical regions, while those prior to 1998 generally took their names from the cities on which they were centered. The new units range in area from under (Opole Voivodeship) to over (Masovian Voivodeship), and in population from nearly one million (Opole Voivodeship) to over five million (Masovian Voivodeship). Administrative authority at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Poland (1025–1385)
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central Europe. It may refer to: Historical political entities *Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1025 to 1031 *Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1076 to 1079 *Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom in Greater Poland existing from 1295 to 1296, under the rule of Przemysł II *Kingdom of Poland, a confederal kingdom existing from 1300 to 1320 *United Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1320 to 1386 *Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1386 to 1569 *Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom which from 1569 to 1795 was a member state of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth See also * List of Polish monarchs * General Confederation of the Kingdom of Poland * Congress Kingdom of Poland * Kingdom of Poland (November Uprising) * Regency Kingdom of Poland A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire was a European great power that exercised territorial control over much of the Baltic region during the 17th and early 18th centuries ( sv, Stormaktstiden, "the Era of Great Power"). The beginning of the empire is usually taken as the reign of Gustavus Adolphus, who ascended the throne in 1611, and its end as the loss of territories in 1721 following the Great Northern War. After the death of Gustavus Adolphus in 1632, the empire was controlled for lengthy periods by part of the high nobility, such as the Oxenstierna family, acting as regents for minor monarchs. The interests of the high nobility contrasted with the uniformity policy (i.e., upholding the traditional equality in status of the Swedish estates favoured by the kings and peasantry). In territories acquired during the periods of ''de facto'' noble rule, serfdom was not abolished, and there was also a trend to set up respective estates in Sweden proper. The Great Reduction of 1680 put an end to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starost
The starosta or starost (Cyrillic: ''старост/а'', Latin: ''capitaneus'', german: link=no, Starost, Hauptmann) is a term of Slavic origin denoting a community elder whose role was to administer the assets of a clan or family estates. The Slavic root of starost translates as "senior". Since the Middle Ages, it has meant an official in a leadership position in a range of civic and social contexts throughout Central and Eastern Europe. In terms of a municipality, a ''starosta'' was historically a senior royal administrative official, equivalent to the County Sheriff or the outdated Seneschal, and analogous to a gubernator. In Poland, a ''starosta'' would administer crown territory or a delineated district called a '' starostwo''. In the early Middle Ages, the ''starosta'' could head a settled urban or rural community or other communities, such as a church starosta, or an ''artel'' starosta, etc. The starosta also functioned as the master of ceremonies. Poland Kingdom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466)
The Thirteen Years' War (german: Dreizehnjähriger Krieg; pl, wojna trzynastoletnia), also called the War of the Cities, was a conflict fought in 1454–1466 between the Prussian Confederation, allied with the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, and the State of the Teutonic Order. The war began as an uprising by Prussian cities and local nobility to win independence from the Teutonic Knights. In 1454 Casimir IV married Elisabeth of Habsburg and the Prussian Confederation asked Poland's King Casimir IV Jagiellon for help and offered to accept the king as protector instead of the Teutonic Order. When the King assented, war broke out between supporters of the Prussian Confederation, backed by Poland, and backers of government by the Teutonic Knights. The Thirteen Years' War ended in the victory of the Prussian Confederation and Poland and in the Second Peace of Thorn (1466). This was soon followed by the War of the Priests (1467–1479), a drawn-out dispute over the independence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Poland (1385–1569)
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, including the Kingdom of Poland proper. The Polish Crown was at the helm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1569 to 1795. Major political events The Kingdom of Poland has been traditionally dated back to c. 966, when Mieszko I and his pagan Slavic realm joined Christian Europe (Baptism of Poland), establishing the state of Poland, a process started by his Polan Piast dynasty ancestors. His oldest son and successor, Prince Bolesław I Chrobry, Duke of Poland, became the first crowned King of Poland in 1025. Union of Krewo The Union of Krewo was a set of prenuptial agreements made in the Kreva Castle on August 13, 1385. Once Jogaila confirmed the prenuptial agreements on August 14, 1385, Poland and Lithuania formed a personal uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casimir IV Jagiellon
Casimir IV (in full Casimir IV Andrew Jagiellon; pl, Kazimierz IV Andrzej Jagiellończyk ; Lithuanian: ; 30 November 1427 – 7 June 1492) was Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1440 and King of Poland from 1447, until his death. He was one of the most active Polish-Lithuanian rulers, under whom Poland, by defeating the Teutonic Knights in the Thirteen Years' War recovered Pomerania, and the Jagiellonian dynasty became one of the leading royal houses in Europe. The great triumph of his reign was bringing Prussia under Polish rule. The rule of Casimir corresponded to the age of "new monarchies" in western Europe. By the 15th century, Poland had narrowed the distance separating it from western Europe and become a significant factor in international relations. The demand for raw materials and semi-finished goods stimulated trade, producing a positive balance, and contributed to the growth of crafts and mining in the entire country. He was a recipient of the English Order of the Gart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian Confederation
The Prussian Confederation (german: Preußischer Bund, pl, Związek Pruski) was an organization formed on 21 February 1440 at Kwidzyn (then officially ''Marienwerder'') by a group of 53 nobles and clergy and 19 cities in Prussia, to oppose the arbitrariness of the Teutonic Knights. It was based on an earlier similar organization, the Lizard Union established in 1397 by the nobles of Chełmno Land. In 1454, the leader of the Confederation, Johannes von Baysen (Jan Bażyński), formally asked King Casimir IV Jagiellon, to incorporate Prussia into the Kingdom of Poland. This marked the beginning of the Thirteen Years' War between the Order's State and Poland, with the cities co-financing the military costs of the latter. Background According to the 1411 First Peace of Thorn which followed the Teutonic Knights' defeat in the Battle of Grunwald, the Teutonic Order had to pay high reparations to the Kingdom of Poland. The monastic state imposed high taxes on the cities to raise t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peace Of Thorn (1411)
The (First) Peace of Thorn was a peace treaty formally ending the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War between allied Kingdom of Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania on one side, and the Teutonic Knights on the other. It was signed on 1 February 1411 in Thorn (Toruń), one of the southernmost cities of the Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights. In historiography, the treaty is often portrayed as a diplomatic failure of Poland–Lithuania as they failed to capitalize on the decisive defeat of the Knights in the Battle of Grunwald in June 1410. The Knights returned Dobrzyń Land which they captured from Poland during the war and made only temporary territorial concessions in Samogitia, which returned to Lithuania only for the lifetimes of Polish King Władysław Jagiełło and Lithuanian Grand Duke Vytautas. The Peace of Thorn was not stable. It took two other brief wars, the Hunger War in 1414 and Gollub War in 1422, to sign the Treaty of Melno that solved the territorial disputes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald, Battle of Žalgiris or First Battle of Tannenberg was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respectively by King Władysław II Jagiełło (Jogaila), who did not participate in the battle himself, and Grand Duke Vytautas, decisively defeated the German Teutonic Order, led by Grand Master Ulrich von Jungingen. Most of the Teutonic Order's leadership were killed or taken prisoner. Although defeated, the Teutonic Order withstood the subsequent siege of the Malbork Castle and suffered minimal territorial losses at the Peace of Thorn (1411), with other territorial disputes continuing until the Treaty of Melno in 1422. The order, however, never recovered their former power, and the financial burden of war reparations caused internal conflicts and an economic downturn in the lands controlled by them. The battle shifted the balance of pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigismund I The Old
Sigismund I the Old ( pl, Zygmunt I Stary, lt, Žygimantas II Senasis; 1 January 1467 – 1 April 1548) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1506 until his death in 1548. Sigismund I was a member of the Jagiellonian dynasty, the son of Casimir IV and younger brother of Kings John I Albert and Alexander I Jagiellon. He was nicknamed "the Old" in later historiography to distinguish him from his son and successor, Sigismund II Augustus. Sigismund was born in the town of Kozienice in 1467 as the fifth son of Casimir IV and his wife Elizabeth of Austria. He was one of thirteen children and was not expected to assume the throne after his father. Sigismund's eldest brother and rightful heir Vladislaus II instead became the King of Bohemia, Hungary and Croatia as the successor to George of Poděbrady in Bohemia and then to Matthias Corvinus in Hungary, thus temporarily uniting these kingdoms. When Casimir died, the Polish-Lithuanian realm was divided between the remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privilege (law)
A privilege is a certain entitlement to immunity granted by the state or another authority to a restricted group, either by birth or on a conditional basis. Land-titles and taxi medallions are examples of transferable privilege – they can be revoked in certain circumstances. In modern democratic states, a ''privilege'' is conditional and granted only after birth. By contrast, a ''right'' is an inherent, irrevocable entitlement held by all citizens or all human beings from the moment of birth. Various Examples of old common law privilege still exist – to title deeds, for example. Etymologically, a privilege (''privilegium'') means a "private law", or rule relating to a specific individual or institution. The principles of conduct that members of the legal profession observe in their practice are called legal ethics. Boniface's abbey of Fulda, to cite an early and prominent example, was granted '' privilegium'', setting the abbot in direct contact with the pope, bypassing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |