|
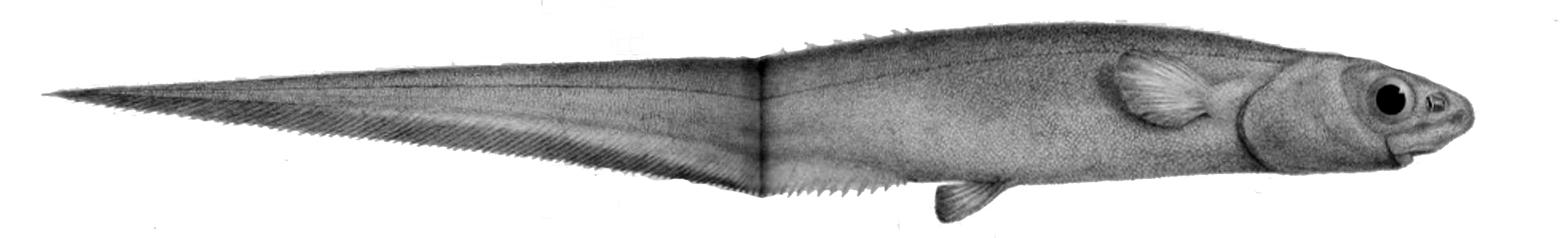
Notacanthus Bonaparte1
Notacanthus is a genus of spiny eels in the family Notacanthidae. Species It currently contains these recognized species: * '' Notacanthus abbotti'' Fowler, 1934 (Mindanao spiny eel) * '' Notacanthus bonaparte'' A. Risso, 1840 (Shortfin spiny eel) * ''Notacanthus chemnitzii'' Bloch, 1788 (Snub-nosed spiny eel) * '' Notacanthus indicus'' Lloyd Lloyd, Lloyd's, or Lloyds may refer to: People * Lloyd (name), a variation of the Welsh word ' or ', which means "grey" or "brown" ** List of people with given name Lloyd ** List of people with surname Lloyd * Lloyd (singer) (born 1986), American ..., 1909 (Arabian spiny eel) * ''Notacanthus sexspinis'' J. Richardson, 1846 ( Spiny-back eel) * '' Notacanthus spinosus'' Garman, 1899 (Panama spiny-back eel) References * Notacanthidae Notacanthiformes {{Notacanthiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snubnosed Spiny Eel
The snub-nosed spiny eel, ''Notacanthus chemnitzii'', is a member of the family Notacanthidae, the deep-sea spiny eels, which are not true eels (Anguilliformes). The snub-nosed spiny eel exists in waters all over the world, except in the tropics,Fishbase.org. 2005.Notacanthus chemnitzii Bloch, 1788 Retrieved on April 14, 2007. ranging in color from light tan to bluish grey in small ones to dark brown in large ones. Its primary food is sea anemone Sea anemones are a group of predation, predatory marine invertebrates of the order (biology), order Actiniaria. Because of their colourful appearance, they are named after the ''Anemone'', a terrestrial flowering plant. Sea anemones are classifi ...s. The eel usually lives in deep waters, mostly more than 200 m below the surface. References Notacanthidae Fish described in 1788 {{Notacanthiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Risso
Giuseppe Antonio Risso (8 April 1777 – 25 August 1845), called Antoine Risso, was a Niçard and naturalist. Risso was born in the city of Nice in the Duchy of Savoy, and studied under Giovanni Battista Balbis. He published ' (1810), ' (1826) and ' (1818–1822). Risso's dolphin was named after him. He is denoted by the author abbreviation Risso when citing a botanical name; the same abbreviation is used for zoological names. Genera and species named after him * ''Rissoa'' : a genus of gastropods * '' Rissoella'' : a genus of gastropod * '' Rissoella'' : a genus of red algae * ''Electrona risso'' : a lanternfish *''Polyacanthonotus rissoanus'' : smallmouth spiny eel Genera and species named by him He named 549 marine genera and species. IPNI The International Plant Names Index (IPNI) describes itself as "a database of the names and associated basic bibliographical details of seed plants, ferns and lycophytes." Coverage of plant names is best at the rank of species and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Garman
Samuel Walton Garman (June 5, 1843 – September 30, 1927), or "Garmann" as he sometimes styled himself, was a naturalist/zoologist from Pennsylvania. He became noted as an ichthyologist and herpetologist. Biography Garman was born in Indiana County, Pennsylvania, on 5 June 1843. In 1868 he joined an expedition to the American West with John Wesley Powell. He graduated from the Illinois State Normal University in 1870, and for the following year was principal of the Mississippi State Normal School. In 1871, he became professor of natural sciences in Ferry Hall Seminary, Lake Forest, Illinois, and a year later became a special pupil of Louis Agassiz. He was a friend and regular correspondent of the naturalist Edward Drinker Cope, and in 1872 accompanied him on a fossil hunting trip to Wyoming. In 1870 he became assistant director of herpetology and ichthyology at Harvard's Museum of Comparative Zoology. His work was mostly in the classification of fish, especially sharks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notacanthus Spinosus
Notacanthus is a genus of spiny eels in the family Notacanthidae. Species It currently contains these recognized species: * '' Notacanthus abbotti'' Fowler, 1934 (Mindanao spiny eel) * '' Notacanthus bonaparte'' A. Risso, 1840 (Shortfin spiny eel) * ''Notacanthus chemnitzii'' Bloch, 1788 (Snub-nosed spiny eel) * '' Notacanthus indicus'' Lloyd Lloyd, Lloyd's, or Lloyds may refer to: People * Lloyd (name), a variation of the Welsh word ' or ', which means "grey" or "brown" ** List of people with given name Lloyd ** List of people with surname Lloyd * Lloyd (singer) (born 1986), American ..., 1909 (Arabian spiny eel) * ''Notacanthus sexspinis'' J. Richardson, 1846 ( Spiny-back eel) * '' Notacanthus spinosus'' Garman, 1899 (Panama spiny-back eel) References * Notacanthidae Notacanthiformes {{Notacanthiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiny-back Eel
The spiny-back eel, ''Notacanthus sexspinis'', is a deep-sea spiny eel of the genus ''Notacanthus'', found in all the Southern Hemisphere oceans at depths between . The length of this fish is up to . Description The spiny-back eel is a slender, laterally compressed, elongated fish that can reach a length of . The snout projects above a small mouth on the underside of the head, and head and body are clothed in tiny cycloid scales. As with other members of the family Notacanthidae, there are no teeth on the maxillary bones and the premaxillary teeth form a comblike cutting edge. The dorsal fin takes the form of between six and fifteen isolated spines, with no soft rays. The anal fin is very long; it has ten to eighteen spines at the front and one hundred and fifty or more soft rays behind. The pelvic fin is in the middle of the abdomen and has one to three spines, and the caudal fin is minute. The general colour of this fish is brown, with darker brown around the mouth and on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Richardson (naturalist)
Sir John Richardson Royal Society of London, FRS FRSE (5 November 1787 – 5 June 1865) was a Scotland, Scottish naval surgeon, natural history, naturalist and Arctic explorer. Life Richardson was born at Nith Place in Dumfries the son of Gabriel Richardson, Provost of Dumfries, and his wife, Anne Mundell. He was educated at Dumfries Grammar School. He was then apprenticed to his maternal uncle, Dr James Mundell, a surgeon in Dumfries. He studied medicine at Edinburgh University, and became a surgeon in the navy in 1807. He traveled with John Franklin in search of the Northwest Passage on the Coppermine Expedition of 1819–1822. Richardson wrote the sections on geology, botany and ichthyology for the official account of the expedition. Franklin and Richardson returned to Canada in 1825 and went overland by fur trade routes to the mouth of the Mackenzie River. Franklin was to go as far west as possible and Richardson was to go east to the mouth of the Coppermine River. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard E
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Frankish language, Old Frankish and is a Compound (linguistics), compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include "Richie", "Dick (nickname), Dick", "Dickon", "Dickie (name), Dickie", "Rich (given name), Rich", "Rick (given name), Rick", "Rico (name), Rico", "Ricky (given name), Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English, German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Catalan "Ricard" and the Italian "Riccardo", among others (see comprehensive variant list below). People ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notacanthus Indicus
Notacanthus is a genus of spiny eels in the family Notacanthidae. Species It currently contains these recognized species: * '' Notacanthus abbotti'' Fowler, 1934 (Mindanao spiny eel) * '' Notacanthus bonaparte'' A. Risso, 1840 (Shortfin spiny eel) * ''Notacanthus chemnitzii'' Bloch, 1788 (Snub-nosed spiny eel) * '' Notacanthus indicus'' Lloyd, 1909 (Arabian spiny eel) * ''Notacanthus sexspinis'' J. Richardson, 1846 (Spiny-back eel) * ''Notacanthus spinosus Notacanthus is a genus of spiny eels in the family Notacanthidae. Species It currently contains these recognized species: * '' Notacanthus abbotti'' Fowler, 1934 (Mindanao spiny eel) * '' Notacanthus bonaparte'' A. Risso, 1840 (Shortfin spi ...'' Garman, 1899 (Panama spiny-back eel) References * Notacanthidae Notacanthiformes {{Notacanthiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snub-nosed Spiny Eel
The snub-nosed spiny eel, ''Notacanthus chemnitzii'', is a member of the family Notacanthidae, the deep-sea spiny eels, which are not true eels (Anguilliformes). The snub-nosed spiny eel exists in waters all over the world, except in the tropics,Fishbase.org. 2005.Notacanthus chemnitzii Bloch, 1788 Retrieved on April 14, 2007. ranging in color from light tan to bluish grey in small ones to dark brown in large ones. Its primary food is sea anemone Sea anemones are a group of predation, predatory marine invertebrates of the order (biology), order Actiniaria. Because of their colourful appearance, they are named after the ''Anemone'', a terrestrial flowering plant. Sea anemones are classifi ...s. The eel usually lives in deep waters, mostly more than 200 m below the surface. References Notacanthidae Fish described in 1788 {{Notacanthiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notacanthus Bonaparte
The shortfin spiny eel (''Notacanthus bonaparte''), also called Bonaparte's spiny eel, is a member of the family Notacanthidae, the deep-sea spiny eels, which are not true eels ( Anguilliformes). Distribution The shortfin spiny eel lives in the Eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea; it has been found in the Adriatic Sea. It lives in the bathypelagic zone at depths of . Description ''Notacanthus bonaparte'' is grey or pink in colour and has a maximum length of . It has a short snout, long head, mouth on the underside. Its dorsal fin has up to nine spines, while the anal fin is long and has up to fourteen spines. Males are smaller and have enlarged nasal rosettes. Behaviour The shortfin spiny eel feeds on bryozoans, ophiuroids, amphipod Amphipoda is an order of malacostracan crustaceans with no carapace and generally with laterally compressed bodies. Amphipods range in size from and are mostly detritivores or scavengers. There are more than 9,900 amphipod species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Elieser Bloch
Marcus Elieser Bloch (1723–1799) was a German physician and naturalist who is best known for his contribution to ichthyology through his multi-volume catalog of plates illustrating the fishes of the world. Brought up in a Hebrew-speaking Jewish family, he learned German and Latin and studied anatomy before settling in Berlin as a physician. He amassed a large natural history collection, particularly of fish specimens. He is generally considered one of the most important ichthyology, ichthyologists of the 18th century, and wrote many papers on natural history, comparative anatomy, and physiology. Life Bloch was born at Ansbach in 1723 where his father was a Torah writer and his mother owned a small shop. Educated at home in Hebrew literature he became a private tutor in Hamburg for a Jewish surgeon. Here he learned German, Latin and anatomy. He then studied medicine in Berlin and received a doctorate in 1762 from Frankfurt (Oder), Frankfort on the Oder with a treatise on skin dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Weed Fowler
Henry Weed Fowler (March 23, 1878 – June 21, 1965) was an American zoologist born in Holmesburg, Pennsylvania. He studied at Stanford University under David Starr Jordan. He joined the Academy of Natural Sciences in Philadelphia and worked as an assistant from 1903 to 1922, associate curator of vertebrates from 1922 to 1934, curator of fish and reptiles from 1934 to 1940 and curator of fish from 1940 to 1965. He published material on numerous topics including crustaceans, birds, reptiles and amphibians, but his most important work was on fish. In 1927 he co-founded the American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists and acted as treasurer until the end of 1927. In 1934 he went to Cuba, alongside Charles Cadwalader (president of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia), at the invitation of Ernest Hemingway to study billfishes, he stayed with Hemingway for six weeks and the three men developed a friendship which continued after this trip and Hemingway sent speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |