|
Norther Wind
Norther is an offshore wind farm in the Belgian North Sea, within the Exclusive Economic Zone of Belgium, approximately 23 kilometres from the Belgian port of Ostend. The concession was granted at the end of 2009, which is when the actual development of the project began. The wind farm has a total of 44 Vestas V164-8.4 MW turbines on monopile foundations for a nameplate capacity of 369.6 MW with a projected annual production of 1,394 GWh, corresponding to a capacity factor of 43.1% and the average consumption of almost 400,000 households. The wind farm spans an area of 38 km2 with water depths up to 33 m. A seaweed farm is planned between the turbines. The Norther offshore wind farm was developed through a joint venture between Elicio NV, a Belgian renewable energy producer operating internationally; and the Dutch utility company Eneco, who is a major producer and supplier of renewable electricity, natural gas and heat in the Netherlands and Belgium; and Diam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to the southwest, and the North Sea to the northwest. It covers an area of and has a population of more than 11.5 million, making it the 22nd most densely populated country in the world and the 6th most densely populated country in Europe, with a density of . Belgium is part of an area known as the Low Countries, historically a somewhat larger region than the Benelux group of states, as it also included parts of northern France. The capital and largest city is Brussels; other major cities are Antwerp, Ghent, Charleroi, Liège, Bruges, Namur, and Leuven. Belgium is a sovereign state and a federal constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. Its institutional organization is complex and is structured on both regional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of '' Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as kelps provide essential nursery habitat for fisheries and other marine species and thus protect food sources; other species, such as planktonic algae, play a vital role in capturing carbon, producing at least 50% of Earth's oxygen. Natural seaweed ecosystems are sometimes under threat from human activity. For example, mechanical dredging of kelp destroys the resource and dependent fisheries. Other forces also threaten some seaweed ecosystems; a wasting disease in predators of purple urchins has led to a urchin population surge which destroyed large kelp forest regions off the coast of California. Humans have a long history of cultivating seaweeds for their uses. In recent years, seaweed farming has become a global agricultural practic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Farms In Belgium
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet (Coriolis effect). Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail. Winds are commonly classified by their spatial scale, their speed and direction, the forces that cause them, the regions in which they occur, and their effect. Winds have various aspe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offshore Wind Farms In The North Sea
Offshore may refer to: Science and technology * Offshore (hydrocarbons) * Offshore construction, construction out at sea * Offshore drilling, discovery and development of oil and gas resources which lie underwater through drilling a well * Offshore hosting, server * Offshore wind power, wind power in a body of water * Offshore geotechnical engineering * Offshore aquaculture Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Offshore'' (novel), a 1979 British novel by Penelope Fitzgerald *The Offshore, an elite enclave of the chosen, in '' 3%'' * ''Offshore'' (album), a 2006 album by Indiana-based post-rock band Early Day Miners * "Offshore" (song), a 1996 song by British electronic dance music act Chicane Finance and law * Offshore bank, relates to the banking industry in offshore centers * Offshore company * Offshore financial centre, jurisdictions which transact financial business with non-residents * Offshore fund, collective investment in offshore centers * Offshore investment, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Offshore Wind Farms
This article lists the largest offshore wind farms that are currently operational rated by nameplate capacity. It also lists the largest offshore wind farms currently under construction, the largest proposed offshore wind farms, and offshore wind farms with notability other than size. As of 2022, Hornsea 2 in the United Kingdom is the largest offshore wind farm in the world at 1,386 MW. Largest operational offshore wind farms This is a list of offshore wind farms with at least 300 MW nameplate capacity that are currently operational. Largest under construction This is a list of wind farms with a nameplate capacity of more than 300MW currently under construction. Largest proposed The following table lists largest offshore wind farm areas (by nameplate capacity) that are only at a ''proposal'' stage, and have achieved at least some of the formal consents required before construction can begin. Other notable offshore wind farms See also * Jackup rig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy In Belgium
Energy in Belgium describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Belgium. It is governed by the energy policy of Belgium, which is split over several levels of government. For example, the regional level is responsible for awarding green certificates (except for offshore wind parks) and the national level for anything concerning nuclear power. As a member country of the European Union Belgium also complies to its energy policy. Overview Primary energy consumption Primary energy is the amount of extractable energy present in fuels as they are found in nature. It is often expressed in tonnes of oil equivalent (toe) or watt-hour (Wh). Unless stated otherwise the lower heating value is used in the remainder of this text. A portion of primary energy is converted into other forms before it is used, depending on the energy conversion efficiency of the installation and method employed this number differs significantly from the final energy as consumed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Power In Belgium
Wind power in Belgium depends partially on regional governments (Brussels-Capital Region, Flemish Region, Walloon Region) and partially on the Belgian federal government. Wind energy producers in both the Flemish and Walloon regions get green certificates but not with the same conditions. By year end 2020 Belgium had 4,670 MW installed capacity of windpower, 2,408 MW of which were land based and 2,262 MW of offshore wind power producing a total of 10.8 TWh of electricity generation. The percentage of electricity demand met by wind grew to about 13.3% by end 2020. Wind turbines are installed offshore and onshore, mainly in the Flemish and in the Walloon Regions. Brussels-Capital Region is an urban area which is not particularly suited for large wind turbines. Smaller turbines more appropriate for urban environments are being studied but until today no technology is deemed sufficiently efficient. Installed capacity and generation Land based installed wind capacity grew to 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Mix
The energy mix is a group of different primary energy sources from which secondary energy for direct use - such as electricity - is produced. Energy mix refers to all direct uses of energy, such as transportation and housing, and should not be confused with power generation mix, which refers only to generation of electricity. Global energy mix In 2007, the global primary energy use was oil equivalent, or . According to the International Energy Agency (IEA) 13.6% of world primary energy was used by the European Union (EU). Within the EU, 75.9% came from fossil fuels, 14.1% from nuclear power, 7% from biofuels, 2.9 from renewable energy resources. Overall primary energy consumption in the United States in 2015 relied most on petroleum (), natural gas () and coal (). Renewables contributed and nuclear power . In the same year, about 4 million GWh of electricity were generated in the United States, 67% of which was generated from fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, and <1% petro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
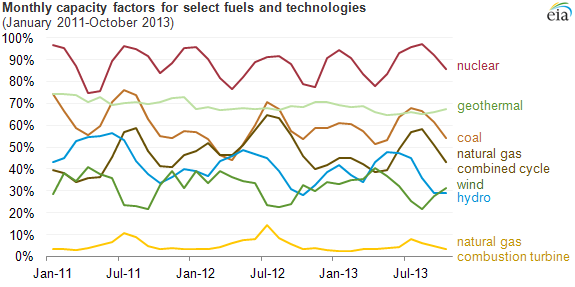
Capacity Factor
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full nameplate capacity over the relevant period. The capacity factor can be calculated for any electricity producing installation, such as a fuel consuming power plant or one using renewable energy, such as wind or the sun. The average capacity factor can also be defined for any class of such installations, and can be used to compare different types of electricity production. The actual energy output during that period and the capacity factor vary greatly depending on a range of factors. The capacity factor can never exceed the availability factor, or uptime during the period. Uptime can be reduced due to, for example, reliability issues and maintenance, scheduled or unscheduled. Other fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Sea in the north. It is more than long and wide, covering . It hosts key north European shipping lanes and is a major fishery. The coast is a popular destination for recreation and tourism in bordering countries, and a rich source of energy resources, including wind and wave power. The North Sea has featured prominently in geopolitical and military affairs, particularly in Northern Europe, from the Middle Ages to the modern era. It was also important globally through the power northern Europeans projected worldwide during much of the Middle Ages and into the modern era. The North Sea was the centre of the Vikings' rise. The Hanseatic League, the Dutch Republic, and the British each sought to gain command of the North Sea and access t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nameplate Capacity
Nameplate capacity, also known as the rated capacity, nominal capacity, installed capacity, or maximum effect, is the intended full-load sustained output of a facility such as a power station,Energy glossary '' Energy Information Administration''. Retrieved: 23 September 2010.Glossary '''', 2 August 2010. Retrieved: 23 September 2010. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopile Foundation
A deep foundation is a type of foundation that transfers building loads to the earth farther down from the surface than a shallow foundation does to a subsurface layer or a range of depths. A pile or piling is a vertical structural element of a deep foundation, driven or drilled deep into the ground at the building site. There are many reasons that a geotechnical engineer would recommend a deep foundation over a shallow foundation, such as for a skyscraper. Some of the common reasons are very large design loads, a poor soil at shallow depth, or site constraints like property lines. There are different terms used to describe different types of deep foundations including the pile (which is analogous to a pole), the pier (which is analogous to a column), drilled shafts, and caissons. Piles are generally driven into the ground in situ; other deep foundations are typically put in place using excavation and drilling. The naming conventions may vary between engineering discipli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)