|
North Pacific (sidewheeler)
''North Pacific'' was an early steamboat operating in Puget Sound, on the Columbia River, and in British Columbia and Alaska. The vessel's nickname was "the White Schooner" which was not based on the vessel's rig, but rather on speed, as "to schoon" in nautical parlance originally meant to go fast. Design and construction ''North Pacific'' was built in San Francisco for E.A. and L.M. Starr.Newell, Gordon R., ''Ships of the Inland Sea -- The Story of the Puget Sound Steamboats'', pp. 2, 13, 56-59, 70, 72, 82, 98, 102, 126, 146, 147, 190, 200, 212, Binford & Mort, Portland, OR (2nd ed. 1960) The Starrs were pioneer businessmen in Portland. The Starrs had been unsuccessfully trying to compete with Finch and Wright, first with the sidewheeler ''Alida'' and then with the small steamer ''Isabel''. The Starrs brought ''North Pacific'' to Puget Sound in 1871 to compete with the firm of D.B. Finch and Capt. Tom Wright (1828–1906). Finch and Wright had run the pioneer sidewheeler ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oregon Railway And Navigation Company
The Oregon Railroad and Navigation Company (OR&N) was a railroad that operated a rail network of running east from Portland, Oregon, United States, to northeastern Oregon, northeastern Washington, and northern Idaho. It operated from 1896 as a consolidation of several smaller railroads. OR&N was initially operated as an independent carrier, but Union Pacific (UP) purchased a majority stake in the line in 1898. It became a subsidiary of UP titled the Oregon–Washington Railroad and Navigation Company in 1910. In 1936, Union Pacific formally absorbed the system, which became UP's gateway to the Pacific Northwest. Predecessors The OR&N was made up of several railroads: *Columbia Southern Railway from Biggs to Shaniko, Oregon. *Oregon ''Railway'' and Navigation Company traces its roots back as far as 1860. It was incorporated in 1879 in Portland, Oregon and operated between Portland and eastern Washington and Oregon until 1896, when it was reorganized into the Oregon ''Railroad'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strait Of Juan De Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca (officially named Juan de Fuca Strait in Canada) is a body of water about long that is the Salish Sea's outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre of the Strait. It was named in 1787 by the maritime fur trader Charles William Barkley, captain of ''Imperial Eagle'', for Juan de Fuca, the Greek navigator who sailed in a Spanish expedition in 1592 to seek the fabled Strait of Anián. Barkley was the first non-indigenous person to find the strait, unless Juan de Fuca's story was true. The strait was explored in detail between 1789 and 1791 by Manuel Quimper, José María Narváez, Juan Carrasco, Gonzalo López de Haro, and Francisco de Eliza. Definition The United States Geological Survey defines the Strait of Juan de Fuca as a channel. It extends east from the Pacific Ocean between Vancouver Island, British Columbia, and the Olympic Peninsula, Washington, to Haro Strait, San Juan Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
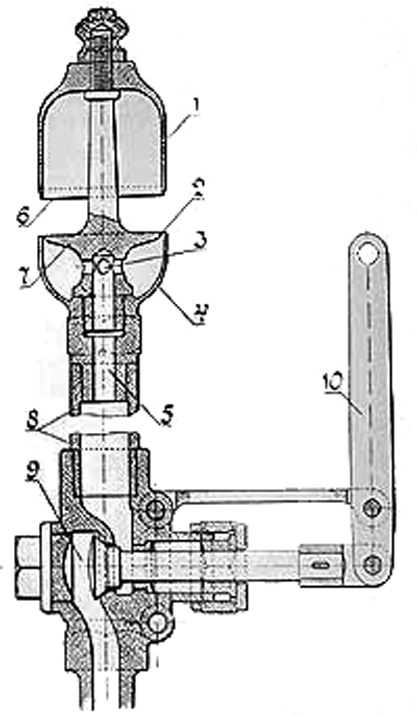
Steam Whistle
A steam whistle is a device used to produce sound in the form of a whistle using live steam, which creates, projects, and amplifies its sound by acting as a vibrating system (compare to train horn). Operation The whistle consists of the following main parts, as seen on the drawing: the whistle bell (1), the steam orifice or aperture (2), and the valve (9). When the lever (10) is actuated (usually via a pull cord), the valve opens and lets the steam escape through the orifice. The steam will alternately compress and rarefy in the bell, creating the sound. The pitch, or tone, is dependent on the length of the bell; and also how far the operator has opened the valve. Some locomotive engineers invented their own distinctive style of whistling. Uses of steam whistles Steam whistles were often used in factories, and similar places to signal the start or end of a shift, etc. steam-powered railway locomotives, traction engines, and steam ships have traditionally been fitted wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Pacific (sidewheeler) Sinking 1903
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
Tacoma, Washington
Tacoma ( ) is the county seat of Pierce County, Washington, United States. A port city, it is situated along Washington's Puget Sound, southwest of Seattle, northeast of the state capital, Olympia, Washington, Olympia, and northwest of Mount Rainier National Park. The city's population was 219,346 at the time of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Tacoma is the second-largest city in the Puget Sound area and the List of municipalities in Washington, third-largest in the state. Tacoma also serves as the center of business activity for the South Sound region, which has a population of about 1 million. Tacoma adopted its name after the nearby Mount Rainier, called wikt:Tacoma, təˡqʷuʔbəʔ in the Lushootseed, Puget Sound Salish dialect. It is locally known as the "City of Destiny" because the area was chosen to be the western terminus of the Northern Pacific Railroad in the late 19th century. The decision of the railroad was influenced by Tacoma's neighboring deep-wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Wave (sidewheeler)
''Ocean Wave'' was a steamboat that was operated from 1891 to 1897 on the Columbia River, from 1897 to 1899 on Puget Sound and from 1899 to 1911 as a ferry on San Francisco Bay. Ocean Wave is perhaps best known for transporting summer vacationers from Portland, Oregon to seaside resorts near Ilwaco, Washington during its service on the Columbia River. This vessel is also known for being the first ferry placed in service by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway. Construction ''Ocean Wave'' was built at Portland, Oregon by J.H. Steffen for the Ilwaco Railway and Navigation Company. ''Ocean Wave'' was a side-wheeler type of steamboat, designed by Jacob Kamm, a wealthy business man who had extensive experience in steamboats. In early July 3, 1891, Jacob Kamm and his son, Charles T. Kamm, were rushing to complete the work on the new steamer, in an effort to have the vessel running by July 15, 1891, as the low water in the river could prevent the river steamer then on the route, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyea, Alaska
Dyea ( ) is a former town in the U.S. state of Alaska. A few people live on individual small homesteads in the valley; however, it is largely abandoned. It is located at the convergence of the Taiya River and Taiya Inlet on the south side of the Chilkoot Pass within the limits of the Municipality of Skagway Borough, Alaska. During the Klondike Gold Rush prospectors disembarked at its port and used the Chilkoot Trail, a Tlingit trade route over the Coast Mountains, to begin their journey to the gold fields around Dawson City, Yukon, about away. Confidence man and crime boss Soapy Smith, famous for his underworld control of the neighboring town of Skagway in 1897–98 is believed to have had control of Dyea as well. The port at Dyea had shallow water, while neighboring Skagway had deep water. Dyea was abandoned when the White Pass and Yukon Route railroad chose the White Pass Trail (instead of the alternative Chilkoot Trail), which began at Skagway, for its route. Use of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skagway, Alaska
The Municipality and Borough of Skagway is a first-class borough in Alaska on the Alaska Panhandle. As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,240, up from 968 in 2010. The population doubles in the summer tourist season in order to deal with more than 1,000,000 visitors each year. Incorporated as a borough on June 25, 2007, it was previously a city (urban Skagway located at ) in the Skagway-Yakutat-Angoon Census Area (now the Hoonah–Angoon Census Area, Alaska).June 5, 2008, election, Skaguay News, summer edition, 2008. Page 17. The most populated community is the census-designated place of Skagway. The port of Skagway is a popular stop for cruise ships, and the tourist trade is a big part of the business of Skagway. The White Pass and Yukon Route narrow gauge railroad, part of the area's mining past, is now in operation purely for the tourist trade and runs throughout the summer months. Skagway is also part of the setting for Jack London's book ''The Call of the Wild'', W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaskan (sidewheeler)
The steamship ''Alaskan'' operated from 1884 to 1889 on the Columbia River and Puget Sound. ''Alaskan'' and her near-sistership ''Olympian'' were known as "Henry Villard's White Elephants."Newell, Gordon R., ed., ''H.W. McCurdy Marine History of the Pacific Northwest'', at 43, 346, n. 10 and 414, Superior Publishing, Seattle 1966 There were a number of vessels named ''Alaska ''and ''Alaskan'', this large side-wheel steamboat should not be confused with them. Construction ''Alaskan'' was built in 1883 by the Delaware River Iron Ship Building and Engine Works shipyard in Chester, Pennsylvania. She was a sidewheeler driven by a single cylinder vertical condensing walking-beam steam engine, which gave her high speed.Newell, Gordon R., ''Ships of the Inland Sea'', p. 92-96, Binford and Mort, Portland, Oregon (2nd Ed. 1960) Her iron hull was long, and she was rated at 1718 tons. She was built primarily for service on Puget Sound.Mills, Randall V., ''Sternwheelers Up Columbia'', p. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vancouver, British Columbia
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the city, up from 631,486 in 2016. The Greater Vancouver, Greater Vancouver area had a population of 2.6million in 2021, making it the List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada#List, third-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Greater Vancouver, along with the Fraser Valley Regional District, Fraser Valley, comprises the Lower Mainland with a regional population of over 3 million. Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada, with over 5,700 people per square kilometre, and fourth highest in North America (after New York City, San Francisco, and Mexico City). Vancouver is one of the most Ethnic origins of people in Canada, ethnically and Languages of Canada, linguistically diverse cities in Canada: 49.3 percent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olympian (sidewheeler)
''Olympian'' was a large side-wheel inland steamship that operated in the Pacific Northwest and Alaska. ''Olympian'' operated from early 1884 to late 1891 on the Columbia River, Puget Sound, and the Inside Passage of British Columbia and Alaska. Built for the Oregon Railway and Navigation Company, then controlled by Henry Villard, ''Olympian'' and its near twin ''Alaskan'' were known as “Henry Villard's White Elephants.” In 1895 they were said to have been the “most expensive and at the same time the most useless steamers yet appearing in the Northwest.” ''Olympian'' was tried on several routes but was unable to make a profit on any of them. The steamer was tied up for good in 1892, and remained so until 1906, when it was sold to New York interests. The buyers intended to tow ''Olympian'' around South America to New York, rehabilitate it, and run it on Long Island Sound. ''Zealandia'' towed ''Olympian'' as far as Possession Bay on the east side of the Straits of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Pacific And TJ Potter (steamboats), Seattle, 1891
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography. Etymology The word ''north'' is related to the Old High German ''nord'', both descending from the Proto-Indo-European unit *''ner-'', meaning "left; below" as north is to left when facing the rising sun. Similarly, the other cardinal directions are also related to the sun's position. The Latin word ''borealis'' comes from the Greek '' boreas'' "north wind, north", which, according to Ovid, was personified as the wind-god Boreas, the father of Calais and Zetes. ''Septentrionalis'' is from ''septentriones'', "the seven plow oxen", a name of ''Ursa Major''. The Greek ἀρκτικός (''arktikós'') is named for the same constellation, and is the source of the English word ''Arctic''. Other languages have other derivations. For example, in Lezgian, ''kefer'' can mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpeg)


