|
Norsey Wood
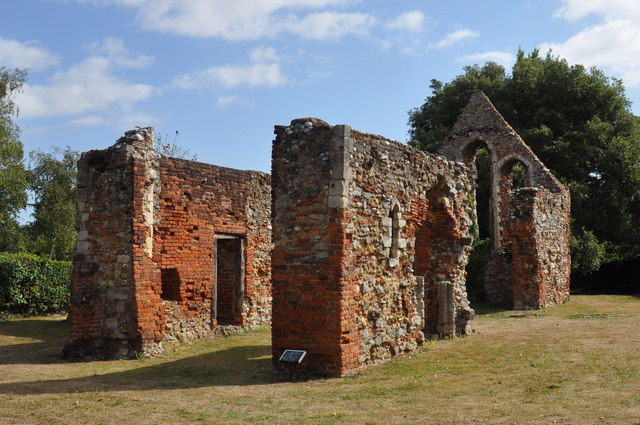
Norsey Wood is a biological Site of Special Scientific Interest in Billericay, Essex. It is also a Local Nature Reserve and a Scheduled Monument. The site is ancient oak woodland on acid soil which has been converted to mixed sweet chestnut ''Castanea sativa'', the sweet chestnut, Spanish chestnut or just chestnut, is a species of tree in the family Fagaceae, native to Southern Europe and Asia Minor, and widely cultivated throughout the temperate world. A substantial, long-lived ... coppice. Bluebell, bracken and bramble are dominant on the ground layer, but there are sphagnum mosses (sphagnum palustre and Sphagnum cuspidatum) in acidic flushes, and the rare water violet in one of the four ponds. There are nine species of dragonfly. Archaeolocal features include a Bronze Age bowl barrow, Iron Age and Roman cemeteries, and a medieval deer bank. Norsey Wood is the likely site of the Battle of Billericay during the Peasants' Revolt of 1381, a battle the peasants lost. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Billericay
The Battle of Billericay took place on 28 June 1381 when the boy King Richard II's soldiers defeated the Essex rebels adjacent to a wood north-east of Billericay, part of the Peasants' Revolt. This is likely to have been Norsey Wood, which maps of 1593 show to cover the same extent as in the early 20th century. After the murder of Wat Tyler and dispersal of the main rebel army, a summons was sent out in Essex for a mobilisation of rebels at Great Baddow and Rettendon, at threat of arson. Hundreds met and gathered in North-East Billericay on the 27th of June, digging trenches and chaining carts together. The King's forces were led by Thomas of Woodstock, the Earl of Buckingham and Sir Thomas Percy. They charged the defensive line as broke it, as the rebels struggled to form a defensive line. Some stayed behind and formed a Saxon fighting ring, as many ran and fled into the woods itself. It is thought that 500 Essex men were killed and buried at Great Burstead churchyard, and 800 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Site Of Special Scientific Interest
A Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Great Britain or an Area of Special Scientific Interest (ASSI) in the Isle of Man and Northern Ireland is a conservation designation denoting a protected area in the United Kingdom and Isle of Man. SSSI/ASSIs are the basic building block of site-based nature conservation legislation and most other legal nature/geological conservation designations in the United Kingdom are based upon them, including national nature reserves, Ramsar sites, Special Protection Areas, and Special Areas of Conservation. The acronym "SSSI" is often pronounced "triple-S I". Selection and conservation Sites notified for their biological interest are known as Biological SSSIs (or ASSIs), and those notified for geological or physiographic interest are Geological SSSIs (or ASSIs). Sites may be divided into management units, with some areas including units that are noted for both biological and geological interest. Biological Biological SSSI/ASSIs may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Violet
''Hottonia palustris'', also water violet or featherfoil, is an aquatic plant in the family Primulaceae. Description The plant has a stem reaching up to in height. Its basal roots are buried in the underlying mud, while other silvery, shiny roots dangle freely in the water. The leaves are deeply divided as far as the central vein, like the teeth of a double comb, and are completely submerged, but can surface after a drastic fall in water level. The leaves are alternate or connected to the stem in more or less regular whorls. The flowers are hermaphrodite and pollinated by insects and cleistogamy; they appear from May to June. The plant is self-fertile. Distribution Featherfoil is found in Europe and northern Asia. The species epithet ''palustris'' is Latin for "of the marsh" and indicates its common habitat.Archibald William Smith Cultivation Naturally a bog or marsh A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheduled Monuments In Essex
There are 425 scheduled monuments in the county of Essex, England. These protected sites date from the Neolithic period and include barrows, moated sites, ruined abbeys, castles, and a windmill. In the United Kingdom, the scheduling of monuments was first initiated to insure the preservation of "nationally important" archaeological sites or historic buildings. The protection given to scheduled monuments is given under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Areas Act 1979 Notable scheduled monuments in Essex See also *Grade I listed buildings in Essex There are over 9000 Grade I listed buildings in England. This page is a list of these buildings in the county of Essex. Basildon Braintree Brentwood C ... * List of scheduled monuments in the United Kingdom References {{reflist Scheduled monuments in Essex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sites Of Special Scientific Interest In Essex
Site most often refers to: * Archaeological site * Campsite, a place used for overnight stay in an outdoor area * Construction site * Location, a point or an area on the Earth's surface or elsewhere * Website, a set of related web pages, typically with a common domain name It may also refer to: * Site, a National Register of Historic Places property type * SITE (originally known as ''Sculpture in the Environment''), an American architecture and design firm * Site (mathematics), a category C together with a Grothendieck topology on C * ''The Site'', a 1990s TV series that aired on MSNBC * SITE Intelligence Group, a for-profit organization tracking jihadist and white supremacist organizations * SITE Institute, a terrorism-tracking organization, precursor to the SITE Intelligence Group * Sindh Industrial and Trading Estate, a company in Sindh, Pakistan * SITE Centers, American commercial real estate company * SITE Town, a densely populated town in Karachi, Pakistan * S.I.T.E Indust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peasants' Revolt
The Peasants' Revolt, also named Wat Tyler's Rebellion or the Great Rising, was a major uprising across large parts of England in 1381. The revolt had various causes, including the socio-economic and political tensions generated by the Black Death in the 1340s, the high taxes resulting from the conflict with France during the Hundred Years' War, and instability within the local leadership of London. The final trigger for the revolt was the intervention of a royal official, John Bampton, in Essex on 30 May 1381. His attempts to collect unpaid poll taxes in Brentwood ended in a violent confrontation, which rapidly spread across the south-east of the country. A wide spectrum of rural society, including many local artisans and village officials, rose up in protest, burning court records and opening the local gaols. The rebels sought a reduction in taxation, an end to serfdom, and the removal of King Richard II's senior officials and law courts. Inspired by the sermons of the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly applied to Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but also, by analogy, to other parts of the Old World. The duration of the Iron Age varies depending on the region under consideration. It is defined by archaeological convention. The "Iron Age" begins locally when the production of iron or steel has advanced to the point where iron tools and weapons replace their bronze equivalents in common use. In the Ancient Near East, this transition took place in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, in the 12th century BC. The technology soon spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin region and to South Asia (Iron Age in India) between the 12th and 11th century BC. Its further spread to Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Central Europe is somewhat dela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second principal period of the three-age system proposed in 1836 by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen for classifying and studying ancient societies and history. An ancient civilization is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age because it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from production areas elsewhere. Bronze is harder and more durable than the other metals available at the time, allowing Bronze Age civilizations to gain a technological advantage. While terrestrial iron is naturally abundant, the higher temperature required for smelting, , in addition to the greater difficulty of working with the metal, placed it out of reach of common use until the end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphagnum Cuspidatum
''Sphagnum cuspidatum'', the feathery bogmoss, toothed sphagnum, or toothed peat moss, is a peat moss found commonly in Great Britain, Norway, Sweden, the eastern coast of the United States, and in Colombia. Description ''Sphagnum cuspidatum'' is brown to greenish brown in color with narrow green stems. Individual plants are slender and weak-stemmed. They are moderately sized compared to other peat mosses. Aquatic forms are flaccid and plumose giving a feathery appearance, whereas the emergent forms are much more compact. Branches are spread in quite obvious sickle shaped patterns, giving the capitulum a twisted appearance. The capitula are often green to yellow, tinged with red-brown in color. The leaves on the stems are triangular-ovate in shape, usually a bit longer than 1.2 mm, and are often very compact with one another. The leaves end in sharp points. Meristem tissue is often fibrillose. The branch stems are green, with pinkish coloration at the proximal ends, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Billericay
Billericay ( ) is a town and civil parish in the Borough of Basildon, Essex, England. It lies within the London Basin and constitutes a commuter town east of Central London. The town has three secondary schools and a variety of open spaces. It is thought to have been occupied since the Bronze Age. Toponym The origin of the name Billericay is unclear. It was first recorded as "Byllyrica" in 1291. The urban settlement, which was within the manor and parish of Great Burstead, was one of many founded in the late 13th century in an already densely populated rural landscape. Several suggestions for the origin of the place name include: * ''Villa Erica'' (Heather Villa), suggesting a Romano-British origin. * ''bellerīca'', a medieval Latin word meaning 'dyehouse or tanhouse'. * ''billers'', a traditional name for watercress, for which Bilbrook in Somerset and Staffordshire are named. Watercress was farmed in Billericay springs during the 20th century. Although the precise etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphagnum Palustre
''Sphagnum palustre'' (Syn. ''Sphagnum cymbifolium''), the prairie sphagnum or blunt-leaved bogmoss, is a species of peat moss from the genus ''Sphagnum'', in the family Sphagnaceae. Like other mosses of this type it can soak up water up to the 30-fold amount of its own dry weight thanks to its elastic spiral fibers. ''S. palustre'' is rather frequent and is spread almost all over the world. It mainly grows in wet forests and—compared to other specimens of this genus—rarely grows in moors. Traits ''Sphagnum palustre'' forms firm plants up to 25 centimeter height. The plants are often light green to light brown with stem diameters of 0.6 to 1.2 millimeters. The epidermis (Hyalodermis) of the stem is built in three layers and their cells form 1 to 3 seldom more pores and contain much spiral fibers. The branches are tufted forming clusters of three to six on the little stems. The heads are a little more pigmented and egg-shaped. Distribution ''Sphagnum palustre'' plants a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
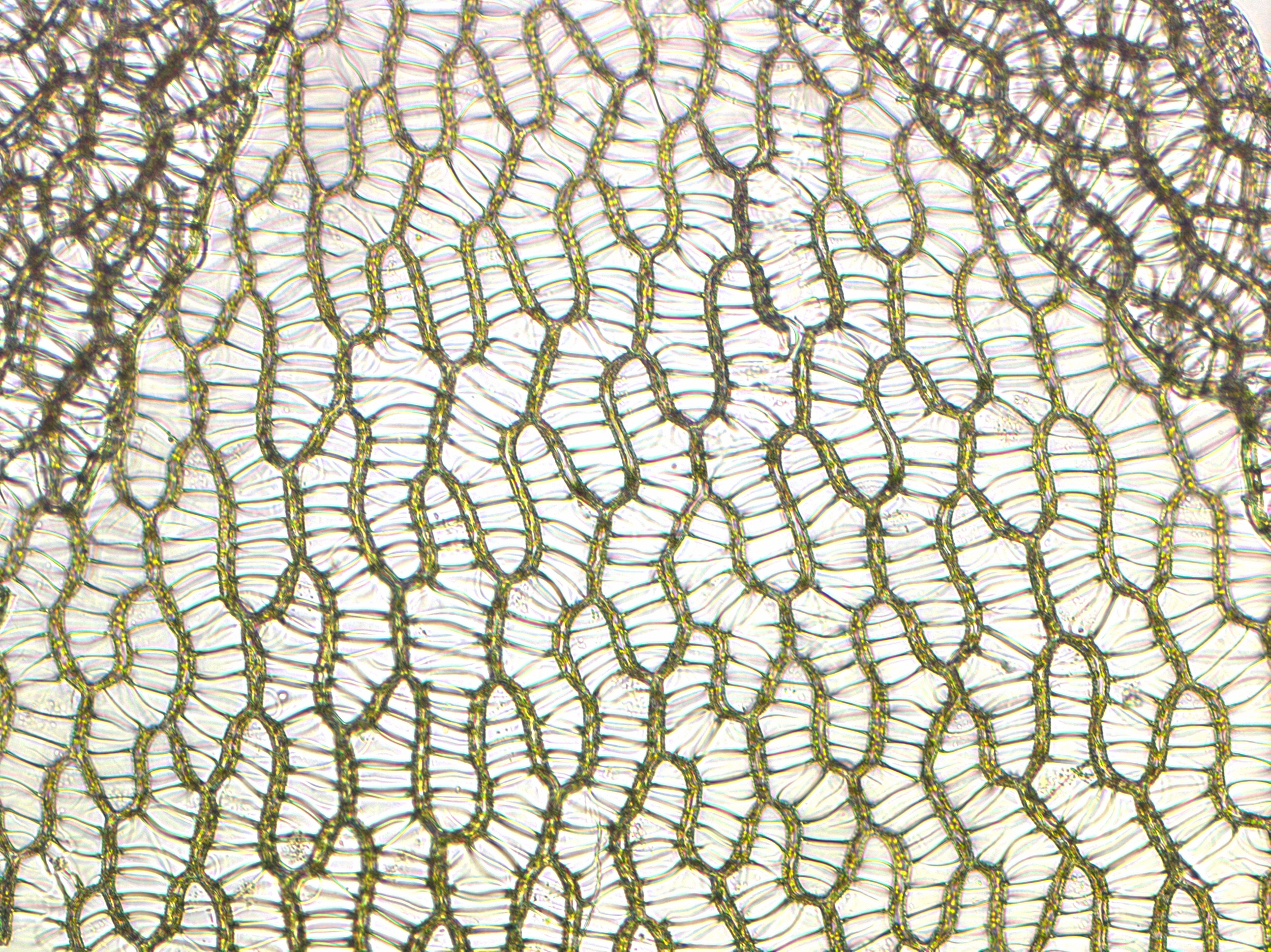
Sphagnum Moss
''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, peat moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store water, since both living and dead plants can hold large quantities of water inside their cells; plants may hold 16 to 26 times as much water as their dry weight, depending on the species.Bold, H. C. 1967. Morphology of Plants. second ed. Harper and Row, New York. p. 225-229. The empty cells help retain water in drier conditions. As sphagnum moss grows, it can slowly spread into drier conditions, forming larger mires, both raised bogs and blanket bogs. Thus, sphagnum can influence the composition of such habitats, with some describing sphagnum as 'habitat manipulators'. These peat accumulations then provide habitat for a wide array of peatland plants, including sedges and ericaceous shrubs, as well as orchids and carnivorous plants.Keddy, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |