|
Norra Kärr
Norra Kärr or Norra Kärr Alkaline Complex is an intrusive complex cropping out at the boundary between Östergötland and Småland, Sweden. The complex is chiefly made up of peralkaline nepheline syenite and is rich in exotic minerals. Rocks of the complex intruded into the Paleoproterozoic-aged Växjo granites of the Transscandinavian Igneous Belt. Alfred Elis Törnebohm was the first to describe the rocks of Norra Kärr in 1906. Norra Kärr was discovered a few years earlier during regional geological maping by the Swedish Geological Survey. The complex derives its name from a local farm, which translates into English as "Northern Fen". In 1968 Harry von Eckermann published his investigations on the complex defining its boundaries and confirming the view of it as an intrusion. A study has shown that the elevated rare-earth element concentrations in the bedrock in the Norra Kärr area are particularly well reflected in high contents of these elements in the fern ''Dryopte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrusion (geology)
Intrusive rock is formed when magma penetrates existing rock, crystallizes, and solidifies underground to form '' intrusions'', such as batholiths, dikes, sills, laccoliths, and volcanic necks.Intrusive RocksIntrusive rocks accessdate: March 27, 2017.Igneous intrusive rocks, accessdate: March 27, 2017.Britannica.comintrusive rock , geology , Britannica.com accessdate: March 27, 2017. Intrusion is one of the two ways igneous rock can form. The other is extrusion, such as a volcanic eruption or similar event. An intrusion is any body of intrusive igneous rock, formed from magma that cools and solidifies within the crust of the planet. In contrast, an ''extrusion'' consists of extrusive rock, formed above the surface of the crust. Some geologists use the term plutonic rock synonymously with intrusive rock, but other geologists subdivide intrusive rock, by crystal size, into coarse-grained plutonic rock (typically formed deeper in the Earth's crust in batholiths or stocks) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogeochemical Prospecting
Biogeochemistry is the scientific discipline that involves the study of the chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes and reactions that govern the composition of the natural environment (including the biosphere, the cryosphere, the hydrosphere, the pedosphere, the atmosphere, and the lithosphere). In particular, biogeochemistry is the study of biogeochemical cycles, the cycles of chemical elements such as carbon and nitrogen, and their interactions with and incorporation into living things transported through earth scale biological systems in space and time. The field focuses on chemical cycles which are either driven by or influence biological activity. Particular emphasis is placed on the study of carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, iron, and phosphorus cycles. Biogeochemistry is a systems science closely related to systems ecology. History Early History Early Greeks established some of the core ideas of biogeochemistry, such as nature consisting of cycl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoproterozoic Geology
The Mesoproterozoic Era is a geologic era that occurred from . The Mesoproterozoic was the first era of Earth's history for which a fairly definitive geological record survives. Continents existed during the preceding era (the Paleoproterozoic), but little is known about them. The continental masses of the Mesoproterozoic were more or less the same ones that exist today, although their arrangement on the Earth's surface was different. Major events and characteristics The major events of this era are the breakup of the Columbia supercontinent, the formation of the Rodinia supercontinent, and the evolution of sexual reproduction. This era is marked by the further development of continental plates and plate tectonics. The supercontinent of Columbia broke up between 1500 and 1350 million years ago, and the fragments reassembled into the supercontinent of Rodinia around 1100 to 900 million years ago, on the time boundary between the Mesoproterozoic and the subsequent Neoproterozoic. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
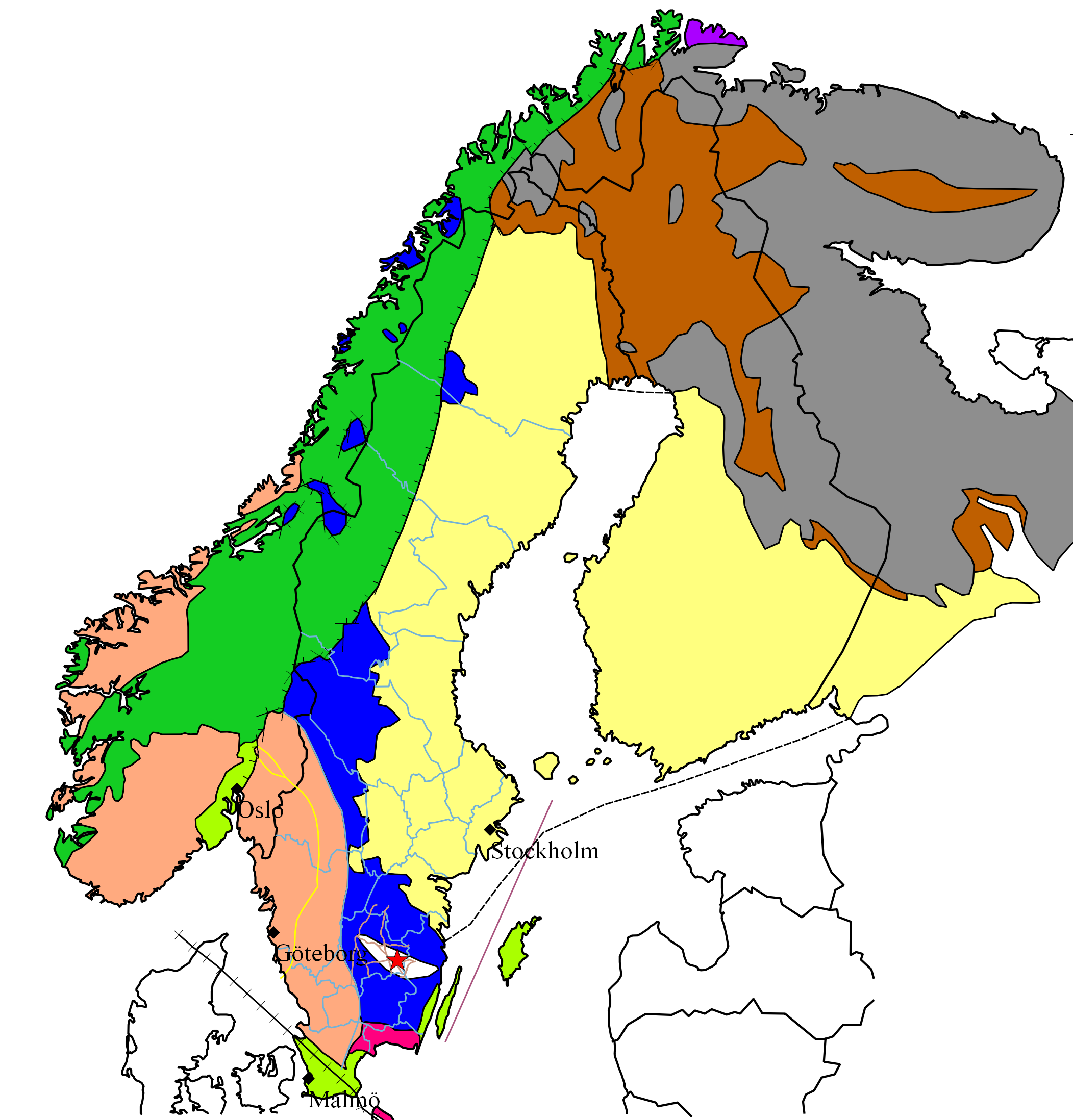
Geology Of Sweden
The geology of Sweden is the regional study of rocks, minerals, tectonics, natural resources and groundwater in the country. The oldest rocks in Sweden date to more than 2.5 billion years ago in the Precambrian. Complex orogeny mountain building events and other tectonic occurrences built up extensive metamorphic crystalline basement rock that often contains valuable metal deposits throughout much of the country. Metamorphism continued into the Paleozoic after the Snowball Earth glaciation as the continent Baltica collided with an island arc and then the continent Laurentia. Sedimentary rocks are most common in southern Sweden with thick sequences from the last 250 million years underlying Malmö and older marine sedimentary rocks forming the surface of Gotland. Stratigraphy, Tectonics & Geologic History The oldest rocks in Sweden date to the Archean, more than 2.5 billion years ago. Archean crystalline basement rocks are restricted to a few areas in the far north and are mainl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tranås
Tranås () is a locality and the seat of Tranås Municipality, Jönköping County, Sweden with 14,197 inhabitants in 2010. Overview It is close to the lake Sommen in the north of Småland. Its main commercial center is located along the main street, Storgatan. The symbol of the town is the crane as featured on the town's coat of arms. Some of the bigger employers in the town arStrömsholmen (European Furniture Group) an IVT The company w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Society For Nature Conservation
Sveriges Natur. The Swedish Society for Nature Conservation ( sv, Naturskyddsföreningen, previously known as , ''SNF'') is a non-profit, non-partisan, Swedish environmental organization. It is the largest and oldest environmental society in Sweden, with 24 county branches and 270 municipality subdivisions. In 2019, it had 230,000 members. History The society was formed in 1909, by a number of professors and academics interested in natural history and environmental issues. One of the founders was botanist Rutger Sernander, who had a prominent position in the society until his death in 1944. Writer Sten Selander was chairman of the society for many years. Mikael Karlsson was chairman in 2002–2014, succeeded by Johanna Sandahl who had been vice chairman. During the first decades, the society mainly worked with protecting selected natural sites and endangered species. It also published a journal, ''Sveriges natur'' ("Swedish nature"). As new environmental problems developed, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rare Earth Elements
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or (in context) rare-earth oxides or sometimes the lanthanides (yttrium and scandium are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly-indistinguishable lustrous silvery-white soft heavy metals. Compounds containing rare earths have diverse applications in electrical and electronic components, lasers, glass, magnetic materials, and industrial processes. Scandium and yttrium are considered rare-earth elements because they tend to occur in the same ore deposits as the lanthanides and exhibit similar chemical properties, but have different electronic and magnetic properties. These metals tarnish slowly in air at room temperature and react slowly with cold water to form hydroxides, liberating hydrogen. They react with steam to form oxides, and at elevated temperature (400°C) ignite spontaneously. These elements and their compounds have no biological function other than in several specialized enzymes, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasman Metals
Tasman Metals, "a Canadian company for jurisdictional and thereby regulatory purposes," is a Vancouver-based mining company that operated in Sweden. From 2009 to 2016 Tasman Metals owned the mining rights to, and explored for, rare earth elements in the Norra Kärr area in the South Swedish highlands. In February 2016 the supreme administrative court of Sweden withdrew Tasman's exploitation concession for Norra Kärr. Until the mid-2010s Tasman Metals had the Kallak south licence in northern Sweden after which it sold it to Beowulf Mining. See also *Canadian mining in Latin America and the Caribbean Canadian mining in Latin America and the Caribbean began in the 20th century. Latin America and the Caribbean's vast resources give the region great geopolitical importance, attracting foreign interest for centuries. From the colonial race of Eu ... References {{reflist Mining companies of Canada Mining in Sweden Non-renewable resource companies established in 2009 2009 esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zirconium
Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name ''zirconium'' is taken from the name of the mineral zircon, the most important source of zirconium. The word is related to Persian '' zargun'' (zircon; ''zar-gun'', "gold-like" or "as gold"). It is a lustrous, grey-white, strong transition metal that closely resembles hafnium and, to a lesser extent, titanium. Zirconium is mainly used as a refractory and opacifier, although small amounts are used as an alloying agent for its strong resistance to corrosion. Zirconium forms a variety of inorganic and organometallic compounds such as zirconium dioxide and zirconocene dichloride, respectively. Five isotopes occur naturally, four of which are stable. Zirconium compounds have no known biological role. Characteristics Zirconium is a lustrous, greyish-white, soft, ductile, malleable metal that is solid at room temperature, though it is hard and brittle at lesser purities. In powder form, zirconium is highl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zirconium
Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name ''zirconium'' is taken from the name of the mineral zircon, the most important source of zirconium. The word is related to Persian '' zargun'' (zircon; ''zar-gun'', "gold-like" or "as gold"). It is a lustrous, grey-white, strong transition metal that closely resembles hafnium and, to a lesser extent, titanium. Zirconium is mainly used as a refractory and opacifier, although small amounts are used as an alloying agent for its strong resistance to corrosion. Zirconium forms a variety of inorganic and organometallic compounds such as zirconium dioxide and zirconocene dichloride, respectively. Five isotopes occur naturally, four of which are stable. Zirconium compounds have no known biological role. Characteristics Zirconium is a lustrous, greyish-white, soft, ductile, malleable metal that is solid at room temperature, though it is hard and brittle at lesser purities. In powder form, zirconium is highl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rare Earth Elements
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or (in context) rare-earth oxides or sometimes the lanthanides (yttrium and scandium are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly-indistinguishable lustrous silvery-white soft heavy metals. Compounds containing rare earths have diverse applications in electrical and electronic components, lasers, glass, magnetic materials, and industrial processes. Scandium and yttrium are considered rare-earth elements because they tend to occur in the same ore deposits as the lanthanides and exhibit similar chemical properties, but have different electronic and magnetic properties. These metals tarnish slowly in air at room temperature and react slowly with cold water to form hydroxides, liberating hydrogen. They react with steam to form oxides, and at elevated temperature (400°C) ignite spontaneously. These elements and their compounds have no biological function other than in several specialized enzymes, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, Finland to the east, and is connected to Denmark in the southwest by a bridgetunnel across the Öresund. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country, the third-largest country in the European Union, and the fifth-largest country in Europe. The capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a total population of 10.5 million, and a low population density of , with around 87% of Swedes residing in urban areas in the central and southern half of the country. Sweden has a nature dominated by forests and a large amount of lakes, including some of the largest in Europe. Many long rivers run from the Scandes range through the landscape, primarily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |