|
Nolina Microcarpa
''Nolina microcarpa'' is a species of flowering plant in the asparagus family known by the common names sacahuista and palmilla. Like other species of ''Nolina'', it may be called beargrass. It is native to northern Mexico and the southwestern United States in Arizona and New Mexico.''Nolina microcarpa''. Flora of North America. Retrieved 12-2-2011. It does occur in the southwestern corner of , where it has a limited distribution on ,Welsh, Stanley L., et al. 2008. ''Nolina'' Michaux, In: A Utah Flora, 4th Ed., revised. but reports of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sereno Watson
Sereno Watson (December 1, 1826 in East Windsor Hill, Connecticut – March 9, 1892 in Cambridge, Massachusetts) was an American botanist. Graduating from Yale in 1847 in Biology, he drifted through various occupations until, in California, he joined the Clarence King Expedition and eventually became its expedition botanist. Appointed by Asa Gray as assistant in the Gray Herbarium of Harvard University in 1873, he later became its curator, a position he maintained until his death. Watson was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1874, and a member of the National Academy of Sciences in 1889. Works * ''Botany'', in ''Report of the geological exploration of the 40th parallel made ... by Clarence King'', 1871 * * Publications by and about S. Watsoon WorldCat References External linksBiographical sketch at the Gray Herbarium site [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the system through photosynthesis and is incorporated into plant tissue. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and microbes. Ecosystems are controlled by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Arizona
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) was first made by Jules Thurmann (1849). Prior to this, the two terms were used indiscriminately.Thurmann, J. (1849). ''Essai de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landscaping
Landscaping refers to any activity that modifies the visible features of an area of land, including the following: # Living elements, such as flora or fauna; or what is commonly called gardening, the art and craft of growing plants with a goal of creating a beauty within the landscape. # Natural abiotic elements, such as landforms, terrain shape and elevation, or bodies of water. # Abstract elements, such as the weather and lighting conditions. Landscaping requires a certain understanding of horticulture and artistic design, but is not limited to plants and horticulture. Sculpting land to enhance usability (patio, walkways, ponds, water features) are also examples of landscaping being used. When intended as purely an aesthetic change, the term Ornamental Landscaping is used. Often, designers refer to landscaping as an extension of rooms in your house (each one has a function). Outdoor spaces have a vast amount of flexibility as far as materials and function. It is often said the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thatching
Thatching is the craft of building a roof with dry vegetation such as straw, water reed, sedge (''Cladium mariscus''), rushes, heather, or palm branches, layering the vegetation so as to shed water away from the inner roof. Since the bulk of the vegetation stays dry and is densely packed—trapping air—thatching also functions as insulation. It is a very old roofing method and has been used in both tropical and temperate climates. Thatch is still employed by builders in developing countries, usually with low-cost local vegetation. By contrast, in some developed countries it is the choice of some affluent people who desire a rustic look for their home, would like a more ecologically friendly roof, or who have purchased an originally thatched abode. History Thatching methods have traditionally been passed down from generation to generation, and numerous descriptions of the materials and methods used in Europe over the past three centuries survive in archives and early publica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The Americas
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples. Many Indigenous peoples of the Americas were traditionally hunter-gatherers and many, especially in the Amazon basin, still are, but many groups practiced aquaculture and agriculture. While some societies depended heavily on agriculture, others practiced a mix of farming, hunting, and gathering. In some regions, the Indigenous peoples created monumental architecture, large-scale organized cities, city-states, chiefdoms, states, kingdoms, republics, confederacies, and empires. Some had varying degrees of knowledge of engineering, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, writing, physics, medicine, planting and irrigation, geology, mining, metallurgy, sculpture, and gold smithing. Many parts of the Americas are still populated by Indigenous peoples; some countries have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chukar Partridge
The chukar partridge (''Alectoris chukar''), or simply chukar, is a Palearctic upland gamebird in the pheasant family Phasianidae. It has been considered to form a superspecies complex along with the rock partridge, Philby's partridge and Przevalski's partridge and treated in the past as conspecific particularly with the first. This partridge has well-marked black and white bars on the flanks and a black band running from the forehead across the eye down the head to form a necklace that encloses a white throat. Native to Asia, the species has been introduced into many other places and feral populations have established themselves in parts of North America and New Zealand. This bird can be found in parts of the Middle East and temperate Asia. Description The chukar is a rotund long partridge, with a light brown back, grey breast, and buff belly. The shades vary across the various populations. The face is white with a black gorget. It has rufous-streaked flanks, red legs and cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
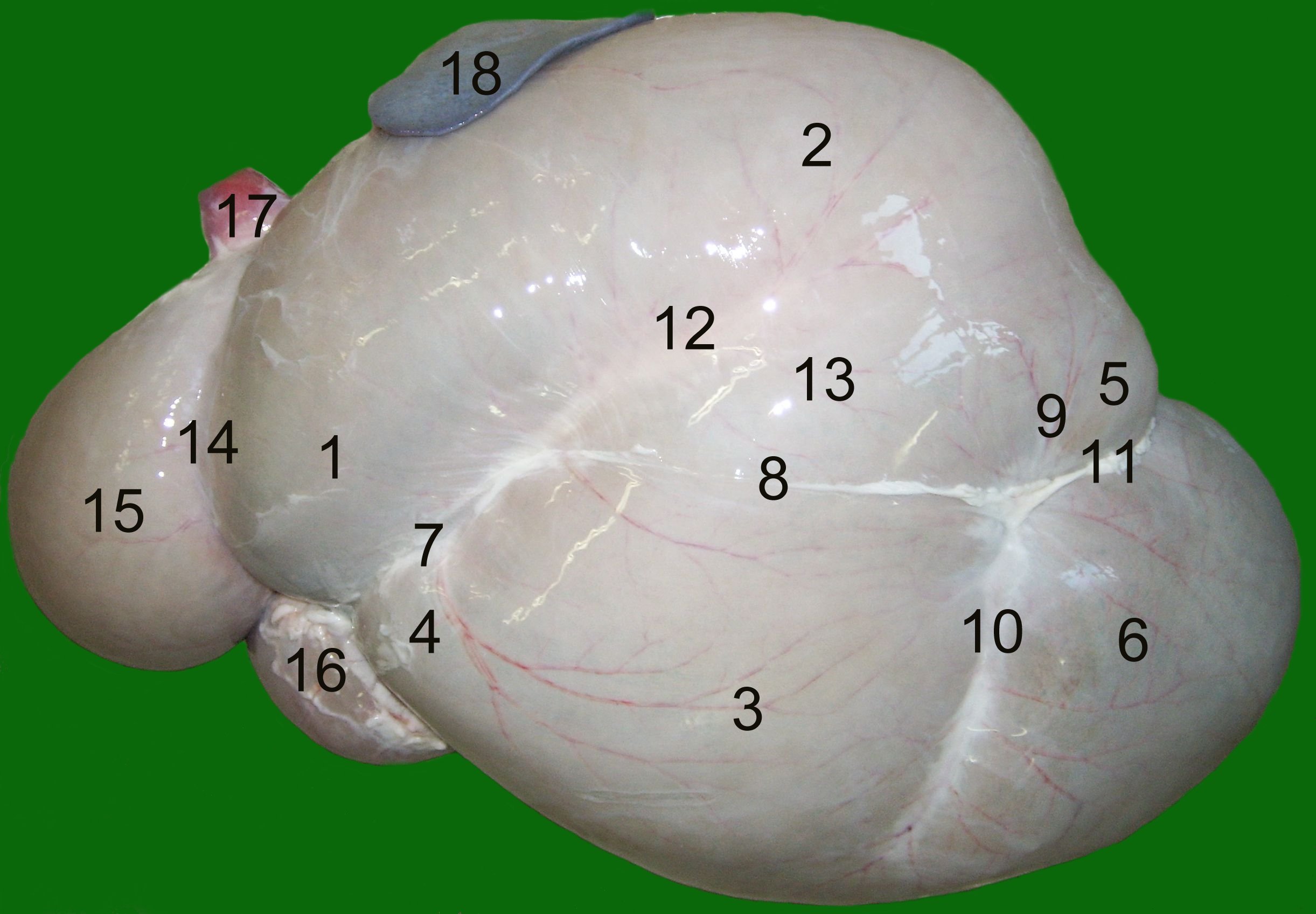
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rumen
The rumen, also known as a paunch, is the largest stomach compartment in ruminants and the larger part of the reticulorumen, which is the first chamber in the alimentary canal of ruminant animals. The rumen's microbial favoring environment allows it to serve as the primary site for microbial fermentation of ingested feed. The smaller part of the reticulorumen is the reticulum, which is fully continuous with the rumen, but differs from it with regard to the texture of its lining. Brief anatomy The rumen is composed of several muscular sacs, the cranial sac, ventral sac, ventral blindsac, and reticulum. The lining of the rumen wall is covered in small fingerlike projections called papillae, which are flattened, approximately 5mm in length and 3mm wide in cattle. The reticulum is lined with ridges that form a hexagonal honeycomb pattern. The ridges are approximately 0.1–0.2mm wide and are raised 5mm above the reticulum wall. The hexagons in the reticulum are approximately 2� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the animal family Bovidae and the tribe Caprini, meaning it is closely related to the sheep. There are over 300 distinct breeds of goat.Hirst, K. Kris"The History of the Domestication of Goats".''About.com''. Accessed August 18, 2008. It is one of the oldest domesticated species of animal, according to archaeological evidence that its earliest domestication occurred in Iran at 10,000 calibrated calendar years ago. Goats have been used for milk, meat, fur, and skins across much of the world. Milk from goats is often turned into goat cheese. Female goats are referred to as ''does'' or ''nannies'', intact males are called ''bucks'' or ''billies'', and juvenile goats of both sexes are called ''kids''. Castrated males are called ''wethers''. Whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sheep. Like all ruminants, sheep are members of the order Artiodactyla, the even-toed ungulates. Numbering a little over one billion, domestic sheep are also the most numerous species of sheep. An adult female is referred to as a ''ewe'' (), an intact male as a ''ram'', occasionally a ''tup'', a castrated male as a ''wether'', and a young sheep as a ''lamb''. Sheep are most likely descended from the wild mouflon of Europe and Asia, with Iran being a geographic envelope of the domestication center. One of the earliest animals to be domesticated for agricultural purposes, sheep are raised for fleeces, meat (lamb, hogget or mutton) and milk. A sheep's wool is the most widely used animal fiber, and is usually harvested by shearing. In Commonw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White-tailed Deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced to New Zealand, all the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean (Cuba, Jamaica Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ..., Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico), and some countries in Europe, such as the Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Romania and Serbia. In the Americas, it is the most widely distributed wild ungulate. In North America, the species is widely distributed east of the Rocky Mountains as well as in southwestern Arizona and most of Mexico, except Baja California peninsula, Lower California. It is mostly displaced by the black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_2007.jpg)