|
No. 80 Squadron RAF
No. 80 Squadron RAF was a Royal Flying Corps and Royal Air Force squadron active from 1917 until 1969. It was operative during both World War I and World War II. Establishment and early service Founded on 1 August 1917 at RAF Montrose, equipped with the Sopwith Camel and intended as a fighter squadron, 80 Squadron was sent to France to serve on the Western Front in January 1918, acting initially in a fighter role.Rawlings ''Air Pictorial'' December 1962, p. 392. However, German offensives in March of the same year resulted in 80 Sqn being reallocated in a ground-attack role, still with Camels. It continued this duty until the end of the war. As a result, the squadron had only one ace, Harold Whistler, although it claimed approximately 60 aerial victories. The Camels were replaced with Sopwith Snipes in December 1918 and in May the following year the squadron moved to Egypt, where it served for a short period of time before being amalgamated into No. 56 Squadron RAF. Reinstate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Flying Corps
"Through Adversity to the Stars" , colors = , colours_label = , march = , mascot = , anniversaries = , decorations = , battle_honours = , battles_label = Wars , battles = First World War , disbanded = merged with RNAS to become Royal Air Force (RAF), 1918 , current_commander = , current_commander_label = , ceremonial_chief = , ceremonial_chief_label = , colonel_of_the_regiment = , colonel_of_the_regiment_label = , notable_commanders = Sir David HendersonHugh Trenchard , identification_symbol = , identification_symbol_label = Roundel , identification_symbol_2 = , identification_symbol_2_label = Flag , aircraft_attack = , aircraft_bomber = , aircraft_el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sopwith Snipe
The Sopwith 7F.1 Snipe was a British single-seat biplane fighter of the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was designed and built by the Sopwith Aviation Company during the First World War, and came into squadron service a few weeks before the end of the conflict, in late 1918. The Snipe was not a fast aircraft by the standards of its time, but its excellent climb and manoeuvrability made it a good match for contemporary German fighters. It was selected as the standard postwar single-seat RAF fighter and the last examples were not retired until 1926. Design and development In April 1917, Herbert Smith, the chief designer of the Sopwith Company, began to design a fighter intended to be the replacement for Sopwith's most famous aeroplane, the Sopwith Camel.Lumsden ''Aeroplane Monthly'' October 1990, p. 588. The design, called Snipe by Sopwith, was in its initial form a single- bay biplane, slightly smaller than the Camel and intended to be powered by similar engines. The pilot sat higher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Second Tactical Air Force
The RAF Second Tactical Air Force (2TAF) was one of three tactical air forces within the Royal Air Force (RAF) during and after the Second World War. It was made up of squadrons and personnel from the RAF, other British Commonwealth air forces, and exiles from German-occupied Europe. Renamed as British Air Forces of Occupation in 1945, 2TAF was recreated in 1951 and became Royal Air Force Germany in 1959. Formation 2TAF was formed on 1 June 1943 as HQ Tactical Air Force from Army Co-operation Command, in connection with preparations then in train to invade Europe a year later. It took units from both Fighter Command and Bomber Command in order to form a force capable of supporting the Army in the field. Bomber Command provided No. 2 Group with light bombers; Fighter Command was split into the Air Defence of Great Britain, retaining fighter units for home defence, and No. 83 Group and No. 84 Group operating aircraft, and No. 85 Group controlling ground-based units, for the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Defence Of Great Britain
The Air Defence of Great Britain (ADGB) was a RAF command comprising substantial army and RAF elements responsible for the air defence of the British Isles. It lasted from 1925, following recommendations that the RAF take control of homeland air defence, until 1936 when it became RAF Fighter Command. History The ADGB was created as a command in 1925 as a result of the 1923 recommendation of the Steel–Bartholomew Committee, including their recommendation to transfer responsibility for home air defence from the War Office to the Air Ministry. It main initial elements were: * The RAF's Metropolitan Air Force, initially comprising 25 squadrons (9 fighter), soon expanding to 52 squadrons (17 fighter) * 264 heavy AA guns (Royal Artillery) and 672 searchlights (Royal Engineers) * The new part-time volunteer Observer Corps ADGB was organised into three defensive zones: * Inner Artillery Zone (IAZ), over London. * Air Fighter Zone (AFZ), divided into two areas controlling regular squadr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Detling
Royal Air Force Detling or more simply RAF Detling is a former Royal Air Force station situated above sea level, located near Detling, a village about miles north-east of Maidstone, Kent. It was a station of the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) in the First World War and the Royal Air Force (RAF) in the Second World War. Although not a fighter base, the airfield suffered several raids by the Luftwaffe, especially during the period of the Battle of Britain. History ''RNAS Detling'' airfield was north east of Maidstone, and was used jointly by the Navy and Air Force between 1916 and 1919. The Fleet Air Arm aircraft also shared some facilities during the second World War. The site was developed in April 1915, covering some , although it was April 1917 before the first occupants, No. 50 Squadron arrived from Dover. The airfield closed in December 1919 to military flying, and after the war it was used by the Short factory at Rochester to test aircraft, and civilian gliding also sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supermarine Spitfire (late Merlin-powered Variants)
The British Supermarine Spitfire was facing several challenges by mid-1942. The debut of the formidable Focke-Wulf Fw 190 in late 1941 had caused problems for RAF fighter squadrons flying the latest Spitfire Mk Vb. Rolls-Royce engineers were already working on a new version of the Merlin incorporating a two-stage supercharger; the combination of the improved Merlin and the Spitfire Mk Vc airframe in a "stop-gap" design allowed the RAF to combat the Fw 190 on equal terms. In a second stream of development Supermarine was working on an improved, reinforced, Spitfire airframe which incorporated several new features and was designed for the Merlin 60 and 70 series engines. This new airframe later formed the basis for the Rolls-Royce Griffon powered Spitfires. This article presents a history of the Spitfire powered by two-stage engine variants and also describes some of the "drawing board" projects and experimental Spitfires. The Griffon powered variants are described in a separa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allies of World War II, Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Front (World War II), Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 (D-Day) with the Normandy landings. A 1,200-plane Airborne forces, airborne assault preceded an amphibious warfare, amphibious assault involving more than 5,000 vessels. Nearly 160,000 troops crossed the English Channel on 6 June, and more than two million Allied troops were in France by the end of August. The decision to undertake a cross-channel invasion in 1944 was taken at the Washington Conference (1943), Trident Conference in Washington, D.C., Washington in May 1943. General Dwight D. Eisenhower was appointed commander of Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force, and General Bernard Montgomery was named commander of the 21st Army Group, which comprised all the land forces involved in the invasio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haifa Airport
Haifa Airport ( he, נְמַל הַתְּעוּפָה חֵיפָה, ''Namal HaTe'ufa Haifa''; ar, مطار حيفا) , also known as U Michaeli Airport is a small international airport located in Haifa, Israel. It is located to the east of the city, close to Kishon Port and Israel Shipyards and mainly serves civilian flights, with some military usage. Most passenger flights utilizing the airport are domestic operations to Eilat and Tel Aviv. The airport is named after Uri Michaeli, one of the pioneers of Jewish aviation and one of the founders of aviation in Israel. The airport has one short runway, in length, and there are plans to extend it by . History Haifa Airport was established by the British Mandate in 1934 as its first international airport at the location of RAF Station Haifa which originally served the British Army and the Iraqi-British oil company, APS. RAF Haifa already had passenger service by Imperial Airways to Alexandria (since 1931) and Baghdad (since 1932) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tel Nof Airbase
Tel Nof Israeli Air Force ( he, בָּסִיס חֵיל-הַאֲוִויר תֵּל נוֹף) , also known as Air Force Base 8, is one of three principal airbases of the Israeli Air Force. It is located near Rehovot, Israel. Tel Nof houses several fighter, helicopter, and airlift squadrons. Also located at the base are several special units of the Israel Defense Forces, including Unit 669 (airborne combat search and rescue) and the paratroopers training center. History Tel Nof was founded in July 1939 during the British Mandate as RAF Aqir and served as the main Royal Air Force station in Palestine. From the 1948 Arab-Israeli War until 1950, it was known as Ekron Airfield. The base housed the IAF flight academy until April 1966 when it was moved to Hatzerim Airbase. On 18 October 2011, Gilad Shalit, an Israeli soldier who had been held captive by Hamas in Gaza for over five years and four months, returned to Israel via Tel Nof as part of a deal to exchange Shalit for 1,027 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by the Supermarine Spitfire during the Battle of Britain in 1940, but the Hurricane inflicted 60 percent of the losses sustained by the Luftwaffe in the campaign, and fought in all the major theatres of the Second World War. The Hurricane originated from discussions between RAF officials and aircraft designer Sir Sydney Camm about a proposed monoplane derivative of the Hawker Fury biplane in the early 1930s. Despite an institutional preference for biplanes and lack of interest by the Air Ministry, Hawker refined their monoplane proposal, incorporating several innovations which became critical to wartime fighter aircraft, including retractable landing gear and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine. The Air Ministry ordered Hawker's ''Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greco-Italian War
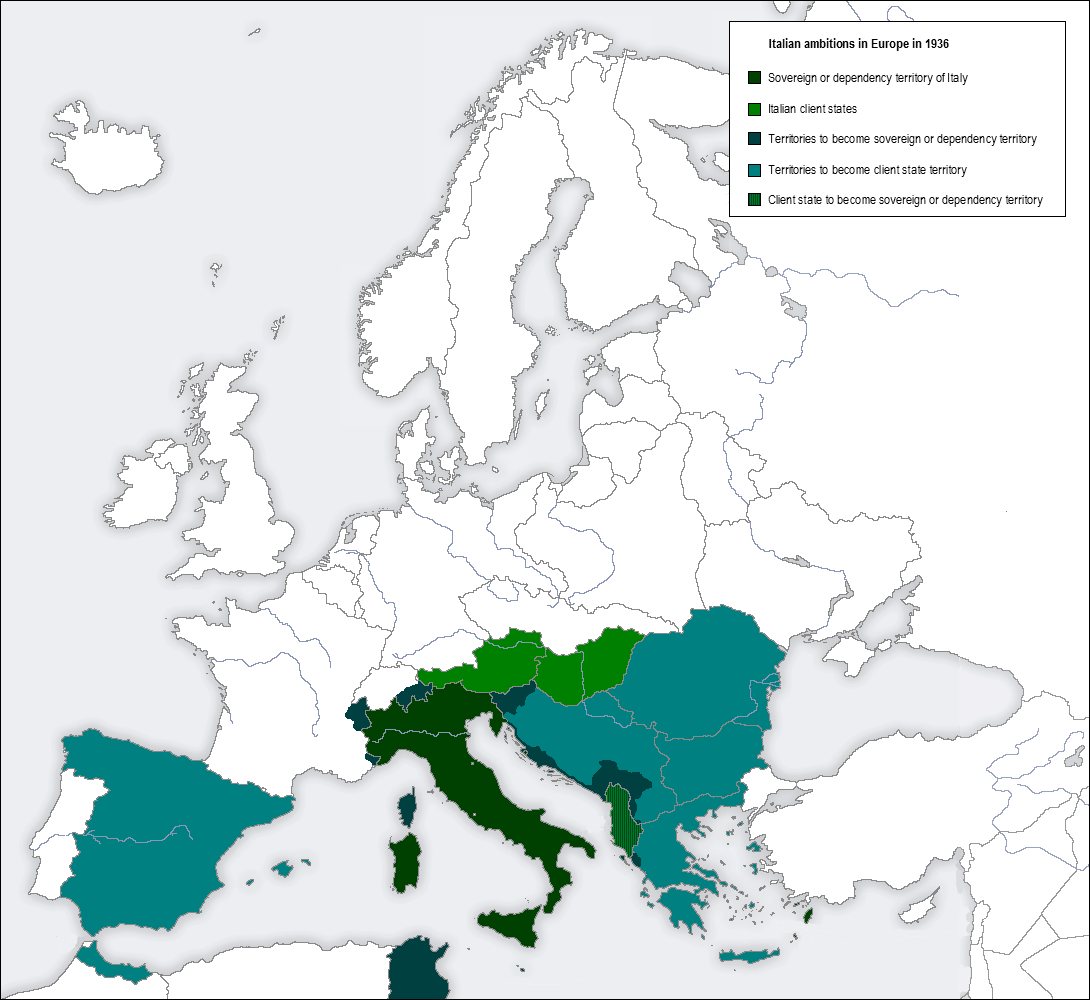
The Greco-Italian War (Greek language, Greek: Ελληνοϊταλικός Πόλεμος, ''Ellinoïtalikós Pólemos''), also called the Italo-Greek War, Italian Campaign in Greece, and the War of '40 in Greece, took place between the kingdoms of Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Italy and Kingdom of Greece, Greece from 28 October 1940 to 23 April 1941. This local war began the Balkans Campaign (World War II), Balkans Campaign of World War II between the Axis powers and the Allies of World War II, Allies and eventually turned into the Battle of Greece with Commonwealth of Nations, British and Nazi Germany, German involvement. On 10 June 1940, Italy declared war on France and the United Kingdom. By September 1940, the Italians had Italian invasion of France, invaded France, Italian conquest of British Somaliland, British Somaliland and Italian invasion of Egypt, Egypt. This was followed by a hostile press campaign in Italy against Greece, accused of being a British ally. A number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloster Gladiator
The Gloster Gladiator is a British biplane fighter. It was used by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) (as the Sea Gladiator variant) and was exported to a number of other air forces during the late 1930s. Developed privately as the Gloster SS.37, it was the RAF's last biplane fighter aircraft, and was rendered obsolete by newer monoplane designs even as it was being introduced. Though often pitted against more formidable foes during the early days of the Second World War, it acquitted itself reasonably well in combat. The Gladiator saw action in almost all theatres during the Second World War, with a large number of air forces, some of them on the Axis side. The RAF used it in France, Norway, Greece, the defence of Malta, the Middle East, and the brief Anglo-Iraqi War (during which the Royal Iraqi Air Force was similarly equipped). Other countries deploying the Gladiator included China against Japan, beginning in 1938; Finland (along with Swedish voluntee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |