|
Nitrosyl Fluoride
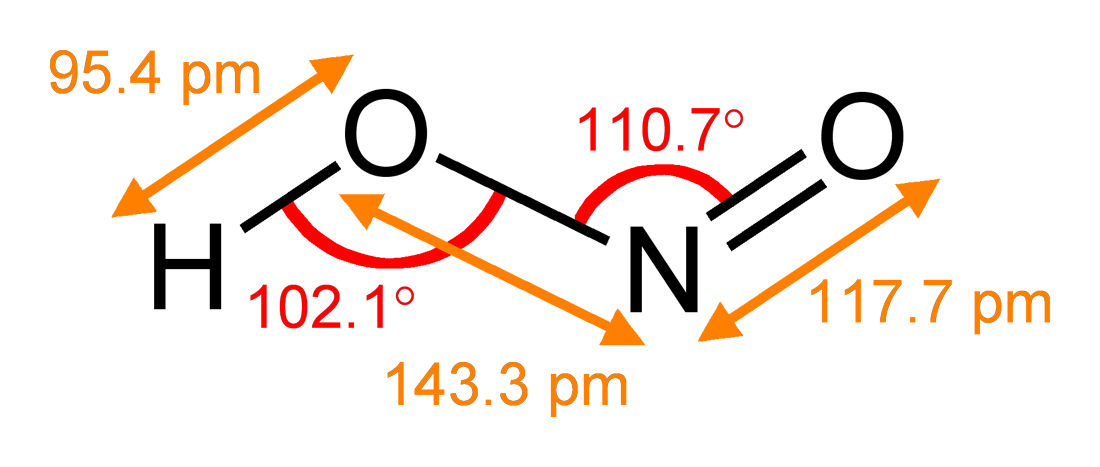
Nitrosyl fluoride ( N O F) is a covalently bonded nitrosyl compound. Reactions NOF is a highly reactive fluorinating agent that converts many metals to their fluorides, releasing nitric oxide in the process: :''n'' NOF + M → MF''n'' + ''n'' NO NOF also fluorinates fluorides to form adducts that have a salt-like character, such as NOBF4. Aqueous solutions of NOF are powerful solvents for metals, by a mechanism similar to that seen in aqua regia. Nitrosyl fluoride reacts with water to form nitrous acid, which then forms nitric acid: :NOF + H2O → HNO2 + HF :3 HNO2 → HNO3 + 2 NO + H2O Nitrosyl fluoride can also convert alcohols to nitrites: :ROH + NOF → RONO + HF It has a bent molecular shape: this can be rationalized in the VSEPR model in terms of the lone-pair of electrons located on the N atom. Uses Nitrosyl fluoride is used as a solvent and as a fluorinating and nitrating agent in organic synthesis. It has also been proposed as an oxidizer in rocket propellant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Nitroxyl
Nitroxyl (common name) or azanone (IUPAC name) is the chemical compound HNO. It is well known in the gas phase. Nitroxyl can be formed as a short-lived intermediate in the solution phase. The conjugate base, NO−, nitroxide anion, is the reduced form of nitric oxide (NO) and is isoelectronic with dioxygen. The bond dissociation energy of H−NO is , which is unusually weak for a bond to the hydrogen atom. Generation Nitroxyl is produced from the reagents Angeli's salt (Na2N2O3) and Piloty's acid (PhSO2NHOH). Other notable studies on the production of HNO exploit cycloadducts of acyl nitroso species, which are known to decompose via hydrolysis to HNO and acyl acid. Upon photolysis these compounds release the acyl nitroso species which then further decompose. HNO is generated via organic oxidation of cyclohexanone oxime with lead tetraacetate to form 1-nitrosocyclohexyl acetate: : This compound can be hydrolyzed under basic conditions in a phosphate buffer to HNO, acetic acid, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
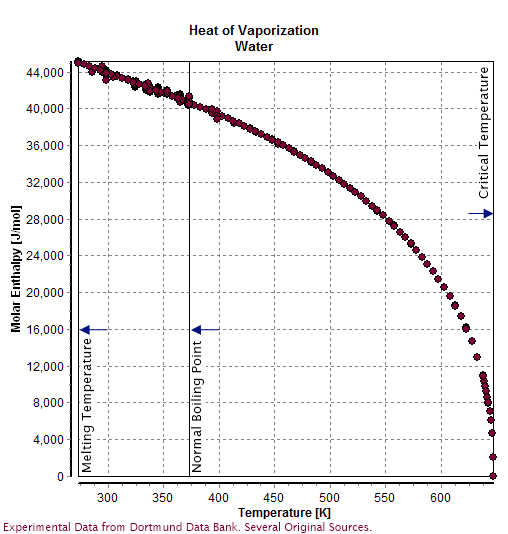 |
Water (molecule)
Water () is a polar inorganic compound that is at room temperature a tasteless and odorless liquid, which is nearly colorless apart from an inherent hint of blue. It is by far the most studied chemical compound and is described as the "universal solvent" and the "solvent of life". It is the most abundant substance on the surface of Earth and the only common substance to exist as a solid, liquid, and gas on Earth's surface. It is also the third most abundant molecule in the universe (behind molecular hydrogen and carbon monoxide). Water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other and are strongly polar. This polarity allows it to dissociate ions in salts and bond to other polar substances such as alcohols and acids, thus dissolving them. Its hydrogen bonding causes its many unique properties, such as having a solid form less dense than its liquid form, a relatively high boiling point of 100 °C for its molar mass, and a high heat capacity. Water is amphoteric, me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Nitrosyl Compounds
In organic chemistry, nitroso refers to a functional group in which the nitric oxide () group is attached to an organic moiety. As such, various nitroso groups can be categorized as ''C''-nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosoalkanes; ), ''S''-nitroso compounds ( nitrosothiols; ), ''N''-nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosamines, ), and ''O''-nitroso compounds (alkyl nitrites; ). Synthesis Nitroso compounds can be prepared by the reduction of nitro compounds or by the oxidation of hydroxylamines. Ortho-nitrosophenols may be produced by the Baudisch reaction. In the Fischer–Hepp rearrangement aromatic 4-nitrosoanilines are prepared from the corresponding nitrosamines. Properties Nitrosoarenes typically participate in a monomer–dimer equilibrium. The dimers, which are often pale yellow, are often favored in the solid state, whereas the deep-green monomers are favored in dilute solution or at higher temperatures. They exist as ''cis'' and ''trans'' isomers. Due to the stability of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
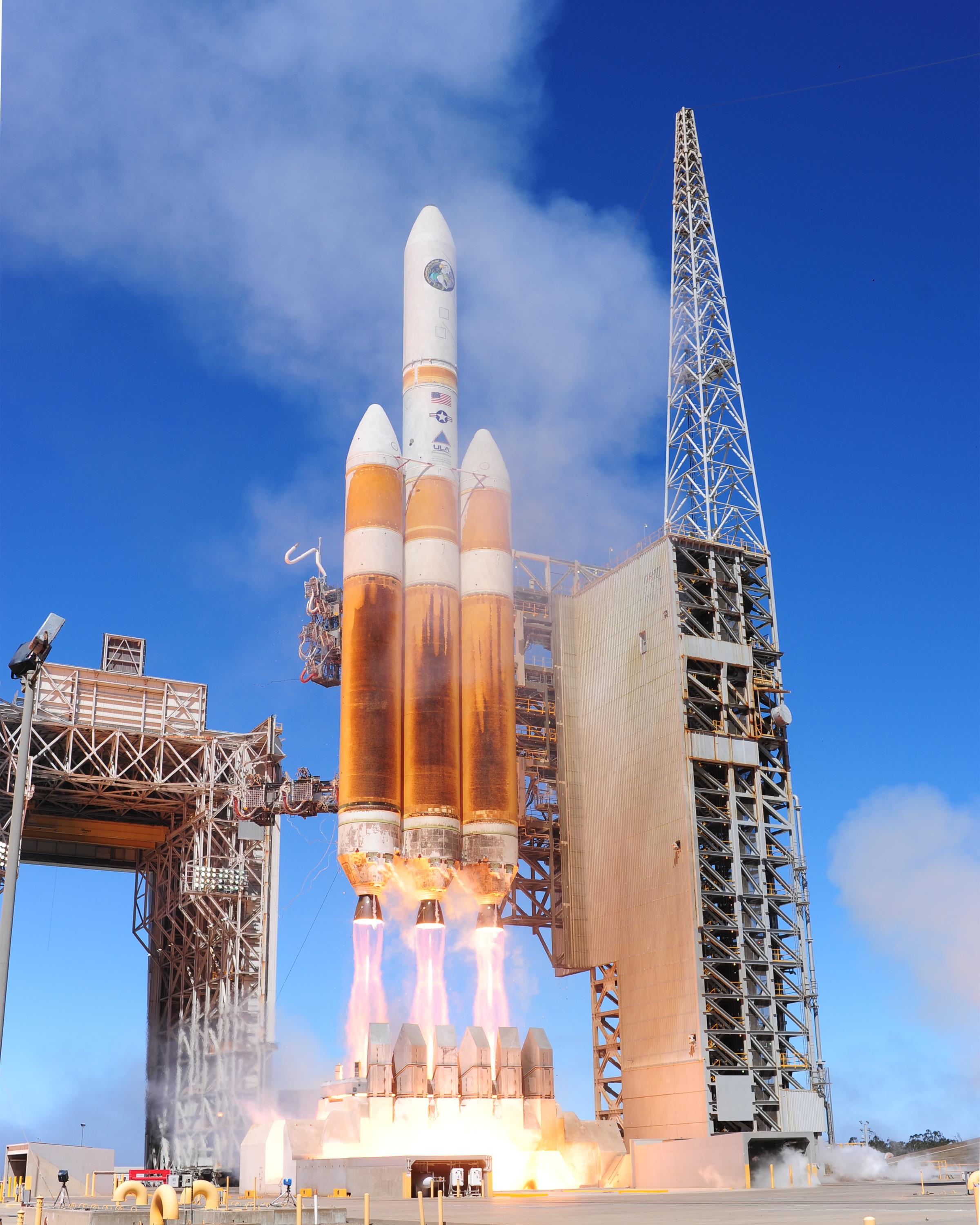 |
Rocket Propellant
Rocket propellant is the reaction mass of a rocket. This reaction mass is ejected at the highest achievable velocity from a rocket engine to produce thrust. The energy required can either come from the propellants themselves, as with a chemical rocket, or from an external source, as with ion engines. Overview Rockets create thrust by expelling mass rear-ward, at high velocity. The thrust produced can be calculated by multiplying the mass flow rate of the propellants by their exhaust velocity relative to the rocket (specific impulse). A rocket can be thought of as being accelerated by the pressure of the combusting gases against the combustion chamber and nozzle, not by "pushing" against the air behind or below it. Rocket engines perform best in outer space because of the lack of air pressure on the outside of the engine. In space it is also possible to fit a longer nozzle without suffering from flow separation. Most chemical propellants release energy through redox chemistry, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Organic Synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one of the most important branches of organic chemistry. There are several main areas of research within the general area of organic synthesis: '' total synthesis'', '' semisynthesis'', and ''methodology''. Total synthesis A total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of complex organic molecules from simple, commercially available petrochemical or natural precursors. Total synthesis may be accomplished either via a linear or convergent approach. In a ''linear'' synthesis—often adequate for simple structures—several steps are performed one after another until the molecule is complete; the chemical compounds made in each step are called synthetic intermediates. Most often, each step in a synthesis refers to a separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Nitrating
In organic chemistry, nitration is a general class of chemical processes for the introduction of a nitro group into an organic compound. The term also is applied incorrectly to the different process of forming nitrate esters between alcohols and nitric acid (as occurs in the synthesis of nitroglycerin). The difference between the resulting molecular structures of nitro compounds and nitrates is that the nitrogen atom in nitro compounds is directly bonded to a non-oxygen atom (typically carbon or another nitrogen atom), whereas in nitrate esters (also called organic nitrates), the nitrogen is bonded to an oxygen atom that in turn usually is bonded to a carbon atom (nitrito group). There are many major industrial applications of nitration in the strict sense; the most important by volume are for the production of nitroaromatic compounds such as nitrobenzene. Nitration reactions are notably used for the production of explosives, for example the conversion of guanidine to nitroguani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for polar molecules and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a cell are dissolved in water within the cell. The quantity of solute that can dissolve in a specific volume of solvent varies with temperature. Major uses of solvents are in paints, paint removers, inks, and dry cleaning. Specific uses for organic Organic may refer to: * Organic, of or relating to an organism, a living entity * Organic, of or relating to an anatomical organ Chemistry * Organic matter, matter that has come from a once-living organism, is capable of decay or is the product ... solvents are in dry cleaning (e.g. tetrachloroethylene); as paint thinners ( toluene, turpentine); as nail polish removers and solvents of glue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
VSEPR Theory
Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory ( , ), is a model used in chemistry to predict the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms. It is also named the Gillespie-Nyholm theory after its two main developers, Ronald Gillespie and Ronald Nyholm. The premise of VSEPR is that the valence electron pairs surrounding an atom tend to repel each other and will, therefore, adopt an arrangement that minimizes this repulsion. This in turn decreases the molecule's energy and increases its stability, which determines the molecular geometry. Gillespie has emphasized that the electron-electron repulsion due to the Pauli exclusion principle is more important in determining molecular geometry than the electrostatic repulsion. The insights of VSEPR theory are derived from topological analysis of the electron density of molecules. Such quantum chemical topology (QCT) methods include the electron localization function (EL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Nitrite
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid. Production Sodium nitrite is made industrially by passing a mixture of nitrogen oxides into aqueous sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate solution: : The product is purified by recrystallization. Alkali metal nitrites are thermally stable up to and beyond their melting point (441 °C for KNO2). Ammonium nitrite can be made from dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3, which is formally the anhydride of nitrous acid: :2 NH3 + H2O + N2O3 → 2 NH4NO2 Structure The nitrite ion has a symmetrical structure (C2v symmetry), with both N–O bonds having equal length and a bond angle of about 115°. In valence bond theory, it is described as a resonance hybrid with equal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |