|
Nitroso
In organic chemistry, nitroso refers to a functional group in which the nitric oxide () group is attached to an organic moiety. As such, various nitroso groups can be categorized as ''C''-nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosoalkanes; ), ''S''-nitroso compounds ( nitrosothiols; ), ''N''-nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosamines, ), and ''O''-nitroso compounds (alkyl nitrites; ). Synthesis Nitroso compounds can be prepared by the reduction of nitro compounds or by the oxidation of hydroxylamines. Ortho-nitrosophenols may be produced by the Baudisch reaction. In the Fischer–Hepp rearrangement aromatic 4-nitrosoanilines are prepared from the corresponding nitrosamines. Properties Nitrosoarenes typically participate in a monomer–dimer equilibrium. The dimers, which are often pale yellow, are often favored in the solid state, whereas the deep-green monomers are favored in dilute solution or at higher temperatures. They exist as ''cis'' and ''trans'' isomers. Due to the stability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-Nitrosothiol
In organic chemistry, ''S''-nitrosothiols, also known as thionitrites, are organic compounds or functional groups containing a nitroso group attached to the sulfur atom of a thiol. ''S''-Nitrosothiols have the general formula , where ''R'' denotes an organic group. Originally suggested by Ignarro to serve as intermediates in the action of organic nitrates, endogenous S-nitrosothiols were discovered by Stamler and colleagues (S-nitrosoalbumin in plasma and S-nitrosoglutathione in airway lining fluid) and shown to represent a main source of NO bioactivity ''in vivo''. More recently, S-nitrosothiols have been implicated as primary mediators of protein S-nitrosylation, the oxidative modification of cysteine thiol that provides ubiquitous regulation of protein function. S-Nitrosothiols have received much attention in biochemistry because they serve as donors of both the nitrosonium ion and of nitric oxide and thus best rationalize the chemistry of NO-based signaling in livin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
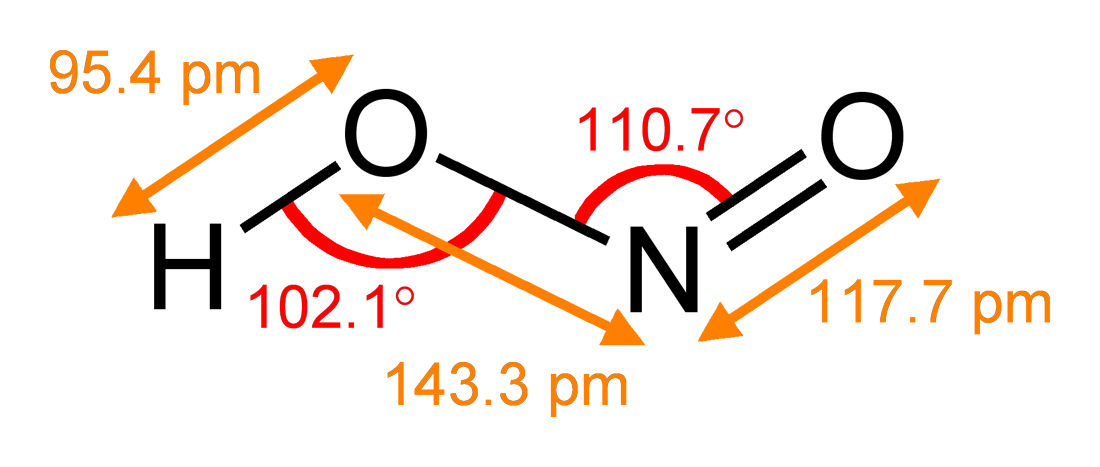
Baudisch Reaction
In organic chemistry, the Baudisch reaction is a process for the synthesis of nitrosophenols using metal ions. Although the products are of limited value, the reaction is of historical interest as an example of metal-promoted functionalization of aromatic substrates. History and Mechanism As described originally by Oskar Baudisch in 1939 and further developed by his colleague Cronheim in 1947, benzene, hydroxylamine, and hydrogen peroxide are combined. Baudisch proposed that the reaction proceeds first via the formation of nitroxyl (HN=O), by the oxidation of hydroxylamine hydrochloride with hydrogen peroxide, possibly catalysed by the cupric ions. : This can also be achieved by the reduction of nitrous acid with cuprous ions or by the action of cuprous ions and hydrogen peroxide on Piloty's acid. The nitroxyl (HN=O) then attacks the aromatic ring, giving a nitroso-cyclohexadiene which is rapidly hydroxylated before being oxidised by the peroxide to give the o-nitrosophenol as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartoli Indole Synthesis
The Bartoli indole synthesis (also called the Bartoli reaction) is the chemical reaction of ortho-substituted nitroarenes and nitrosoarenes with vinyl Grignard reagents to form substituted indoles. The reaction is often unsuccessful without substitution ortho to the nitro group, with bulkier ortho substituents usually resulting in higher yields for the reaction. The steric bulk of the ortho group assists in the ,3sigmatropic rearrangement required for product formation. Three equivalents of the vinyl Grignard reagent are necessary for the reaction to achieve full conversion when performed on nitroarenes, and only two equivalents when performed on nitrosoarenes. This method has become one of the shortest and most flexible routes to 7-substituted indoles. The Leimgruber-Batcho indole synthesis gives similar flexibility and regiospecificity to indole derivatives. One advantage of the Bartoli indole synthesis is the ability to produce indoles substituted on both the carbocycli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrosonium Ion
The nitrosonium ion is , in which the nitrogen atom is bonded to an oxygen atom with a bond order of 3, and the overall diatomic species bears a positive charge. It can be viewed as nitric oxide with one electron removed. This ion is usually obtained as the following salts: , (nitrosylsulfuric acid, more descriptively written ) and . The and salts are slightly soluble in acetonitrile . NOBF4 can be purified by sublimation at 200–250 °C and . is isoelectronic with CO, and . It arises via protonation of nitrous acid: :HONO + H+ NO+ + H2O Chemical properties Hydrolysis reacts readily with water to form nitrous acid: : For this reason, nitrosonium compounds must be protected from water or even moist air. With base, the reaction generates nitrite: : As a diazotizing agent reacts with aryl amines, , to give diazonium salts, . The resulting diazonium group is easily displaced (unlike the amino group) by a variety of nucleophiles. As an oxidizing agent , e.g. a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrosation
Nitrosation is a process of converting organic compounds into nitroso derivatives, i.e. compounds containing the R-NO functionality. ''C''-Nitroso compounds ''C''-Nitroso compounds, such as nitrosobenzene, are typically prepared by oxidation of hydroxylamines: :RNHOH + → RNO + H2O ''S''-Nitroso compounds ''S''-Nitroso compounds ( ''S''-nitrosothiols) are typically prepared by condensation of a thiol and nitrous acid: :RSH + HONO → RSNO + H2O ''O''-Nitroso compounds ''O''- Nitroso compounds are similar to ''S''-nitroso compounds, but are less reactive because the oxygen atom is less nucleophilic than the sulfur atom. The formation of an alkyl nitrite from an alcohol and nitrous acid is a common example: :ROH + HONO → RONO + H2O ''N''-Nitrosamines ''N''-Nitrosamines, including the carcinogenic variety, arise from the reaction of nitrite sources with amino compounds, which can happen during the curing of meat. Typically this reaction proceeds via the attack of the nit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrosamine
In organic chemistry, nitrosamines (or more formally ''N''-Nitrosamines) are organic compounds with the chemical structure , where R is usually an alkyl group. They feature a nitroso group () bonded to a deprotonated amine. Most nitrosamines are carcinogenic in nonhuman animals. A 2006 systematic review supports a "positive association between nitrite and nitrosamine intake and gastric cancer, between meat and processed meat intake and gastric cancer and oesophageal cancer, and between preserved fish, vegetable and smoked food intake and gastric cancer, but is not conclusive". Chemistry The organic chemistry of nitrosamines is well developed with regard to their syntheses, their structures, and their reactions. They usually are produced by the reaction of nitrous acid () and secondary amines. :HONO + R2NH -> R2N-NO + H2O The nitrous acid usually arises from protonation of a nitrite. This synthesis method is relevant to the generation of nitrosamines under some biological co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fischer–Hepp Rearrangement
The Fischer–Hepp rearrangement is a rearrangement reaction in which an aromatic N-nitroso or nitrosamine converts to a carbon nitroso compound: This organic reaction was first described by the German chemist Otto Philipp Fischer (1852–1932) and Eduard Hepp (June 11, 1851 – June 18, 1917) W Pötsch. ''Lexikon bedeutender Chemiker'' (VEB Bibliographisches Institut Leipzig, 1989) in 1886, and is of importance because para- NO secondary anilines cannot be prepared in a direct reaction. The rearrangement reaction takes place by reacting the nitrosamine precursor with hydrochloric acid. The chemical yield is generally good under these conditions, but often much poorer if a different acid is used. The exact reaction mechanism is unknown but there is evidence suggesting an intramolecular reaction. Sources''Named Things in Chemical Industry'' See also * Friedel–Crafts alkylation-like reactions: ** Hofmann-Martius rearrangement **Fries rearrangement The Fries rearrangement, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barton Reaction
The Barton reaction, also known as the Barton nitrite ester reaction, is a photochemical reaction that involves the photolysis of an alkyl nitrite to form a δ-nitroso Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol. Discovered in 1960, the reaction is named for its discoverer, Nobel Laureate Sir Derek Barton. Barton's Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1969 was awarded for his work on understanding conformations of organic molecules, work which was key to realizing the utility of the Barton Reaction. The Barton reaction involves a homolysis (chemistry), homolytic RO–NO cleavage, followed by δ-hydrogen abstraction, free radical recombination, and tautomerization to form an oxime. Selectivity for the δ-hydrogen is a result of the conformation of the 6-membered radical intermediate. Often, the site of hydrogen atom abstraction can be easily predicted. This allows the regio- and stereo-selective introduction of functionality into complicated molecules with high yield. Due to its unique property at the time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. For repeating units of polymers, functional groups attach to their nonpolar core of carbon atoms and thus add chemical character to carbon chains. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrosamines
In organic chemistry, nitrosamines (or more formally ''N''-Nitrosamines) are organic compounds with the chemical structure , where R is usually an alkyl group. They feature a nitroso group () bonded to a deprotonated amine. Most nitrosamines are carcinogenic in nonhuman animals. A 2006 systematic review supports a "positive association between nitrite and nitrosamine intake and gastric cancer, between meat and processed meat intake and gastric cancer and oesophageal cancer, and between preserved fish, vegetable and smoked food intake and gastric cancer, but is not conclusive". Chemistry The organic chemistry of nitrosamines is well developed with regard to their syntheses, their structures, and their reactions. They usually are produced by the reaction of nitrous acid () and secondary amines. :HONO + R2NH -> R2N-NO + H2O The nitrous acid usually arises from protonation of a nitrite. This synthesis method is relevant to the generation of nitrosamines under some biological co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrite
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid. Production Sodium nitrite is made industrially by passing a mixture of nitrogen oxides into aqueous sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate solution: : The product is purified by recrystallization. Alkali metal nitrites are thermally stable up to and beyond their melting point (441 °C for KNO2). Ammonium nitrite can be made from dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3, which is formally the anhydride of nitrous acid: :2 NH3 + H2O + N2O3 → 2 NH4NO2 Structure The nitrite ion has a symmetrical structure (C2v symmetry), with both N–O bonds having equal length and a bond angle of about 115°. In valence bond theory, it is described as a resonance hybrid with equal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxylamine
Hydroxylamine is an inorganic compound with the formula . The material is a white crystalline, hygroscopic compound.Greenwood and Earnshaw. ''Chemistry of the Elements.'' 2nd Edition. Reed Educational and Professional Publishing Ltd. pp. 431–432. 1997. Hydroxylamine is almost always provided and used as an aqueous solution. It is consumed almost exclusively to produce Nylon-6. It is also an intermediate in biological nitrification. The oxidation of to hydroxylamine is a step in biological nitrification. History Hydroxylamine was first prepared as hydroxylammonium chloride in 1865 by the German chemist Wilhelm Clemens Lossen (1838-1906); he reacted tin and hydrochloric acid in the presence of ethyl nitrate. It was first prepared in pure form in 1891 by the Dutch chemist Lobry de Bruyn and by the French chemist Léon Maurice Crismer (1858-1944). The coordination complex , known as Crismer's salt, releases hydroxylamine upon heating. Production Hydroxylamine or its salts can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |