|
Nissen-Lie Classification
Nissen-Lie classification is a system of categorizing Colles' fractures. In the Nissen-Lie classification system there are seven types of fractures. The classification system was first published in 1939. Classification * Type 1: A fracture at the junction of the shaft and distal extremity of the radius (occurs only in children between the age of 1 and 15 years, and is most commonly a greenstick fracture) * Type 2: Slipping of the epiphysis with dorsal displacement, often with a dorsally avulsed triangular fragment of the radius (occurs in the age range 10-20 years) * Type 3: Minimal displacement * Type 4: Dorsal angulation, extra-articular, no comminution * Type 5: Intra-articular, comminuted * Type 6: Fractures of the radial styloid * Type 7: Fractures with dorsal displacement See also * Frykman classification * Gartland & Werley classification Gartland & Werley classification is a system of categorizing Colles' fractures. In the Gartland & Werley classification system there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colles' Fracture
A Colles' fracture is a type of fracture of the distal forearm in which the broken end of the radius is bent backwards. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, deformity, and bruising. Complications may include damage to the median nerve. It typically occurs as a result of a fall on an outstretched hand. Risk factors include osteoporosis. The diagnosis may be confirmed via X-rays. The tip of the ulna may also be broken. Treatment may include casting or surgery. Surgical reduction and casting is possible in the majority of cases in people over the age of 50. Pain management can be achieved during the reduction with procedural sedation and analgesia or a hematoma block. A year or two may be required for healing to occur. About 15% of people have a Colles' fracture at some point in their life. They occur more commonly in young adults and older people than in children and middle-aged adults. Women are more frequently affected than men. The fracture is named after Abraham Colles w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Fracture
A bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a ''comminuted fracture''. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture. Signs and symptoms Although bone tissue contains no pain receptors, a bone fracture is painful for several reasons: * Breaking in the continuity of the periosteum, with or without similar discontinuity in endosteum, as both contain multiple pain receptors. * Edema and hematoma of nearby soft tissues caused by ruptured bone marrow evokes pressure pain. * Involuntary muscle spasms trying to hold bone fragments in place. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenstick Fracture
A greenstick fracture is a fracture in a young, soft bone in which the bone bends and breaks. Greenstick fractures occur most often during infancy and childhood when bones are soft. The name is by analogy with green (i.e., fresh) wood which similarly breaks on the outside when bent. Signs and symptoms Some clinical features of a greenstick fracture are similar to those of a standard long bone fracture greenstick fractures normally cause pain at the injured area. As these fractures are specifically a pediatric problem, an older child will be protective of the fractured part and babies may cry inconsolably. As per a standard fracture, the area may be swollen and either red or bruised. Greenstick fractures are stable fractures as a part of the bone remains intact and unbroken so this type of fracture normally causes a bend to the injured part, rather than a distinct deformity, which is problematic. Symptoms include pain in the area and can start from overuse in that specific bone. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
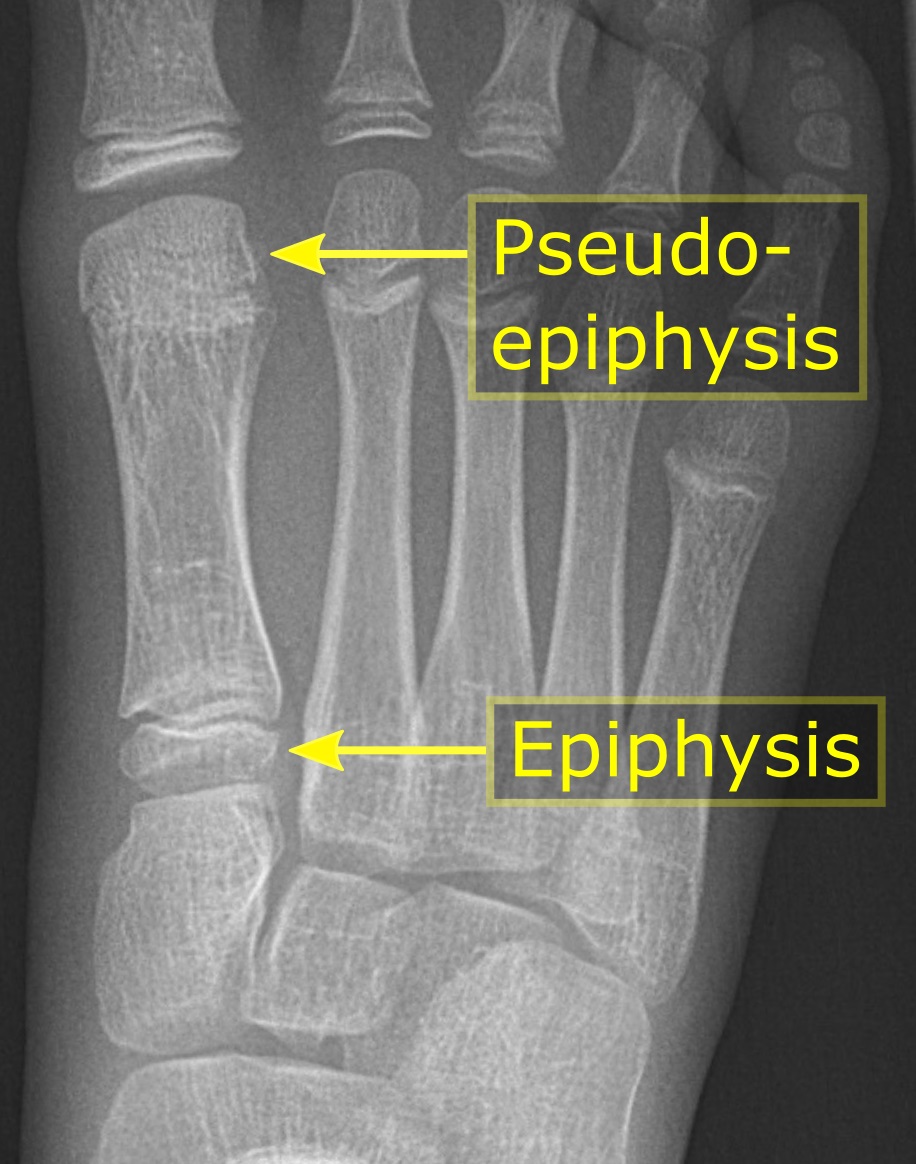
Epiphysis
The epiphysis () is the rounded end of a long bone, at its joint with adjacent bone(s). Between the epiphysis and diaphysis (the long midsection of the long bone) lies the metaphysis, including the epiphyseal plate (growth plate). At the joint, the epiphysis is covered with articular cartilage; below that covering is a zone similar to the epiphyseal plate, known as subchondral bone. The epiphysis is filled with red bone marrow, which produces erythrocytes (red blood cells). Structure There are four types of epiphysis: # Pressure epiphysis: The region of the long bone that forms the joint is a pressure epiphysis (e.g. the head of the femur, part of the hip joint complex). Pressure epiphyses assist in transmitting the weight of the human body and are the regions of the bone that are under pressure during movement or locomotion. Another example of a pressure epiphysis is the head of the humerus which is part of the shoulder complex. condyles of femur and tibia also comes under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Styloid
The radial styloid process is a projection of bone on the lateral surface of the distal radius bone. Structure The radial styloid process is found on the lateral surface of the distal radius bone. It extends obliquely downward into a strong, conical projection. The tendon of the brachioradialis attaches at its base. The radial collateral ligament of the wrist attaches at its apex. The lateral surface is marked by a flat groove for the tendons of the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis. Clinical significance Breakage of the radius at the radial styloid is known as a Chauffeur's fracture; it is typically caused by compression of the scaphoid bone of the hand against the styloid. De Quervain syndrome causes pain over the styloid process of the radius. This is due to the passage of the inflamed extensor pollicis brevis tendon and abductor pollicis longus tendon around it. The styloid process of the radius is a useful landmark during arthroscopic resection o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frykman Classification
Frykman classification is a system of categorizing Colles' fractures. In the Frykman classification system there are four types of fractures. Classification Though the Frykman classification system has traditionally been used, there is little value in its use because it does not help direct treatment. The classification is as follows: See also * Gartland & Werley classification Gartland & Werley classification is a system of categorizing Colles' fractures. In the Gartland & Werley classification system there are three types of fractures. The classification system is based on metaphysical comminution, intra-articular exte ... * Lidström classification * Nissen-Lie classification * Older's classification References {{Reflist Orthopedic classifications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gartland & Werley Classification
Gartland & Werley classification is a system of categorizing Colles' fractures. In the Gartland & Werley classification system there are three types of fractures. The classification system is based on metaphysical comminution, intra-articular extension and displacement, and was first published in 1951. Classification * Type 1: Extra-articular, displaced * Type 2: Intra-articular, no displacement * Type 3: Intra-articular, displaced See also * Frykman classification Frykman classification is a system of categorizing Colles' fractures. In the Frykman classification system there are four types of fractures. Classification Though the Frykman classification system has traditionally been used, there is little valu ... * Lidström classification * Nissen-Lie classification * Older's classification References {{DEFAULTSORT:Gartland and Werley classification Orthopedic classifications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lidström Classification
Lidström classification is a system of categorizing Colles' fractures. In the Lidström classification system there are six types of fractures. The classification system is based on fracture line, direction and degree of displacement, extent of articular involvement and involvement of the distal radioulnar joint, and was first published in 1959. Classification * Group 1: Minimal displacement * Group 2-A: Extra-articular, dorsal angulation * Group 2-B: Intra-articular, dorsal angulation, joint surface not comminuted * Group 2-C: Extra-articular, dorsal angulation and dorsal displacement * Group 2-D: Intra-articular, dorsal angulation and displacement, joint surface not comminuted * Group 2-F: Intra-articular, dorsal angulation and displacement, joint surface comminuted See also * Frykman classification * Gartland & Werley classification Gartland & Werley classification is a system of categorizing Colles' fractures. In the Gartland & Werley classification system there are three t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Older's Classification
Older's classification is a system of categorizing Colles' fractures, proposed in 1965. In the Older's classification system there are four types of fractures. Classification * Type 1: Dorsal angulation up to five degrees, radial length distal to ulna at least 7 mm. * Type 2: Dorsal angulation, radial length 1 to 7 mm, no comminution. * Type 3: Dorsal radius comminuted, radial length less than 4 mm, distal fragment slightly comminuted. * Type 4: Marked comminution, radial length usually negative. See also * Frykman classification * Gartland & Werley classification * Lidström classification * Nissen-Lie classification Nissen-Lie classification is a system of categorizing Colles' fractures. In the Nissen-Lie classification system there are seven types of fractures. The classification system was first published in 1939. Classification * Type 1: A fracture at the j ... References {{Reflist Orthopedic classifications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |