|
Niobium-95
Naturally occurring niobium (41Nb) is composed of one stable isotope (93Nb). The most stable radioisotope is 92Nb with a half-life of 34.7 million years. The next longest-lived niobium isotopes are 94Nb (half-life: 20,300 years) and 91Nb with a half-life of 680 years. There is also a meta state of 93Nb at 31 keV whose half-life is 16.13 years. Twenty-seven other radioisotopes have been characterized. Most of these have half-lives that are less than two hours, except 95Nb (35 days), 96Nb (23.4 hours) and 90Nb (14.6 hours). The primary decay mode before stable 93Nb is electron capture and the primary mode after is beta emission with some neutron emission occurring in 104–110Nb. Only 95Nb (35 days) and 97Nb (72 minutes) and heavier isotopes (half-lives in seconds) are fission products in significant quantity, as the other isotopes are shadowed by stable or very long-lived ( 93Zr) isotopes of the preceding element zirconium from production via beta decay of neutron-rich fission f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fission Fragment
Nuclear fission products are the atomic fragments left after a large atomic nucleus undergoes nuclear fission. Typically, a large nucleus like that of uranium fissions by splitting into two smaller nuclei, along with a few neutrons, the release of heat energy (kinetic energy of the nuclei), and gamma rays. The two smaller nuclei are the ''fission products''. (See also Fission products (by element)). About 0.2% to 0.4% of fissions are ternary fissions, producing a third light nucleus such as helium-4 (90%) or tritium (7%). The fission products themselves are usually unstable and therefore radioactive. Due to being relatively neutron-rich for their atomic number, many of them quickly undergo beta decay. This releases additional energy in the form of beta particles, antineutrinos, and gamma rays. Thus, fission events normally result in beta and gamma radiation, even though this radiation is not produced directly by the fission event itself. The produced radionuclides have var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fission Products
Nuclear fission products are the atomic fragments left after a large atomic nucleus undergoes nuclear fission. Typically, a large nucleus like that of uranium fissions by splitting into two smaller nuclei, along with a few neutrons, the release of heat energy (kinetic energy of the nuclei), and gamma rays. The two smaller nuclei are the ''fission products''. (See also Fission products (by element)). About 0.2% to 0.4% of fissions are ternary fissions, producing a third light nucleus such as helium-4 (90%) or tritium (7%). The fission products themselves are usually unstable and therefore radioactive. Due to being relatively neutron-rich for their atomic number, many of them quickly undergo beta decay. This releases additional energy in the form of beta particles, antineutrinos, and gamma rays. Thus, fission events normally result in beta and gamma radiation, even though this radiation is not produced directly by the fission event itself. The produced radionuclides have vary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has similar ductility to iron. Niobium oxidizes in Earth's atmosphere very slowly, hence its application in jewelry as a hypoallergenic alternative to nickel. Niobium is often found in the minerals pyrochlore and columbite, hence the former name "columbium". Its name comes from Greek mythology: Niobe, daughter of Tantalus, the namesake of tantalum. The name reflects the great similarity between the two elements in their physical and chemical properties, which makes them difficult to distinguish. English chemist Charles Hatchett reported a new element similar to tantalum in 1801 and named it columbium. In 1809, English chemist William Hyde Wollaston wrongly concluded that tantalum and columbium were identical. German chemist Heinrich Rose determin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes Of Niobium
Naturally occurring niobium (41Nb) is composed of one stable isotope (93Nb). The most stable radioisotope is 92Nb with a half-life of 34.7 million years. The next longest-lived niobium isotopes are 94Nb (half-life: 20,300 years) and 91Nb with a half-life of 680 years. There is also a meta state of 93Nb at 31 keV whose half-life is 16.13 years. Twenty-seven other radioisotopes have been characterized. Most of these have half-lives that are less than two hours, except 95Nb (35 days), 96Nb (23.4 hours) and 90Nb (14.6 hours). The primary decay mode before stable 93Nb is electron capture and the primary mode after is beta emission with some neutron emission occurring in 104–110Nb. Only 95Nb (35 days) and 97Nb (72 minutes) and heavier isotopes (half-lives in seconds) are fission products in significant quantity, as the other isotopes are shadowed by stable or very long-lived ( 93Zr) isotopes of the preceding element zirconium from production via beta decay of neutron-rich fission fragm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muon
A muon ( ; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 '' e'' and a spin of , but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a lepton. As with other leptons, the muon is not thought to be composed of any simpler particles; that is, it is a fundamental particle. The muon is an unstable subatomic particle with a mean lifetime of , much longer than many other subatomic particles. As with the decay of the non-elementary neutron (with a lifetime around 15 minutes), muon decay is slow (by subatomic standards) because the decay is mediated only by the weak interaction (rather than the more powerful strong interaction or electromagnetic interaction), and because the mass difference between the muon and the set of its decay products is small, providing few kinetic degrees of freedom for decay. Muon decay almost always produces at least three particles, which must include an electron o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the surface, although the bulk is deflected off into space by the magnetosphere or the heliosphere. Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Hess in 1912 in balloon experiments, for which he was awarded the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics. Direct measurement of cosmic rays, especially at lower energies, has been possible since the launch of the first satellites in the late 1950s. Particle detectors similar to those used in nuclear and high-energy physics are used on satellites and space probes for research into cosmic rays. Data from the Fermi Space Telescope (2013) have been interpreted as evidenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-nuclei
p-nuclei (''p'' stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury inclusive which cannot be produced in either the s- or the r-process. Definition The classical, ground-breaking works of Burbidge, Burbidge, Fowler and Hoyle (1957) and of A. G. W. Cameron (1957) showed how the majority of naturally occurring nuclides beyond the element iron can be made in two kinds of neutron capture processes, the s- and the r-process. Some proton-rich nuclides found in nature are not reached in these processes and therefore at least one additional process is required to synthesize them. These nuclei are called p-nuclei. Since the definition of the p-nuclei depends on the current knowledge of the s- and r-process (see also nucleosynthesis), the original list of 35 p-nuclei may be modified over the years, as indicated in the Table below. For example, it is recognized today that the abundances of 152Gd and 164Er conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Radionuclide
An extinct radionuclide is a radionuclide that was formed by nucleosynthesis before the formation of the Solar System, about 4.6 billion years ago, but has since decayed to virtually zero abundance and is no longer detectable as a primordial nuclide. Extinct radionuclides were generated by various processes in the early Solar system, and became part of the composition of meteorites and protoplanets. All widely documented extinct radionuclides have half-lives shorter than 100 million years. Short-lived radioisotopes that are found in nature are continuously generated or replenished by natural processes, such as cosmic rays (cosmogenic nuclides), background radiation, or the decay chain or spontaneous fission of other radionuclides. Short-lived isotopes that are not generated or replenished by natural processes are not found in nature, so they are known as extinct radionuclides. Their former existence is inferred from a superabundance of their stable or nearly stable decay products ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spontaneous Fission
Spontaneous fission (SF) is a form of radioactive decay that is found only in very heavy chemical elements. The nuclear binding energy of the elements reaches its maximum at an atomic mass number of about 56 (e.g., iron-56); spontaneous breakdown into smaller nuclei and a few isolated nuclear particles becomes possible at greater atomic mass numbers. History By 1908, physicists understood that alpha decay involved ejection of helium nuclei from a decaying atom. Like cluster decay, alpha decay is not typically categorized as a process of fission. The first nuclear fission process discovered was fission induced by neutrons. Because cosmic rays produce some neutrons, it was difficult to distinguish between induced and spontaneous events. Cosmic rays can be reliably shielded by a thick layer of rock or water. Spontaneous fission was identified in 1940 by Soviet physicists Georgy Flyorov and Konstantin Petrzhak by their observations of uranium in the Moscow Metro Dinamo station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
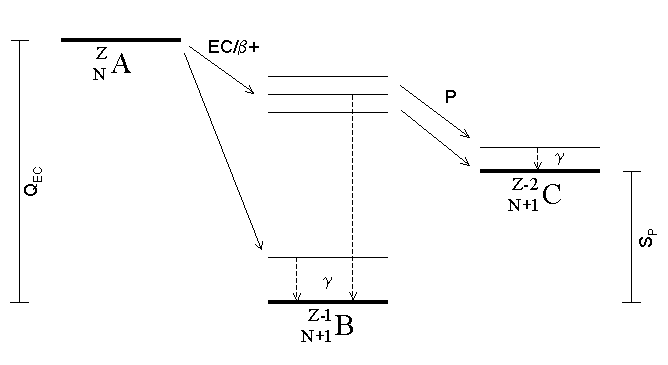
Electron Capture
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. This process thereby changes a nuclear proton to a neutron and simultaneously causes the emission of an electron neutrino. : : or when written as a nuclear reaction equation, ^_e + ^_p -> ^_n + ^_ ν_e Since this single emitted neutrino carries the entire decay energy, it has this single characteristic energy. Similarly, the momentum of the neutrino emission causes the daughter atom to recoil with a single characteristic momentum. The resulting daughter nuclide, if it is in an excited state, then transitions to its ground state. Usually, a gamma ray is emitted during this transition, but nuclear de-excitation may also take place by internal conversion. Following capture of an inner electron from the atom, an outer electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
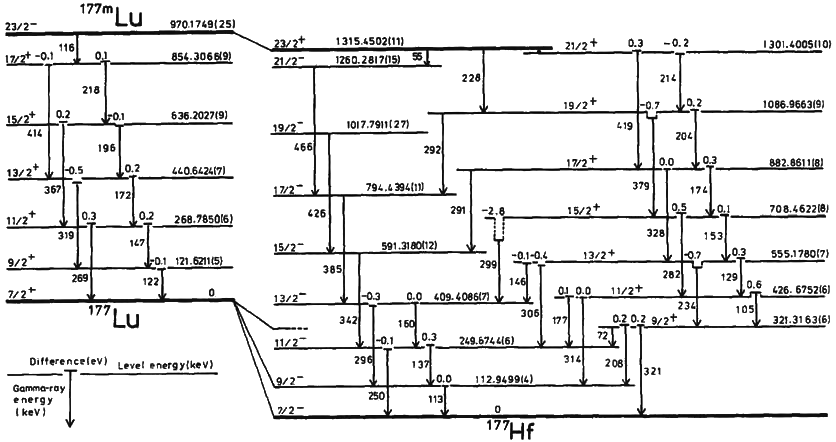
Isomeric Transition
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy higher energy levels than in the ground state of the same nucleus. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have half-lives 100 to 1000 times longer than the half-lives of the excited nuclear states that decay with a "prompt" half life (ordinarily on the order of 10−12 seconds). The term "metastable" is usually restricted to isomers with half-lives of 10−9 seconds or longer. Some references recommend 5 × 10−9 seconds to distinguish the metastable half life from the normal "prompt" gamma-emission half-life. Occasionally the half-lives are far longer than this and can last minutes, hours, or years. For example, the nuclear isomer survives so long (at least 1015 years) that it has never been observed to decay spontaneously. The half-life of a nuclear isomer can even exceed that of the ground state of the same nuclide, as shown by as well as , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton Emission
Proton emission (also known as proton radioactivity) is a rare type of radioactive decay in which a proton is ejected from a nucleus. Proton emission can occur from high-lying excited states in a nucleus following a beta decay, in which case the process is known as beta-delayed proton emission, or can occur from the ground state (or a low-lying isomer) of very proton-rich nuclei, in which case the process is very similar to alpha decay. For a proton to escape a nucleus, the proton separation energy must be negative—the proton is therefore unbound, and tunnels out of the nucleus in a finite time. Proton emission is not seen in naturally occurring isotopes; proton emitters can be produced via nuclear reactions, usually using linear particle accelerators. Although prompt (i.e. not beta-delayed) proton emission was observed from an isomer in cobalt-53 as early as 1969, no other proton-emitting states were found until 1981, when the proton radioactive ground states of lutetium-15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Halflife_of_Radionulides_depending_on_Z²_to_A_ratio.png)