|
Nikephoros
Nikephoros (), Nikiforos or Nicephorus is a Greek male name, meaning "Bringer of Victory", which was commonly used among the Byzantine Empire's aristocracy. It may refer to: Rulers * Nikephoros I Logothetes, Byzantine emperor 802–811 * Nikephoros II Phokas, Byzantine emperor 963–969 * Nikephoros III Botaneiates, Byzantine emperor 1078–1081 * Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas, despot of Epirus 1267–1297 * Nikephoros II Orsini, ruler of Epirus 1335–1338 and 1356–1359 Ecclesiastical leaders * Nicephorus I of Constantinople, Byzantine writer and patriarch, 758–828, author of the ''Stichometry'' and other works * Nicephorus II of Constantinople, patriarch in exile at Nicaea * Nicephorus of Antioch, List of Greek Orthodox Patriarchs of Antioch, Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Antioch, 1084–1090 * Nicephorus II of Kiev, Metropolitan of Kyiv and all Ruthenia, 1183–1198 * Patriarch Nicephorus of Alexandria, Orthodox Patriarch of Alexandria between 1639 and 1645 * Nikiforos of Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros III Botaneiates
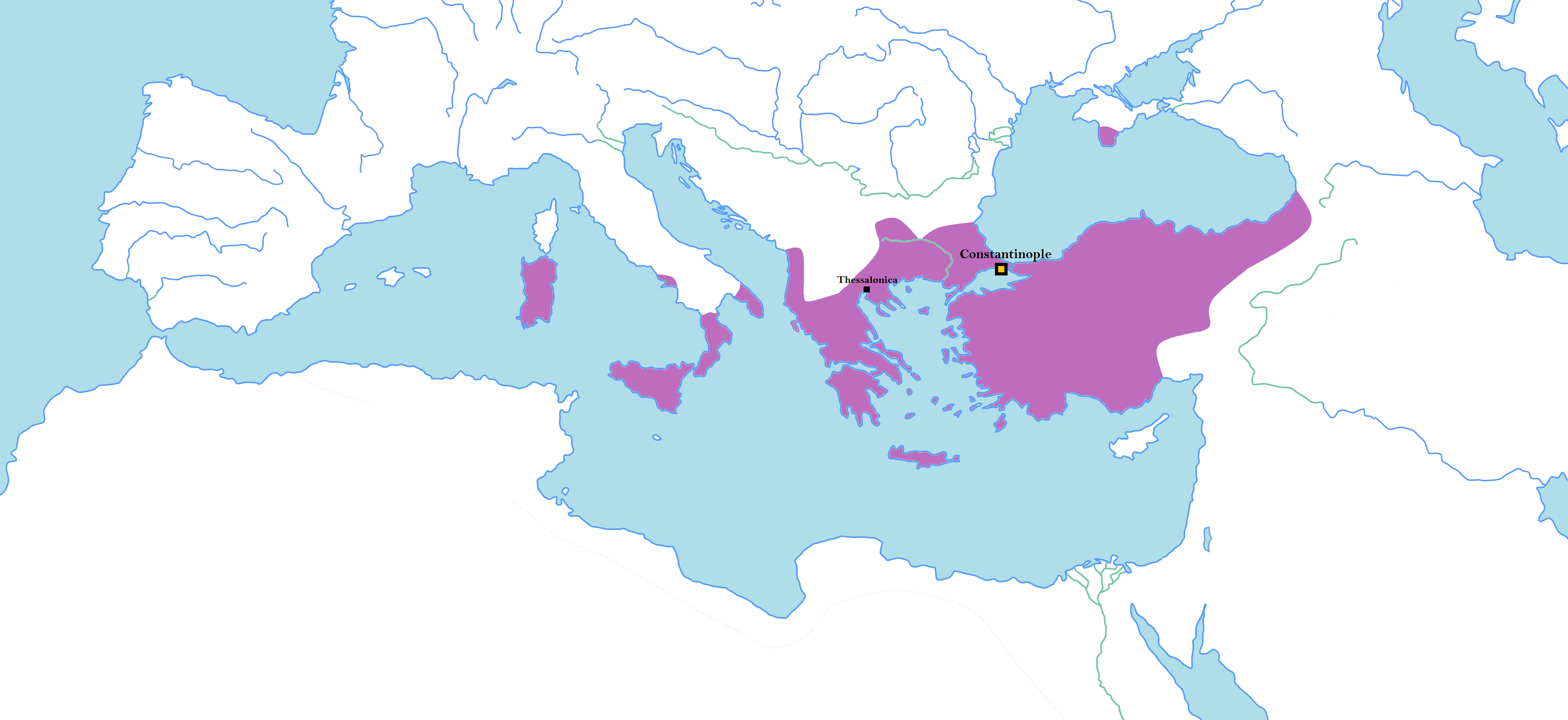
Nikephoros III Botaneiates (; 1002–1081), Romanization of Greek, Latinized as Nicephorus III Botaniates, was Byzantine Empire, Byzantine List of Byzantine Emperors, Emperor from 7 January 1078 to 1 April 1081. He became a general during the reign of Byzantine Emperor Constantine IX Monomachos, serving with distinction during the Pecheneg revolt of 1048–1053. In 1057 he aided Isaac I Komnenos in overthrowing Emperor Michael VI Bringas, leading forces at the decisive Battle of Petroe. Under the Emperor Constantine X Doukas Nikephoros was made ''dux, doux'', first of Thessalonica (theme), Thessalonica and subsequently Duchy of Antioch, of Antioch. In the latter position he repelled numerous incursions from the Emirate of Aleppo. Constantine X died in 1067 and Empress Eudokia Makrembolitissa married Romanos IV Diogenes; Nikephoros, who had also been a candidate for Eudokia's hand and the position of emperor, was exiled and remained in retirement until Emperor Michael VI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros II Phokas
Nikephoros II Phokas (; – 11 December 969), Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless greatly contributed to the resurgence of the Byzantine Empire during the 10th century. In the east, Nikephoros completed the conquest of Cilicia and retook the islands of Crete and Cyprus, opening the path for subsequent Byzantine incursions reaching as far as Upper Mesopotamia and the Levant; these campaigns earned him the sobriquet "pale death of the Saracens". Early life and career Nikephoros Phokas was born around 912. From his paternal side, he belonged to the Phokas family which had produced several distinguished generals, including Nikephoros' father Bardas Phokas, brother Leo Phokas, and grandfather Nikephoros Phokas the Elder, who had all served as commanders of the field army ('' domestikos tōn scholōn''). From his maternal side he belonged to the Maleinoi, a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros Phokas The Elder
Nikephoros Phokas (; died 895/6 or ), usually surnamed the Elder to distinguish him from his grandson, Emperor Nikephoros II Phokas, was one of the most prominent Byzantine generals of the late 9th century, and the first important member of the Phokas family. As a youth he was taken into the personal retinue of Emperor Basil I the Macedonian, rising quickly to the posts of '' protostrator'' and then governor of Charsianon, whence he fought with success against the Arabs. In he led a major expedition in southern Italy, where his victories laid the foundation for the Byzantine resurgence in the peninsula. After his return, he was raised to the post of Domestic of the Schools, in effect commander-in-chief of the army, which he led with success against the Arabs in the east and the Bulgarians of Tsar Simeon in the Balkans. He died either in 895/6 or, less likely, sometime . Contemporaries and later historians lauded him for his military ability and character. Both of his sons la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros I Logothetes
Nikephoros I (; 750 – 26 July 811), also known as Nicephorus I, was Byzantine emperor from 802 to 811. He was General Logothete (finance minister) under Empress Irene, but later overthrew her to seize the throne for himself. Prior to becoming emperor, he was sometimes referred to as "the Logothete" () and "Genikos" or "Genicus" (), in recognition of his previous role as General Logothete. During his reign, Nikephoros engaged in military campaigns against both the Arabs and the Bulgarians, although the outcomes were varied. While leading an invasion into Bulgaria, he suffered a defeat and was killed at the Battle of Pliska. Background According to several sources outside the Byzantine context, such as Michael the Syrian, al-Tabari, and Mas'udi, there is a tradition that suggests Nikephoros had Ghassanid Arab origins and that he descended from the final Ghassanid ruler Jabala ibn al-Ayham. Al-Tabari assets that he obtained this information from Byzantine sources, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros Diogenes
Nikephoros Diogenes (), Latinized as Nicephorus Diogenes, was presumably a junior Byzantine emperor around 1069–1071. He was born 1069 to Emperor Romanos IV Diogenes and Empress Eudokia Makrembolitissa. He was elevated to junior emperor in 1070, although he lost this position when his father was overthrown in 1071. Emperor Alexios I Komnenos, after overthrowing Nikephoros III, made Nikephoros Diogenes '' doux'' of Crete. Nikephoros conspired against him in 1094, involving numerous confidants and relatives of Alexios, including Alexios' brother, Adrianos. For this conspiracy, he was blinded, in accordance with Byzantine traditions. After this, he retired to his estates, and spent the last years of his life studying classical literature. History Nikephoros was born 1069 to Romanos IV Diogenes and Eudokia Makrembolitissa, who married and were crowned on 1 January 1068. Nikephoros was presumably elevated to junior emperor shortly after alongside his brother (and possibly twin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas
Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas, Latinized as Nicephorus I Comnenus Ducas (; – ) was ruler of Epirus from 1267/8 to his death in 1296/98. Life Born around 1240, Nikephoros was the eldest son of the Despot of Epirus, Michael II Komnenos Doukas, and Theodora Petraliphaina. In , at Pegai, Nikephoros was betrothed to Maria Laskaris Vatatzaina, the daughter of Theodore II Laskaris and granddaughter of the Nicaean emperor John III Doukas Vatatzes, who conferred on him the dignity of . The marriage took place at Thessalonica in October 1256, but Maria died in 1258. In the following years Nikephoros was engaged in his father's struggle against Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos and together with his father retreated before the Battle of Pelagonia. After the Nicaeans overran most of Epirus in 1259, Nikephoros left for the Italian Peninsula, where he received reinforcements from his brother-in-law King Manfred of Sicily. With this support Nikephoros helped his father reconquer Epirus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicephorus Of Antioch
Nikephoros (), Nikiforos or Nicephorus is a Greek male name, meaning "Bringer of Victory", which was commonly used among the Byzantine Empire's aristocracy. It may refer to: Rulers * Nikephoros I Logothetes, Byzantine emperor 802–811 * Nikephoros II Phokas, Byzantine emperor 963–969 * Nikephoros III Botaneiates, Byzantine emperor 1078–1081 * Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas, despot of Epirus 1267–1297 * Nikephoros II Orsini, ruler of Epirus 1335–1338 and 1356–1359 Ecclesiastical leaders * Nicephorus I of Constantinople, Byzantine writer and patriarch, 758–828, author of the ''Stichometry'' and other works * Nicephorus II of Constantinople, patriarch in exile at Nicaea * Nicephorus of Antioch, Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Antioch, 1084–1090 * Nicephorus II of Kiev, Metropolitan of Kyiv and all Ruthenia, 1183–1198 * Patriarch Nicephorus of Alexandria, Orthodox Patriarch of Alexandria between 1639 and 1645 * Nikiforos of Didymoteicho, Metropolitan of Didymoteicho i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicephorus II Of Constantinople
Nikephoros (), Nikiforos or Nicephorus is a Greek male name, meaning "Bringer of Victory", which was commonly used among the Byzantine Empire's aristocracy. It may refer to: Rulers * Nikephoros I Logothetes, Byzantine emperor 802–811 * Nikephoros II Phokas, Byzantine emperor 963–969 * Nikephoros III Botaneiates, Byzantine emperor 1078–1081 * Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas, despot of Epirus 1267–1297 * Nikephoros II Orsini, ruler of Epirus 1335–1338 and 1356–1359 Ecclesiastical leaders * Nicephorus I of Constantinople, Byzantine writer and patriarch, 758–828, author of the ''Stichometry'' and other works * Nicephorus II of Constantinople, patriarch in exile at Nicaea * Nicephorus of Antioch, Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Antioch, 1084–1090 * Nicephorus II of Kiev, Metropolitan of Kyiv and all Ruthenia, 1183–1198 * Patriarch Nicephorus of Alexandria, Orthodox Patriarch of Alexandria between 1639 and 1645 * Nikiforos of Didymoteicho, Metropolitan of Didymotei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros Komnenos
Nikephoros Komnenos (, ''Nikēphoros Komnēnos''; – after 1026/7) was a Byzantine military leader under the emperors Basil II () and Constantine VIII (). He served as governor of the Armenian region of Vaspurakan, and is one of the first known members of the Komnenos family, which came to rule the Byzantine Empire in 1081–1185. Biography Nikephoros Komnenos is one of the first documented members of the Komnenos family, but nothing is known of his early life or his connection to the main branch of the family, which eventually gave rise to the imperial dynasty. The Greek scholar Konstantinos Varzos suggested that he was born , and that he was the younger brother of the Komnenian dynasty's patriarch, Manuel Erotikos Komnenos, but neither assumption can be verified. Nikephoros is first mentioned in the historical record in , shortly after the King of Vaspurakan, Senekerim-Hovhannes (), unable to resist the pressure of his Muslim neighbours, surrendered his kingdom to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros Basilakes
Nikephoros Basilakes (), frequently encountered simply as Basilakios (Βασιλάκιος), Latinized as Nicephorus Basilacius, was a Byzantine general and aristocrat of the late 11th century, who in 1078 tried to overthrow the Emperor Nikephoros III Botaneiates and was defeated by Alexios Komnenos. Nikephoros is described as the most illustrious member of his family. His father was named Phloros, and his brother was Manuel Basilakes. During the campaigns of Emperor Romanos IV Diogenes preceding the Battle of Mantzikert, Nikephoros Basilakes served as '' doux'' of Theodosioupolis, and was captured by the enemy after pursuing a retreating Turkish band too far, in 1068. Under Michael VII Doukas, Nikephoros Basilakes was posted to Paphlagonia and subsequently made ''doux'' of Dyrrachion. In the collapse of the regime of Michael VII Doukas, Nikephoros Basilakes, still ''doux'' of Dyrrachion, began to plan a revolt as early as the summer of 1077, initially as a supporter of Nik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros Theotokis
Nikephoros Theotokis or Nikiforos Theotokis (; or Никифор Феотокис; 1731–1800) was a Greek scholar and theologian, who became an archbishop in the southern provinces of the Russian Empire. A polymath, he is respected by the Greek Orthodox church as one of the "teachers of the nation". Life and work in Greece and Western Europe Born in the Greek Island of Corfu (then a possession of Republic of Venice), Nikephoros studied in Italian universities of Bologna and Padua. In 1748, he returned to Corfu to join the Church as a monk, reaching the rank of hieromonk in 1754. However, he was more interested in educating the youth of his country than in church services, and by 1758 he was able to set up his own school in Corfu, the first school on the island where a range of subjects were taught: Greek and Italian literature, grammar, geography, rhetorics, physics and mathematics, philosophy. He acquired some renown as a preacher at the local church of John the Baptist an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
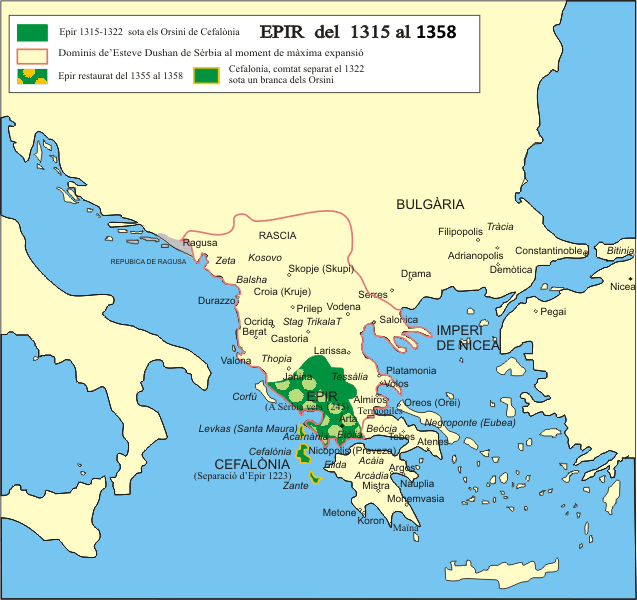
Nikephoros II Orsini
Nikephoros II Orsini Doukas (Greek: Νικηφόρος Β΄ Δούκας, ''Nikēphoros II Doukas''), was the ruler of Epirus from 1335 to 1338 and from 1356 until his death in 1359. Life Nikephoros was the son of John Orsini of Epirus and Anna Palaiologina. When his mother allegedly poisoned his father in 1335, Nikephoros II succeeded as a 7-year-old child. His mother Anna assumed the regency for her young son but failed to allay the enmity of the Byzantine Emperor Andronikos III Palaiologos, who invaded and annexed the Epirote part of Thessaly in 1336 and advanced on Ioannina. The Albanians took advantage of conflict to the south to raid the Byzantine possessions in the north, but were defeated by the emperor in 1337. Andronikos summoned Anna to negotiate in 1338 but refused to accept her son as Byzantine vassal and installed his governors in Epirus. Keeping Anna as hostage, Andronikos arranged for the marriage between Nikephoros and Maria Kantakouzene, the daughter of his r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |