|
Nikephorian Dynasty
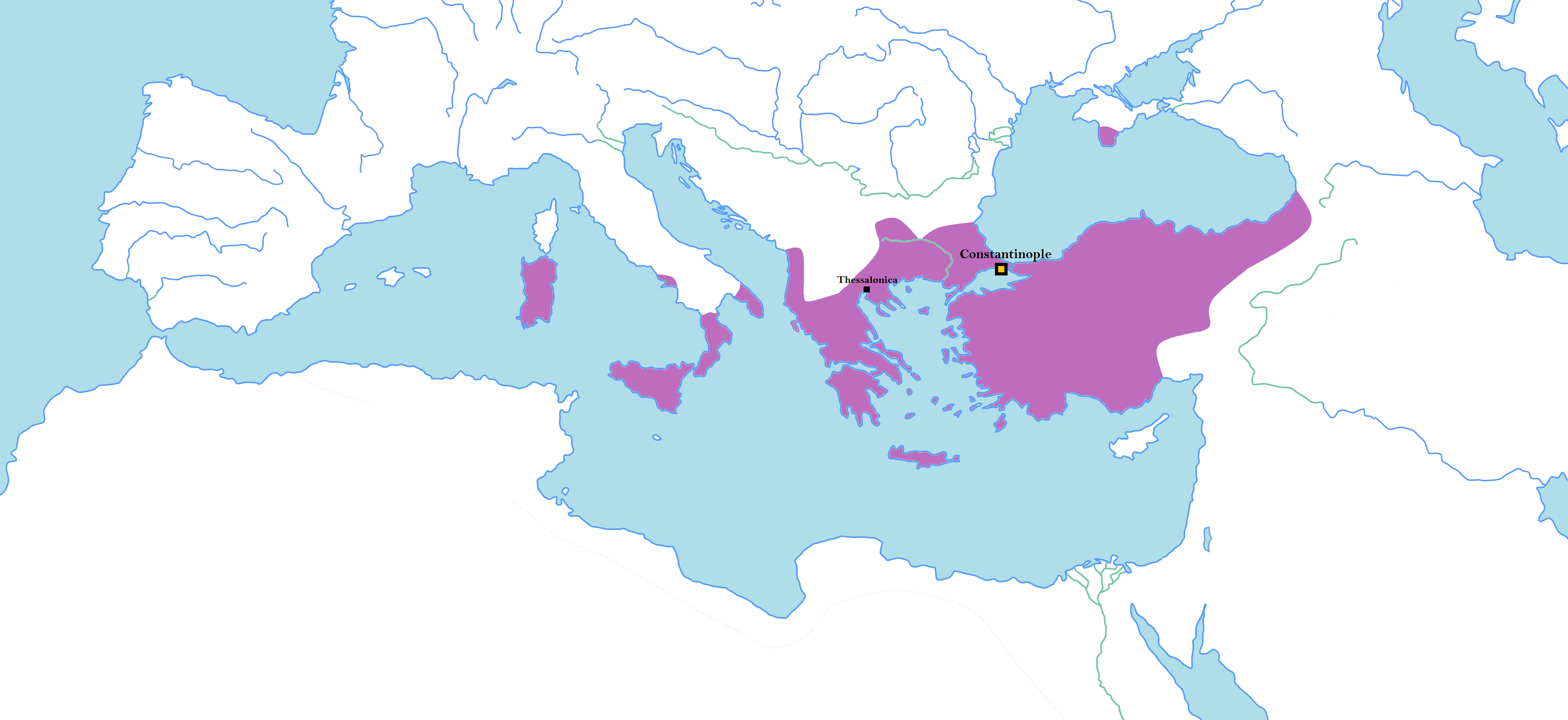
Following the deposition of the Byzantine empress Irene of Athens, the throne of the Byzantine Empire passed to a relatively short-lived dynasty, the Nikephorian dynasty, named after its founder, Nikephoros I. The empire was in a weaker and more precarious position than it had been for a long time and its finances were problematic.Jenkins. Byzantium The Imperial Centuries AD 610-1071. p. 117 During this era Byzantium was almost continually at war on two frontiers which drained its resources, and like many of his predecessors, Nikephoros (802–811) himself died while campaigning against the Bulgars to the north. Furthermore, Byzantium's influence continued to wane in the west with the crowning of Charlemagne (800–814) as Holy Roman emperor by Pope Leo III at Old St. Peter's Basilica in Rome in the year 800 and the establishment of a new empire in Western Europe laying claim to the universal Roman monarchy. Nikephoros I, 802–811 Nikephoros I had been the empire's finance mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros I
Nikephoros I or Nicephorus I ( gr, Νικηφόρος; 750 – 26 July 811) was Byzantine emperor from 802 to 811. Having served Empress Irene as '' genikos logothetēs'', he subsequently ousted her from power and took the throne himself. In reference to his career before becoming emperor, he is sometimes surnamed "the Logothete" (ὁ Λογοθέτης) and "Genikos" or "Genicus" (ὁ Γενικός). Nikephoros pursued wars against the Arabs and Bulgarians, with mixed results; while invading Bulgaria he was defeated and killed at the Battle of Pliska. Background Sources outside the Byzantine context, including Michael the Syrian, al-Tabari, and Mas'udi, preserve the tradition that Nikephoros was of Ghassanid Arab origin. al-Tabari claims that he derived this information from Byzantine sources, but no surviving Byzantine chronicle makes explicit mention of the emperor's ethnic background. The modern scholar Paul Julius Alexander suggests that al-Tabari did transmit informat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khan (title)
Khan ''khan/qan''; tr, han; Azerbaijani: ''xan''; Ottoman: ''han''; Old Turkic: ''kan''; Chinese: 汗 ''hán''; Goguryeo: 皆 ''key''; Buyeo: 加 ''ka''; Silla: 干 ''kan''; Gaya: 旱 ''kan''; Baekje: 瑕 ''ke''; Manchu: ; Persian: خان; Punjabi: ਖ਼ਾਨ; Hindustani: ख़ान or ख़ां (Devanagari), or (Nastaleeq); Balochi: خان; Bulgarian: хан, ''khan''; Chuvash: хун, ''hun''; Arabic: خان; bn, খান or ) () is a historic Turko-Mongol title originating among nomadic tribes in the Central and Eastern Eurasian Steppe to refer to a chief or ruler. It first appears among the Rouran and then the Göktürks as a variant of khagan (sovereign, emperor) and implied a subordinate ruler. In the Seljuk Empire, it was the highest noble title, ranking above malik (king) and emir (prince). In the Mongol Empire it signified the ruler of a horde (''ulus''), while the ruler of all the Mongols was the khagan or great khan. The title subsequently de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thekla, Wife Of Michael II
Thekla (Θέκλα; died c. 823) was the first Empress consort of Michael II of the Byzantine Empire. Family According to Theophanes the Confessor, Thekla was the daughter of an unnamed '' strategos'' of the Anatolic Theme, where Michael served. On this account, her father has been identified with the general and later rebel Bardanes Tourkos. Michael, along with Leo the Armenian and Thomas the Slav, were close associates of Bardanes, although during his revolt in summer 803, both Michael and Leo deserted him. Thekla and Michael had only one known son, the Emperor Theophilos (813 – 20 January 842). The existence of a daughter called Helena is possible but there is a contradiction between different sources. Helena is known as the wife of Theophobos, a patrician executed in 842 for conspiring to gain the throne for himself. George Hamartolus and Theophanes report him marrying the sister of the Empress Theodora. Joseph Genesius records Theophobos marrying the sister of the Empe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire Under The Amorian Dynasty
The Byzantine Empire was ruled by the Amorian or Phrygian dynasty from 820 to 867. The Amorian dynasty continued the policy of restored iconoclasm (the "Second Iconoclasm") started by the previous non-dynastic emperor Leo V in 813, until its abolition by Empress Theodora with the help of Patriarch Methodios in 842. The continued iconoclasm further worsened relations between the East and the West, which were already bad following the papal coronations of a rival line of " Roman Emperors" beginning with Charlemagne in 800. Relations worsened even further during the so-called Photian Schism, when Pope Nicholas I challenged Photios' elevation to the patriarchate. However, the era also saw a revival in intellectual activity which was marked by the end of iconoclasm under Michael III, which contributed to the upcoming Macedonian Renaissance. During the Second Iconoclasm, the Empire began to see systems resembling feudalism being put in place, with large and local landholders becoming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael II
Michael II ( gr, Μιχαὴλ, , translit=Michaēl; 770–829), called the Amorian ( gr, ὁ ἐξ Ἀμορίου, ho ex Amoríou) and the Stammerer (, ''ho Travlós'' or , ''ho Psellós''), reigned as Byzantine Emperor from 25 December 820 to his death on 2 October 829, the first ruler of the Amorian dynasty. Born in Amorium, Michael was a soldier, rising to high rank along with his colleague Leo V the Armenian ( 813–820). He helped Leo overthrow and take the place of Emperor Michael I Rangabe. However, after they fell out Leo sentenced Michael to death. Michael then masterminded a conspiracy which resulted in Leo's assassination at Christmas in 820. Immediately he faced the long revolt of Thomas the Slav, which almost cost him his throne and was not completely quelled until spring 824. The later years of his reign were marked by two major military disasters that had long-term effects: the beginning of the Muslim conquest of Sicily, and the loss of Crete to the Saracens. Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrosyne (9th Century)
Euphrosyne (Greek: Εὐφροσύνη; 790 – after 836), was a Byzantine empress by marriage to Michael II. She was a daughter of Byzantine emperor Constantine VI, the last representative of the Isaurian dynasty, and his empress Maria of Amnia. Life In January, 795, Constantine divorced Maria and sent her along with Euphrosyne and her sister Irene to a convent on the island of Prinkipo. The Emperor then proceeded to marry his mistress Theodote. Euphrosyne spent her life in the monastery until c. 823. Michael II had risen to the throne three years before but his dynastic claims were at best shaky. His first wife Thekla died early in the reign and he decided to strengthen his claim by marrying Euphrosyne. She was thus taken from her convent and entered the court as the new empress, but the highly controversial marriage proved barren. Michael II died on 2 October 829 and was succeeded by Theophilos, his son with Tekla. As his stepmother, Euphrosyne was still able to take so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bardanes Tourkos
Bardanes, nicknamed ''Tourkos'', "the Turk" ( gr, Βαρδάνης ὁ Τοῦρκος, Bardanēs ho Tourkos, ), was a Byzantine general of Armenian origin who launched an unsuccessful rebellion against Emperor Nikephoros I () in 803. Although a major supporter of Byzantine empress Irene of Athens (), soon after her overthrow he was appointed by Nikephoros as commander-in-chief of the Anatolian armies. From this position, he launched a revolt in July 803, probably in opposition to Nikephoros's economic and religious policies. His troops marched towards Constantinople, but failed to win popular support. At this point, some of his major supporters deserted him and, reluctant to engage the loyalist forces in battle, Bardanes gave up and chose to surrender himself. He retired as a monk to a monastery he had founded. There he was blinded, possibly on Nikephoros's orders. Origin and early career Nothing is known of the early life of Bardanes. He is usually regarded by modern scholars a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Of Amnia
Maria of Amnia (Greek: Μαρία, 770 – after 823) was a Byzantine empress, the first wife of Constantine VI. She was a granddaughter of Saint Philaretos,Leslie Brubaker, Julia M. H. Smith (2004). ''Gender in the Early Medieval World: East and West, 300-900''. „''The bride show described in this saint's life is the one which resulred in the marriage of Philareros' granddaughrer, Maria of Amnia, to Constantine VI, the son of the empress Eirene, in 788''.” a magnate from the Armeniakon Theme known for his charitable activities, a relation mentioned in his hagiography. The name of her father is unknown and her mother has been identified as Hypatia by Christian Settipani. Maria was born in Amnia, Paphlagonia. Empress In 788, Maria was one of thirteen candidates in the earliest recorded bride-show. The bride-show had been ordered by the Empress-regent Irene in search of a suitable bride for her son Constantine VI. Constantine was previously betrothed to Rotrude, daughter of Charl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine VI
Constantine VI ( gr, Κωνσταντῖνος, ''Kōnstantinos''; 14 January 771 – before 805Cutler & Hollingsworth (1991), pp. 501–502) was Byzantine emperor from 780 to 797. The only child of Emperor Leo IV, Constantine was named co-emperor with him at the age of five in 776 and succeeded him as sole Emperor in 780, aged nine. His mother Irene exercised control over him as regent until 790, assisted by her chief minister Staurakios. The regency ended when Constantine reached maturity, but Irene sought to remain an active participant in the government. After a brief interval of sole rule Constantine named his mother empress in 792, making her his official colleague. Constantine suffered military defeats and made controversial decisions, such as blinding his loyal general Alexios Mosele and illicitly marrying his mistress, Theodote. Taking advantage of her son's unpopularity, Irene had Constantine deposed, blinded and imprisoned in 797 and seized power for herself alone, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophano Of Athens
Theophano ( gr, Θεοφανώ; died after 811) was the Empress consort of Staurakios of the Byzantine Empire. According to the chronicle of Theophanes the Confessor, Theophano was a relative of Irene (reigned 797–802). Both women were from Athens but the nature of their relation to each other is not known. On 20 December 807, Theophano married Staurakios. The date of their marriage was recorded by Theophanes. Staurakios was the only known son of Nikephoros I. He was co-emperor with his father since 803. Theophano had been betrothed to another man but took place in the imperial bride-show. She was possibly chosen to legitimise the connection of the new dynasty to their predecessor. Her father-in-law is presumed to have been a widower by the time he was elevated to the throne. In the absence of a senior empress, Theophano was the only Empress during his reign. On 26 July 811, Nikephoros was killed while fighting against Krum of Bulgaria at the Battle of Pliska. Much of the Byzant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo IV The Khazar
Leo IV the Khazar (Greek: Λέων ὁ Χάζαρος, ''Leōn IV ho Khazaros''; 25 January 750 – 8 September 780) was Byzantine emperor from 775 to 780 AD. He was born to Emperor Constantine V and Empress Tzitzak in 750. He was elevated to co-emperor on the next year, in 751, and married to Irene of Athens in 768. When Constantine V died in September 775, while campaigning against the Bulgarians, Leo IV became senior emperor. In 778 Leo raided Abbasid Syria, decisively defeating the Abbasid army outside of Germanicia. Leo died on 8 September 780, of tuberculosis. He was succeeded by his underage son Constantine VI, with Irene serving as regent. History Leo IV was born on 25 January 750AD, to Emperor Constantine V and his first wife, Empress Tzitzak. Because his mother was a Khazar, Leo was given the epithet 'the Khazar'. Leo was elevated to co-emperor in 751, while still an infant. He became emperor on 14 September 775, after Constantine V died while campaigning against the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tzitzak
:''This individual is sometimes confused with Byzantine Empress Irene, who was her daughter-in-law.'' Tzitzak ( el, Τζιτζάκ) (died 750), baptised Irene ( el, Εἰρήνη), was a Khazar princess, the daughter of ''khagan'' Bihar, who became empress by marriage to Eastern Roman Emperor Constantine V (r. 741–775). Etymology According to Gyula Moravcsik, ''Tzitzak'' is most likely a Hellenized version of a Turkic word descending from Proto-Turkic * and cognate with Chuvash and Turkish , all meaning 'flower'. However, Marcel Erdal notes that Constantine VII used ''tzitzak'' to denote the empress's garment and deems Moravcsik's idea that Tzitzak was her personal name "far-fetched". Therefore, Erdal thinks that ''tzitzak'' more likely described the colourfulness of the empress's garment; Erdal additionally reminds readers of Hebrew ṣiṣiṯ 'fringed Jewish ceremonial shawl' and 'fringes'.Erdal, Marcel, "The Khazar Language" in ''The World of the Khazars''. Brill, 2007 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |