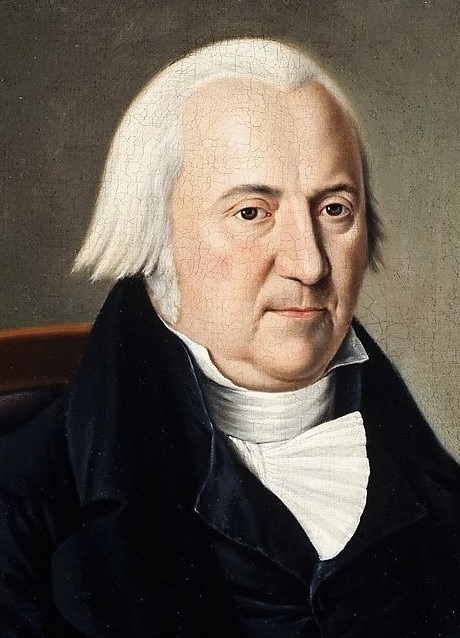|
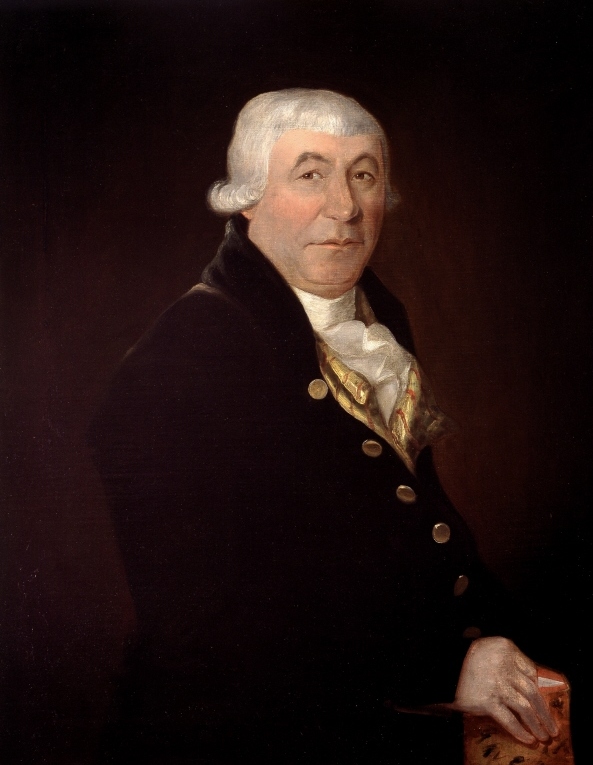
Nicolas Saint-Martin
Nicolas Saint-Martin (August 10, 1753 – July 12, 1823) was a militia officer and political figure in Lower Canada. He is sometimes also referred to as Nicolas de Saint-Martin or Nicolas Gorge de Saint-Martin. He was born Jacques-Nicolas Saint-Martin at Trois-Rivières in 1753, the son of a captain in the French navy who took part in the defence of Quebec City. Saint-Martin volunteered to serve in the British Army during the American invasion of 1775–6. He retired on half pay in 1783. In 1784, he married Marie-Louise, the daughter of seigneur Louis-Joseph Godefroy de Tonnancour. He was named justice of the peace for the Trois-Rivières district in 1790 and was also served as commissioner for various public works projects in the region. He was elected to the 1st Parliament of Lower Canada for Trois-Rivières in 1792. Saint-Martin joined the local militia, becoming lieutenant-colonel in 1812, and served during the War of 1812 The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 Februar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada (french: province du Bas-Canada) was a British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence (1791–1841). It covered the southern portion of the current Province of Quebec and the Labrador region of the current Province of Newfoundland and Labrador (until the Labrador region was transferred to Newfoundland in 1809). Lower Canada consisted of part of the former colony of Canada of New France, conquered by Great Britain in the Seven Years' War ending in 1763 (also called the French and Indian War in the United States). Other parts of New France conquered by Britain became the Colonies of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island. The Province of Lower Canada was created by the ''Constitutional Act 1791'' from the partition of the British colony of the Province of Quebec (1763–1791) into the Province of Lower Canada and the Province of Upper Canada. The prefix "lower" in its name refers to its geog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamachiche, Quebec
Yamachiche () is a municipality in the Mauricie region of the province of Quebec in Canada. Etymology The name Yamachiche was first used to identify the Little Yamachiche River (''Petite rivière Yamachiche'') which runs through the town. It came from the First Nations (possibly Cree) words ''iyamitaw'' (meaning "much") and ''achichki'' (meaning "mud"). Therefore Yamachiche could have the general meaning of "muddy river", which is a characteristic of this stream. In Abenaki, it was identified as ''Namasis'' (small fish) and ''Obamasis'' (small white fish). The name has gone through many spelling variations: Machiche, Ouabmachiche, Yabamachiche, Hyamachiche, Yamachiste, Amachis, à Machis, à Mashis, Machis, Augmachiche, Ouamachiche, Yabmachiche, etc., which have mainly affected the name of the river, whereas the parish and municipal names have remained more stable. History In 1653, the area was part of a fief granted to Pierre Boucher de Grosbois, Governor of Trois-Rivières, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1753 Births
Events January–March * January 3 – King Binnya Dala of the Hanthawaddy Kingdom orders the burning of Ava, the former capital of the Kingdom of Burma. * January 29 – After a month's absence, Elizabeth Canning returns to her mother's home in London and claims that she was abducted; the following criminal trial causes an uproar. * February 17 – The concept of electrical telegraphy is first published in the form of a letter to ''Scots' Magazine'' from a writer who identifies himself only as "C.M.". Titled "An Expeditious Method of Conveying Intelligence", C.M. suggests that static electricity (generated by 1753 from "frictional machines") could send electric signals across wires to a receiver. Rather than the dot and dash system later used by Samuel F.B. Morse, C.M. proposes that "a set of wires equal in number to the letters of the alphabet, be extended horizontally between two given places" and that on the receiving side, "Let a ball be suspende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre-Amable De Bonne
Pierre-Amable de Bonne (November 25, 1758 – September 6, 1816) was a seigneur, lawyer, judge and political figure in Lower Canada. He was born in Montreal in 1758, the son of Louis de Bonne de Missègle (1717-1760), Chevalier de Saint-Louis, and studied at a college operated by the Sulpicians, then the Collège Saint-Raphaël and the Petit Séminaire de Québec. He served in the militia defending the town of Quebec during the siege by the Americans in 1775–6. He participated in the campaign at Lake Champlain, becoming lieutenant, and was taken prisoner in 1777 at the Battle of Saratoga. De Bonne continued to serve in the militia after this time, becoming colonel in 1809. He studied law at Montreal and qualified as a lawyer and notary in 1780. De Bonne inherited the seigneury of Sault-Sainte-Marie from his father; he acquired additional properties over the years. In 1781, he married Louise, daughter of Michel Chartier de Lotbinière; they separated by mutual consent in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Château Clique
The Château Clique, or Clique du Château, was a group of wealthy families in Lower Canada in the early 19th century. They were the Lower Canadian equivalent of the Family Compact in Upper Canada. They were also known on the electoral scene as the Parti bureaucrate (Bureaucratic Party, also known as the British Party or the Tory Party). Like the Family Compact, the Château Clique gained most of its influence after the War of 1812. Most of its families were British merchants, but some were French Canadian seigneurs who felt that their own interests were best served by an affiliation with this group. Some of the most prominent members were brewer John Molson and James McGill, the founder of McGill University. Generally, they wanted the French Canadian majority of Lower Canada to assimilate to English culture. That included the abolition of the seigneurial system, replacing French civil law with British common law, and replacing the established Roman Catholic Church with the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Lees (politician)
John Lees (ca 1740 – March 4, 1807) was a businessman, judge and political figure in Lower Canada. He was born in Scotland around 1740 and came to the town of Quebec with his family around 1761. With Alexander Dawson, he formed a company in 1773 that was involved in importing goods and supplying the British Army; they also speculated in land. In 1774, he signed a petition requesting a legislative assembly for the province. Lees served in the militia during the siege of the town by the American army during the American Revolution. In 1787, his company acquired the lease for the Saint-Maurice ironworks at Trois-Rivières. In 1792, Lees was elected to the Legislative Assembly of Lower Canada for Trois-Rivières; he was reelected in 1796, 1800 and 1804. He was also an honorary member of the Executive Committee from 1794 to 1804, becoming an active member in 1804 and serving until his death. He was named storekeeper general for the Department of Indian Affairs at Lachine and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trois-Rivières (Lower Canada)
Trois-Rivières (, – 'Three Rivers') is a city in the Mauricie administrative region of Quebec, Canada, at the confluence of the Saint-Maurice and Saint Lawrence rivers, on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River across from the city of Bécancour. It is part of the densely populated Quebec City–Windsor Corridor and is approximately halfway between Montreal and Quebec City. Trois-Rivières is the economic and cultural hub of the Mauricie region. The settlement was founded by French colonists on July 4, 1634, as the second permanent settlement in New France, after Quebec City in 1608. The city's name, which is French for 'three rivers', is named for the fact the Saint-Maurice River has three mouths at the Saint Lawrence River; it is divided by two islands in the river. Historically, in English this city was once known as Three Rivers. Since the late 20th century, when there has been more recognition of Quebec and French speakers, the city has generally been referred to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legislative Assembly Of Lower Canada
The Legislative Assembly of Lower Canada was the lower house of the bicameral structure of provincial government in Lower Canada until 1838. The legislative assembly was created by the Constitutional Act of 1791. The lower house consisted of elected legislative councilors who created bills to be passed up to the Legislative Council of Lower Canada, whose members were appointed by the governor general. Following the Lower Canada Rebellion, the lower house was dissolved on March 27, 1838, and Lower Canada was administered by an appointed Special Council. With the Act of Union in 1840, a new lower chamber, the Legislative Assembly of Canada, was created for both Upper and Lower Canada which existed until 1867, when the Legislative Assembly of Quebec was created. Speaker of the House of Assembly of Lower Canada * Jean-Antoine Panet 1792–1794 * Michel-Eustache-Gaspard-Alain Chartier de Lotbinière 1794–1796 * Jean-Antoine Panet 1797-1814 * Louis-Joseph Papineau 1815–182 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It began when the United States declared war on 18 June 1812 and, although peace terms were agreed upon in the December 1814 Treaty of Ghent, did not officially end until the peace treaty was ratified by Congress on 17 February 1815. Tensions originated in long-standing differences over territorial expansion in North America and British support for Native American tribes who opposed US colonial settlement in the Northwest Territory. These escalated in 1807 after the Royal Navy began enforcing tighter restrictions on American trade with France and press-ganged men they claimed as British subjects, even those with American citizenship certificates. Opinion in the US was split on how to respond, and although majorities in both the House and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trois-Rivières
Trois-Rivières (, – 'Three Rivers') is a city in the Mauricie administrative region of Quebec, Canada, at the confluence of the Saint-Maurice River, Saint-Maurice and Saint Lawrence River, Saint Lawrence rivers, on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River across from the city of Bécancour, Quebec, Bécancour. It is part of the densely populated Quebec City–Windsor Corridor and is approximately halfway between Montreal and Quebec City. Trois-Rivières is the economic and cultural hub of the Mauricie region. The settlement was founded by French colonists on July 4, 1634, as the second permanent settlement in New France, after Quebec City in 1608. The city's name, which is French for 'three rivers', is named for the fact the Saint-Maurice River has three mouths at the Saint Lawrence River; it is divided by two islands in the river. Historically, in English this city was once known as Three Rivers. Since the late 20th century, when there has been more recognition of Quebec a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Parliament Of Lower Canada
The 1st Parliament of Lower Canada was in session from December 17, 1792, to May 31, 1796. Elections for the Legislative Assembly in Lower Canada had been held in June 1792. All sessions were held at Quebec City Quebec City ( or ; french: Ville de Québec), officially Québec (), is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Communauté métrop .... References External links ''Les députés au premier Parlement du Bas-Canada (1792-1796)'', F-J Audet (1946) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis-Joseph Godefroy De Tonnancour
Louis-Joseph may refer to: *Louis Joseph Bahin (1813-1857), American painter in the Antebellum South * Louis-Joseph de Montcalm (1712-1759), French military commander * Prince Louis-Joseph of France (1781-1789), son of Louis XVI of France * Louis-Joseph Papineau Louis-Joseph Papineau (October 7, 1786 – September 23, 1871), born in Montreal, Quebec, was a politician, lawyer, and the landlord of the ''seigneurie de la Petite-Nation''. He was the leader of the reformist Patriote movement before the Low ... (1786-1871), Canadian politician {{given name Compound given names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |