|
Nickel(IV) Organometallic Complex
Organonickel(IV) complex are organonickel compounds that feature nickel in the +4 oxidation state. These high-valent nickel compounds are intermediates or models thereof for various catalytic reactions. Representative preparation Ni(IV) complexes are typically supported by highly basic and chelating ligands. They are often produced by oxidation of related Ni(II) and Ni(III) complexes using both conventional and exotic oxidants, such as ferrocenium Ferrocenium tetrafluoroborate is an organometallic compound with the formula e(C5H5)2F4. This salt is composed of the cation e(C5H5)2sup>+ and the tetrafluoroborate anion (). The related hexafluorophosphate is also a popular reagent with simil ... and S-(trifluoromethyl)dibenzothiophenium triflate (Umemoto reagent). For example, one of the first isolated NiIV complexes that was used in a cross coupling transformation was reported by Linden and Dimitrov in 2003 and was prepared by simple air-induced oxidation of the following anio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organonickel
Organonickel chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic compounds featuring nickel-carbon bonds. They are used as a catalyst, as a building block in organic chemistry and in chemical vapor deposition. Organonickel compounds are also short-lived intermediates in organic reactions. The first organonickel compound was nickel tetracarbonyl Ni(CO)4, reported in 1890 and quickly applied in the Mond process for nickel purification. Organonickel complexes are prominent in numerous industrial processes including carbonylations, hydrocyanation, and the Shell higher olefin process. Classes of compounds : Alkyl and aryl complexes A popular reagent is Ni(CH3)2(tetramethylethylenediamine). Many alkyl and aryl complexes are known with the formula NiR(X)L2. Examples include dppf)Ni(cinnamyl)Cl) ''trans''-(PCy2Ph)2Ni(''o''-tolyl)Cl, (dppf)Ni(''o''-tolyl)Cl, (TMEDA)Ni(''o''-tolyl)Cl, and (TMEDA)NiMe2. Nickel compounds of the type NiR2 also exist with just 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation State
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. Conceptually, the oxidation state may be positive, negative or zero. While fully ionic bonds are not found in nature, many bonds exhibit strong ionicity, making oxidation state a useful predictor of charge. The oxidation state of an atom does not represent the "real" formal charge on that atom, or any other actual atomic property. This is particularly true of high oxidation states, where the ionization energy required to produce a multiply positive ion is far greater than the energies available in chemical reactions. Additionally, the oxidation states of atoms in a given compound may vary depending on the choice of electronegativity scale used in their calculation. Thus, the oxidation state of an atom in a compound is purely a formalism. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferrocenium
Ferrocenium tetrafluoroborate is an organometallic compound with the formula e(C5H5)2F4. This salt is composed of the cation e(C5H5)2sup>+ and the tetrafluoroborate anion (). The related hexafluorophosphate is also a popular reagent with similar properties. The cation is often abbreviated Fc+ or Cp2Fe+. The salt is deep blue in color and paramagnetic. Ferrocenium salts are sometimes used as one-electron oxidizing agents, and the reduced product, ferrocene, is inert and readily separated from ionic products. The ferrocene–ferrocenium couple is often used as a reference in electrochemistry. The standard potential of ferrocene-ferrocenium is 0.400 V vs. the normal hydrogen electrode (NHE) and is often assumed to be invariant between different solvents. Preparation Commercially available, this compound may be prepared by oxidizing ferrocene typically with ferric salts followed by addition of fluoroboric acid. A variety of other oxidants work well also, such as nitrosyl tetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
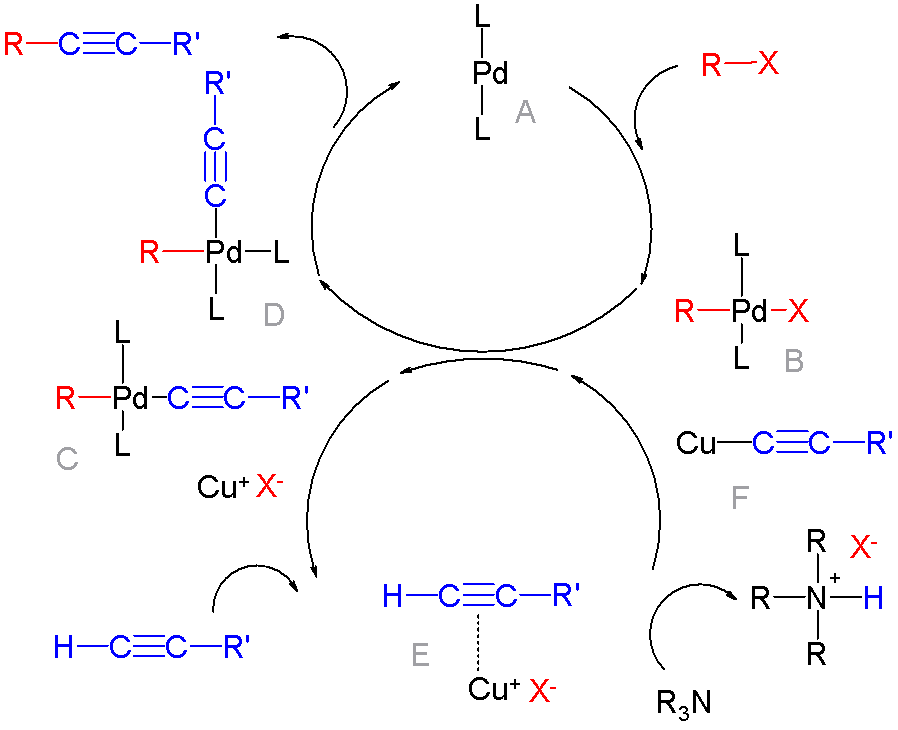
Cross-coupling Reaction
In organic chemistry, a cross-coupling reaction is a reaction where two fragments are joined together with the aid of a metal catalyst. In one important reaction type, a main group organometallic compound of the type R-M (R = organic fragment, M = main group center) reacts with an organic halide of the type R'-X with formation of a new carbon–carbon bond in the product R-R'. Cross-coupling reaction are a subset of coupling reactions. It is often used in arylations. Richard F. Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki were awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions. Mechanism The mechanism generally involves reductive elimination of the organic substituents R and R' on a metal complex of the type LnMR(R') (where L is some arbitrary spectator ligand). The crucial intermediate LnMR(R') is formed in a two step process from a low valence precursor Ln. The oxidative addition of an organic halide (RX) to LnM gives LnMR(X). Subsequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linden And Dimitrov Ni(II) To Ni(IV)
Linden may refer to: Trees * ''Tilia'' (also known as lime and basswood Basswood), a genus ** American linden, a common name for ''Tilia americana'' ** Large-leaved linden, a common name for ''Tilia platyphyllos'' ** Little-leaf linden, a common name for ''Tilia cordata'' ** Silver linden, a common name for ''Tilia tomentosa'' * Viburnum linden, a common name for '' Viburnum dilatatum'' Places Australia * Linden, New South Wales, a village in the Blue Mountains * Linden, Queensland, a rural locality * Linden, Western Australia, a ghost town in the goldfields of Western Australia Canada * Linden, Alberta, a village * Linden, Nova Scotia Germany * Linden, Hanover, a quarter in the district of Hanover, Lower Saxony * Linden, Hesse, a town in the district of Gießen, Hessen * Linden, Kaiserslautern, a municipality in the district of Kaiserslautern, Rhineland-Palatinate * Linden, Schleswig-Holstein, a municipality in the district Dithmarschen, Schleswig-Holstein * Linden, Wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trispyrazolylborate
In inorganic chemistry, the trispyrazolylborate ligand, abbreviated Tp−, is an anionic tridentate and tripodal ligand. Trispyrazolylborate refers specifically to the anion B(C3N2H3)3sup>−, but the term trispyrazolylborate refers to derivatives substituted at on the pyrazolyl rings. This family of compounds are sometimes called scorpionate ligands. Tp ligands As suggested by the resonance structures, the nitrogen centers that are not bonded to boron are basic. These centers bind to three adjacent sites of a metal such that the simple adducts have C3v symmetry. The facial bonding mode is reminiscent of cyclopentadienyl ligands, although the ligand field stabilization energy of Tp− is weaker as indicated by the fact that Fe(Tp)2 is a spin-crossover complex whereas ferrocene is low-spin. The Tp ligands are usually prepared from the reaction of pyrazole with potassium borohydride: :KBH4 + 3 C3H3N2H → K B(C3N2H3)3 + 3H2 Intermediates include the monopyrazolylborate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanford Ni(IV) 2015
Sanford may refer to: People * Sanford (given name), including a list of people with the name * Sanford (surname), including a list of people with the name Places United States * Sanford, Alabama, a town in Covington County * Sanford, Colorado, a statutory town in Conejos County * Sanford, Florida, the county seat of Seminole County ** Orlando Sanford International Airport, in Sanford, Floria * Sanford, Georgia, an unincorporated community * Sanford, Kansas, an unincorporated community in Pawnee County * Sanford, Maine, a city in York County ** Sanford (CDP), Maine, a former census-designated place in downtown Sanford * Sanford, Michigan, a village in Midland County * Sanford, Mississippi, an unincorporated community in Covington County * Sanford, New York, a town in Broome County * Sanford, North Carolina, a city in Lee County * Sanford, Texas, a town in Hutchinson County * Sanford, Virginia, a census-designated place in Accomack County * Mount Sanford (Alaska), a shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trifluoromethylation
Trifluoromethylation in organic chemistry describes any organic reaction that introduces a trifluoromethyl group in an organic compound. Trifluoromethylated compounds are of some importance in pharmaceutical industry and agrochemicals. Several notable pharmaceutical compounds have a trifluoromethyl group incorporated: fluoxetine, mefloquine, Leflunomide, nulitamide, dutasteride, bicalutamide, aprepitant, celecoxib, fipronil, fluazinam, penthiopyrad, picoxystrobin, fluridone, norflurazon, sorafenib and triflurazin. A relevant agrochemical is trifluralin. The development of synthetic methods for adding trifluoromethyl groups to chemical compounds is actively pursued in academic research. History The first to investigate trifluoromethyl groups in relationship to biological activity was F. Lehmann in 1927. An early review appeared in 1958. An early synthetic method was developed by Frédéric Swarts in 1892, based on antimony fluoride. In this reaction benzotrichloride was reacted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trifluoromethylation
Trifluoromethylation in organic chemistry describes any organic reaction that introduces a trifluoromethyl group in an organic compound. Trifluoromethylated compounds are of some importance in pharmaceutical industry and agrochemicals. Several notable pharmaceutical compounds have a trifluoromethyl group incorporated: fluoxetine, mefloquine, Leflunomide, nulitamide, dutasteride, bicalutamide, aprepitant, celecoxib, fipronil, fluazinam, penthiopyrad, picoxystrobin, fluridone, norflurazon, sorafenib and triflurazin. A relevant agrochemical is trifluralin. The development of synthetic methods for adding trifluoromethyl groups to chemical compounds is actively pursued in academic research. History The first to investigate trifluoromethyl groups in relationship to biological activity was F. Lehmann in 1927. An early review appeared in 1958. An early synthetic method was developed by Frédéric Swarts in 1892, based on antimony fluoride. In this reaction benzotrichloride was reacted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanford Catalytic Trifluoromethylation Of Arenes
Sanford may refer to: People * Sanford (given name), including a list of people with the name * Sanford (surname), including a list of people with the name Places United States * Sanford, Alabama, a town in Covington County * Sanford, Colorado, a statutory town in Conejos County * Sanford, Florida, the county seat of Seminole County ** Orlando Sanford International Airport, in Sanford, Floria * Sanford, Georgia, an unincorporated community * Sanford, Kansas, an unincorporated community in Pawnee County * Sanford, Maine, a city in York County ** Sanford (CDP), Maine, a former census-designated place in downtown Sanford * Sanford, Michigan, a village in Midland County * Sanford, Mississippi, an unincorporated community in Covington County * Sanford, New York, a town in Broome County * Sanford, North Carolina, a city in Lee County * Sanford, Texas, a town in Hutchinson County * Sanford, Virginia, a census-designated place in Accomack County * Mount Sanford (Alaska), a shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic Compounds
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide (metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term " metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_to_Ni(IV).png)