|
Ngāpuna
Ngapuna ( mi, Ngāpuna) is a suburb in eastern Rotorua in the Bay of Plenty Region of New Zealand's North Island. The New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage gives a translation of "the springs" for ''Ngāpuna''. The Rotorua Wastewater Treatment Plant is in Ngapuna. Marae The suburb has two marae. Ngāpuna or Hurunga o te Rangi Marae and meeting house is a meeting place for the Ngāti Whakaue hapū of Ngāti Hurunga Te Rangi and Ngāti Taeotu, and the Tūhourangi hapū of Hurunga Te Rangi and Ngāti Kahu Upoko. Hinemihi Marae and meeting house is a meeting place for the Tūhourangi hapū of Ngāti Hinemihi and Ngāti Tuohonoa), and the Ngāti Tarāwhai hapū of Ngāti Hinemihi. In October 2020, the Government committed $4,525,104 from the Provincial Growth Fund to upgrade the marae and nine other marae, creating an estimated 34 jobs. Demographics Ngapuna covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. Ngapuna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotorua
Rotorua () is a city in the Bay of Plenty region of New Zealand's North Island. The city lies on the southern shores of Lake Rotorua, from which it takes its name. It is the seat of the Rotorua Lakes District, a territorial authority encompassing Rotorua and several other nearby towns. Rotorua has an estimated resident population of , making it the country's 12th largest urban area, and the Bay of Plenty's second largest urban area behind Tauranga. Rotorua is a major destination for both domestic and international tourists; the tourism industry is by far the largest industry in the district. It is known for its geothermal activity, and features geysers – notably the Pōhutu Geyser at Whakarewarewa – and hot mud pools. This thermal activity is sourced to the Rotorua Caldera, in which the town lies. Rotorua is home to the Toi Ohomai Institute of Technology. History The name Rotorua comes from the Māori language, where the full name for the city and lake is . ''Roto'' m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lynmore
Lynmore is a suburb of Rotorua in the Bay of Plenty Region of New Zealand's North Island. In April 2018, Lynmore had the highest house prices in Rotorua. The local Apumoana Marae and Apumoana o te Ao Kohatu meeting house is meeting place for the Tūhourangi hapū of Hurunga Te Rangi, Ngāti Kahupoko, Ngāti Taeotu and Ngāti Tumatawera. Demographics Lynmore covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. Lynmore had a population of 3,288 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 33 people (1.0%) since the 2013 census, and an increase of 159 people (5.1%) since the 2006 census. There were 1,179 households, comprising 1,596 males and 1,692 females, giving a sex ratio of 0.94 males per female. The median age was 41.7 years (compared with 37.4 years nationally), with 693 people (21.1%) aged under 15 years, 492 (15.0%) aged 15 to 29, 1,590 (48.4%) aged 30 to 64, and 513 (15.6%) aged 65 or older. Ethnicities were 81.0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whakarewarewa
Whakarewarewa (reduced version of Te Whakarewarewatanga O Te Ope Taua A Wahiao, meaning ''The gathering place for the war parties of Wahiao'', often abbreviated to Whaka by locals) is a Rotorua semi-rural geothermal area in the Taupo Volcanic Zone of New Zealand. This was the site of the Māori fortress of Te Puia, first occupied around 1325, and known as an impenetrable stronghold never taken in battle. Māori have lived here ever since, taking full advantage of the geothermal activity in the valley for heating and cooking. Whakarewarewa has some 500 pools, most of which are alkaline chloride hot springs, and at least 65 geyser vents, each with their own name. Seven geysers are currently active. Pohutu Geyser, meaning big splash or explosion, erupts approximately hourly to heights of up to . Many of the thermal features at Whakarewarewa have been adversely affected by Rotorua residents taking advantage of the underlying geothermal fluids of the city by drawing shallow well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tūhourangi
Tūhourangi is a Māori iwi of New Zealand with a rohe centered on Lake Tarawera, Lake Rotomahana, Lake Okaro, Lake Okareka, Lake Rotokākahi, Lake Tikitapu and Lake Rotorua. They have 3 marae, Te Pakira Marae in Whakarewarewa, Hinemihi (Te Papatere-a-Rātorua) Marae in Ngāpuna and Tūhourangi Marae in Waitangi. Te Arawa FM is the radio station of Te Arawa iwi, including Tūhourangi, Ngāti Pikiao and Ngāti Whakaue. It was established in the early 1980s and became a charitable entity in November 1990. The station underwent a major transformation in 1993, becoming Whanau FM. One of the station's frequencies was taken over by Mai FM in 1998; the other became Pumanawa FM before later reverting to Te Arawa FM. It is available on in Rotorua. See also *List of Māori iwi This is a list of iwi (New Zealand Māori tribes). List of iwi This list includes groups recognised as iwi (tribes) in certain contexts. Many are also hapū (sub-tribes) of larger iwi. Moriori are included ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ōwhata
Ōwhata is a semi-rural suburb of Rotorua in the Bay of Plenty region of New Zealand's North Island. In 2015, it had the highest house sales of any suburb in Rotorua. The New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage gives a translation of "place of the elevated stage" for . Marae The local Ōwhata or Hinemoa Marae and is a meeting place for the Ngāti Whakaue hapū of Ngāti Korouateka and Ngāti te Roro o te Rangi. It includes the Tūtanekai meeting house. In October 2020, the Government committed $4,525,104 from the Provincial Growth Fund to upgrade the marae and nine others, creating an estimated 34 jobs. Demographics Ōwhata covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. Ōwhata had a population of 6,216 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 720 people (13.1%) since the 2013 census, and an increase of 777 people (14.3%) since the 2006 census. There were 2,022 households, comprising 2,991 males and 3,225 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Te Puni Kōkiri
Te Puni Kōkiri (TPK), the Ministry of Māori Development, is the principal policy advisor of the Government of New Zealand on Māori wellbeing and development. Te Puni Kōkiri was established under the Māori Development Act 1991 with responsibilities to promote Māori achievement in education, training and employment, health, and economic development; and monitor the provision of government services to Māori. The name means "a group moving forward together". History Protectorate Department (1840-1846) Te Puni Kōkiri, or the Ministry of Māori Development, traces its origins to the missionary-influenced Protectorate Department, which existed between 1840 and 1846. The Department was headed by the missionary and civil servant George Clarke, who held the position of Chief Protector. Its goal was to protect the rights of the Māori people in accordance with the Treaty of Waitangi. The Protectorate was also tasked with advising the Governor on matters relating to Māori and actin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
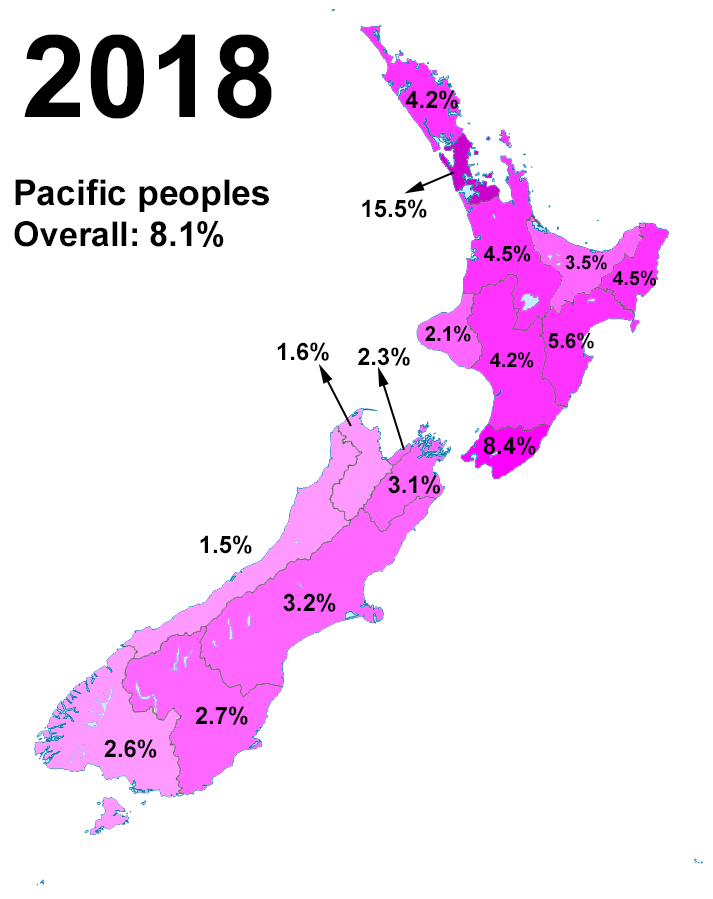
Pasifika New Zealanders
Pasifika New Zealanders are a pan-ethnic group of New Zealanders associated with, and descended from, the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands outside of New Zealand itself (also known as Pacific Islanders). They form the fourth-largest ethnic grouping in the country, after European-descended Pākehā, indigenous Māori, and Asian New Zealanders. There are over 380,000 Pasifika people in New Zealand, with the majority living in Auckland. 8% of the population of New Zealand identifies as being of Pacific origin. History Prior to the Second World War Pasifika in New Zealand numbered only a few hundred. Wide-scale Pasifika migration to New Zealand began in the 1950s and 1960s, typically from countries associated with the Commonwealth and the Realm of New Zealand, including Western Samoa (modern-day Samoa), the Cook Islands and Niue. In the 1970s, governments (both Labour and National), migration officials, and special police squads targeted Pasifika illegal overstayers. Paci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori People
The Māori (, ) are the indigenous Polynesian people of mainland New Zealand (). Māori originated with settlers from East Polynesia, who arrived in New Zealand in several waves of canoe voyages between roughly 1320 and 1350. Over several centuries in isolation, these settlers developed their own distinctive culture, whose language, mythology, crafts, and performing arts evolved independently from those of other eastern Polynesian cultures. Some early Māori moved to the Chatham Islands, where their descendants became New Zealand's other indigenous Polynesian ethnic group, the Moriori. Initial contact between Māori and Europeans, starting in the 18th century, ranged from beneficial trade to lethal violence; Māori actively adopted many technologies from the newcomers. With the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi in 1840, the two cultures coexisted for a generation. Rising tensions over disputed land sales led to conflict in the 1860s, and massive land confiscations, to which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pākehā
Pākehā (or Pakeha; ; ) is a Māori term for New Zealanders primarily of European descent. Pākehā is not a legal concept and has no definition under New Zealand law. The term can apply to fair-skinned persons, or to any non-Māori New Zealander. Papa'a has a similar meaning in Cook Islands Māori. Historically before the arrival of other ethnic groups the word Māori meant 'ordinary' or 'normal'. The arrival of Europeans led to the formation of a new term to distinguish the self-regarded 'ordinary' or 'normal' Māori from the new arrivals. The etymology of the word ''Pākehā'' remains unclear, but the term was in use by the late-18th century. In December 1814 the Māori children at Rangihoua in the Bay of Islands were "no less eager to see the ''packaha'' than the grown folks". In Māori, plural noun-phrases of the term include (the definite article) and (the indefinite article). When the word was first adopted into English, the usual plural was 'Pakehas'. However, spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2006 New Zealand Census
The New Zealand Census of Population and Dwellings ( mi, Te Tatauranga o ngā Tāngata Huri Noa i Aotearoa me ō rātou Whare Noho) is a national population and housing census conducted by government department Statistics New Zealand every five years. There have been 34 censuses since 1851. In addition to providing detailed information about national demographics, the results of the census play an important part in the calculation of resource allocation to local service providers. The 2018 census took place on Tuesday 6 March 2018. The next census is expected in March 2023. Census date Since 1926, the census has always been held on a Tuesday and since 1966, the census always occurs in March. These are statistically the month and weekday on which New Zealanders are least likely to be travelling. The census forms have to be returned by midnight on census day for them to be valid. Conducting the census Until 2018, census forms were hand-delivered by census workers during the lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2013 New Zealand Census
The 2013 New Zealand census was the thirty-third national census. "The National Census Day" used for the census was on Tuesday, 5 March 2013. The population of New Zealand was counted as 4,242,048, – an increase of 214,101 or 5.3% over the 2006 census. The 2013 census forms were the same as the forms developed for the 2011 census which was cancelled due to the February 2011 major earthquake in Christchurch. There were no new topics or questions. New Zealand's next census was conducted in March 2018. Collection methods The results from the post-enumeration survey showed that the 2013 census recorded 97.6 percent of the residents in New Zealand on census night. However, the overall response rate was 92.9 percent, with a non-response rate of 7.1 percent made up of the net undercount and people who were counted in the census but had not received a form. Results Population and dwellings Population counts for New Zealand regions. Note: All figures are for the census usually r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2018 New Zealand Census
Eighteen or 18 may refer to: * 18 (number), the natural number following 17 and preceding 19 * one of the years 18 BC, AD 18, 1918, 2018 Film, television and entertainment * ''18'' (film), a 1993 Taiwanese experimental film based on the short story ''God's Dice'' * ''Eighteen'' (film), a 2005 Canadian dramatic feature film * 18 (British Board of Film Classification), a film rating in the United Kingdom, also used in Ireland by the Irish Film Classification Office * 18 (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the ''Dragon Ball'' franchise * "Eighteen", a 2006 episode of the animated television series ''12 oz. Mouse'' Music Albums * ''18'' (Moby album), 2002 * ''18'' (Nana Kitade album), 2005 * '' 18...'', 2009 debut album by G.E.M. Songs * "18" (5 Seconds of Summer song), from their 2014 eponymous debut album * "18" (One Direction song), from their 2014 studio album ''Four'' * "18", by Anarbor from their 2013 studio album '' Burnout'' * "I'm Eighteen", by Alice Cooper commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |