|
Next To Normal (musical)
''Next to Normal'' (stylized in all lowercase) is a 2008 American rock musical with book and lyrics by Brian Yorkey and music by Tom Kitt. The story centers on a mother who struggles with worsening bipolar disorder and the effects that managing her illness has on her family. The musical addresses grief, depression, suicide, drug abuse, ethics in modern psychiatry, and the underbelly of suburban life. Before its Off-Broadway debut, ''Next to Normal'' received several workshop performances and won the Outer Critics Circle Award for Outstanding New Score and received Drama Desk Awards nominations for Outstanding Actress ( Alice Ripley) and Outstanding Score. After its Off-Broadway run, the show played from November 2008 to January 2009 at the Arena Stage while the theater was in its temporary venue in Virginia. The musical opened on Broadway in April 2009. It was nominated for eleven Tony Awards that year and won three: Best Original Score, Best Orchestration, and Best ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tom Kitt (musician)
Thomas Robert Kitt is an American composer, conductor, orchestrator, and musician. For his score for the musical ''Next to Normal'', he shared the 2010 Pulitzer Prize for Drama with Brian Yorkey. He has also won two Tony Awards and an Outer Critics Circle Award for ''Next to Normal'', as well as Tony and Outer Critics Circle nominations for ''If/Then'' and ''SpongeBob SquarePants.'' He has been nominated for eight Drama Desk Awards, winning one, and a Grammy Award for Best Musical Theater Album for '' Jagged Little Pill'' in 2021''.'' Early life Kitt was raised in Port Washington, New York, on Long Island, until age 13, when his family moved to Bedford, New York, in Westchester County. He attended Byram Hills High School in neighboring Armonk, New York, where he participated in various theatrical productions. He graduated in 1992. As a youth he attended Interlochen Arts Camp. He then attended Columbia College, New York City, graduating with a degree in economics in 1996. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arena Stage
Arena Stage is a not-for-profit regional theater based in Southwest, Washington, D.C. Established in 1950, it was the first racially integrated theater in Washington, D.C. and its founders helped start the U.S. regional theater movement. It is located at a theater complex called the Mead Center for American Theater. The theater's Artistic Director is Molly Smith and the Executive Producer is Edgar Dobie. It is the largest company in the country dedicated to American plays and playwrights. Arena Stage commissions and develops new plays through its Power Plays initiative. The company now serves an annual audience of more than 300,000. Its productions have received numerous local and national awards, including the Tony Award for best regional theater and over 600 Helen Hayes Awards. History Founding, location, and theaters The theatre company was founded in Washington, D.C. in 1950 by Zelda and Thomas Fichandler and Edward Mangum. Its first home was the Hippodrome Theatre, a for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacotherapy
Pharmacotherapy is therapy using pharmaceutical drugs, as distinguished from therapy using surgery (surgical therapy), radiation (radiation therapy), movement ( physical therapy), or other modes. Among physicians, sometimes the term ''medical therapy'' refers specifically to pharmacotherapy as opposed to surgical or other therapy; for example, in oncology, medical oncology is thus distinguished from surgical oncology. Pharmacists are experts in pharmacotherapy and are responsible for ensuring the safe, appropriate, and economical use of pharmaceutical drugs. The skills required to function as a pharmacist require knowledge, training and experience in biomedical, pharmaceutical and clinical sciences. Pharmacology is the science that aims to continually improve pharmacotherapy. The pharmaceutical industry and academia use basic science, applied science, and translational science to create new pharmaceutical drugs. As pharmacotherapy specialists and pharmacists have responsibil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychopharmacology
Psychopharmacology (from Greek grc, ψῡχή, psȳkhē, breath, life, soul, label=none; grc, φάρμακον, pharmakon, drug, label=none; and grc, -λογία, -logia, label=none) is the scientific study of the effects drugs have on mood, sensation, thinking, behavior, judgment and evaluation, and memory. It is distinguished from neuropsychopharmacology, which emphasizes the correlation between drug-induced changes in the functioning of cells in the nervous system and changes in consciousness and behavior. The field of psychopharmacology studies a wide range of substances with various types of psychoactive properties, focusing primarily on the chemical interactions with the brain. The term "psychopharmacology" was likely first coined by David Macht in 1920. Psychoactive drugs interact with particular target sites or receptors found in the nervous system to induce widespread changes in physiological or psychological functions. The specific interaction between drugs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
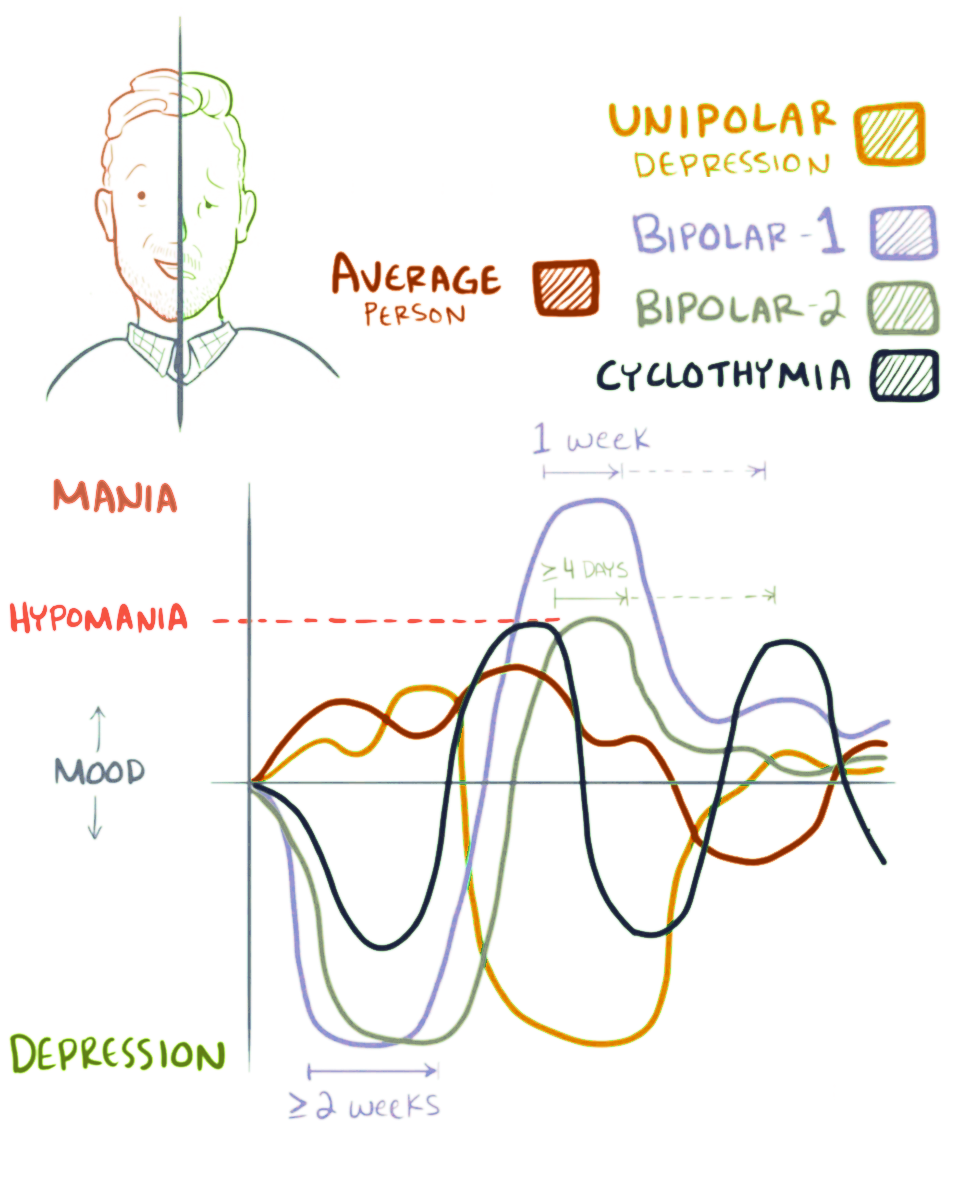
Hypomania
Hypomania (literally "under mania" or "less than mania") is a mental and behavioural disorder, characterised essentially by an apparently non-contextual elevation of mood (euphoria) that contributes to persistently disinhibited behaviour. The individual with the condition may experience irritability, not necessarily less severe than full mania; in fact, the presence of marked irritability is a documented feature of hypomanic and mixed episodes in Bipolar type II. According to DSM-5 criteria, hypomania is distinct from mania in that there is no significant functional impairment; mania, by DSM-5 definition, does include significant functional impairment and may have psychotic features. Characteristic behaviors of persons experiencing hypomania are a notable decrease in the need for sleep, an overall increase in energy, unusual behaviors and actions, and a markedly distinctive increase in talkativeness and confidence, commonly exhibited with a flight of creative ideas. Other symp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mania
Mania, also known as manic syndrome, is a mental and behavioral disorder defined as a state of abnormally elevated arousal, affect, and energy level, or "a state of heightened overall activation with enhanced affective expression together with lability of affect." During a manic episode, an individual will experience rapidly changing emotions and moods, highly influenced by surrounding stimuli. Although mania is often conceived as a "mirror image" to depression, the heightened mood can be either euphoric or dysphoric. As the mania intensifies, irritability can be more pronounced and result in anxiety or anger. The symptoms of mania include elevated mood (either euphoric or irritable), flight of ideas and pressure of speech, increased energy, decreased need and desire for sleep, and hyperactivity. They are most plainly evident in fully developed hypomanic states. However, in full-blown mania, they undergo progressively severe exacerbations and become more and more obscured by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called mania; if it is less severe, it is called hypomania. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually also a reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying and have a negative outlook on life and poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high; over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, while 30–40% engaged in self-harm. Other mental health issues, such as anxiety disorders and substance use disorders, are commonly associated with bipolar disorder. While the causes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallucination
A hallucination is a perception in the absence of an external stimulus that has the qualities of a real perception. Hallucinations are vivid, substantial, and are perceived to be located in external objective space. Hallucination is a combination of 2 conscious states of brain wakefulness and REM sleep. They are distinguishable from several related phenomena, such as dreaming ( REM sleep), which does not involve wakefulness; pseudohallucination, which does not mimic real perception, and is accurately perceived as unreal; illusion, which involves distorted or misinterpreted real perception; and mental imagery, which does not mimic real perception, and is under voluntary control. Hallucinations also differ from "delusional perceptions", in which a correctly sensed and interpreted stimulus (i.e., a real perception) is given some additional significance. Many hallucinations happen also during sleep paralyses. Hallucinations can occur in any sensory modality—visual, auditory, olfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychosis
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior that is inappropriate for a given situation. There may also be sleep problems, social withdrawal, lack of motivation, and difficulties carrying out daily activities. Psychosis can have serious adverse outcomes. As with many psychiatric phenomena, psychosis has several different causes. These include mental illness, such as schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, sensory deprivation and in rare cases, major depression (psychotic depression). Other causes include: trauma, sleep deprivation, some medical conditions, certain medications, and drugs such as cannabis, hallucinogens, and stimulants. One type, known as postpartum psychosis, can occur after giving birth. The neurotransmitter dopamine is believed to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnostic And Statistical Manual Of Mental Disorders
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM; latest edition: DSM-5-TR, published in March 2022) is a publication by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) for the classification of mental disorders using a common language and standard criteria and is the main book for the diagnosis and treatment of mental disorders in the United States and is considered one of the "Bibles" of psychiatry along with the ICD, CCMD and the Psychodynamic Diagnostic Manual. It is usedmainly in the United Statesby researchers, psychiatric drug regulation agencies, health insurance companies, pharmaceutical companies, the legal system, and policymakers. Mental health professionals use the manual to determine and help communicate a patient's diagnosis after an evaluation. Hospitals, clinics, and insurance companies in the United States may require a DSM diagnosis for all patients with mental disorders. Health-care researchers use the DSM to categorize patients for research purp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Psychiatric Association
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) is the main professional organization of psychiatrists and trainee psychiatrists in the United States, and the largest psychiatric organization in the world. It has more than 37,000 members are involved in psychiatric practice, research, and academia representing a diverse population of patients in more than 100 countries. The association publishes various journals and pamphlets, as well as the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM). The DSM codifies psychiatric conditions and is used mostly in the United States as a guide for diagnosing mental disorders. The organization has its headquarters in Washington, DC. History At a meeting in 1844 in Philadelphia, thirteen superintendents and organizers of insane asylums and hospitals formed the Association of Medical Superintendents of American Institutions for the Insane (AMSAII). The group included Thomas Kirkbride, creator of the asylum model which was used thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroconvulsive Therapy
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a psychiatry, psychiatric treatment where a generalized seizure (without muscular convulsions) is electrically induced to manage refractory mental disorders.Rudorfer, MV, Henry, ME, Sackeim, HA (2003)"Electroconvulsive therapy". In A Tasman, J Kay, JA Lieberman (eds) ''Psychiatry, Second Edition''. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 1865–1901. Typically, 70 to 120 volts are applied externally to the patient's head, resulting in approximately 800 amperes, milliamperes of direct current passing between the electrodes, for a duration of 100 milliseconds to 6 seconds, either from temple to temple (bilateral ECT) or from front to back of one side of the head (unilateral ECT). However, only about 1% of the electrical current crosses the bony skull into the brain because skull Electrical impedance, impedance is about 100 times higher than skin Electrical impedance, impedance. The ECT procedure was first conducted in 1938 by Italian psychiatrist Ugo C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |