|
Newport News Waterworks
Newport News () is an independent city in the U.S. state of Virginia. At the 2020 census, the population was 186,247. Located in the Hampton Roads region, it is the 5th most populous city in Virginia and 140th most populous city in the United States. Newport News is included in the Hampton Roads metropolitan area. It is at the southeastern end of the Virginia Peninsula, on the northern shore of the James River extending southeast from Skiffe's Creek along many miles of waterfront to the river's mouth at Newport News Point on the harbor of Hampton Roads. The area now known as Newport News was once a part of Warwick County. Warwick County was one of the eight original shires of Virginia, formed by the House of Burgesses in the British Colony of Virginia by order of King Charles I in 1634. In 1881, fifteen years of rapid development began under the leadership of Collis P. Huntington, whose new Peninsula Extension of the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway from Richmond opened up m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independent City (United States)
In the United States, an independent city is a city that is not in the territory of any County (United States), county or counties and is considered a primary administrative division of its state. Independent cities are classified by the United States Census Bureau as "county equivalents" and may also have similar governmental powers to a consolidated city-county. However, in the case of a consolidated city-county, a city and a county were merged into a unified jurisdiction in which the county at least nominally exists to this day, whereas an independent city was legally separated from any county or merged with a county that simultaneously ceased to exist even in name.Cities 101 -- Consolidations from National League of Cities Of the 41 independent U.S. cities, 38 are in Virginia, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
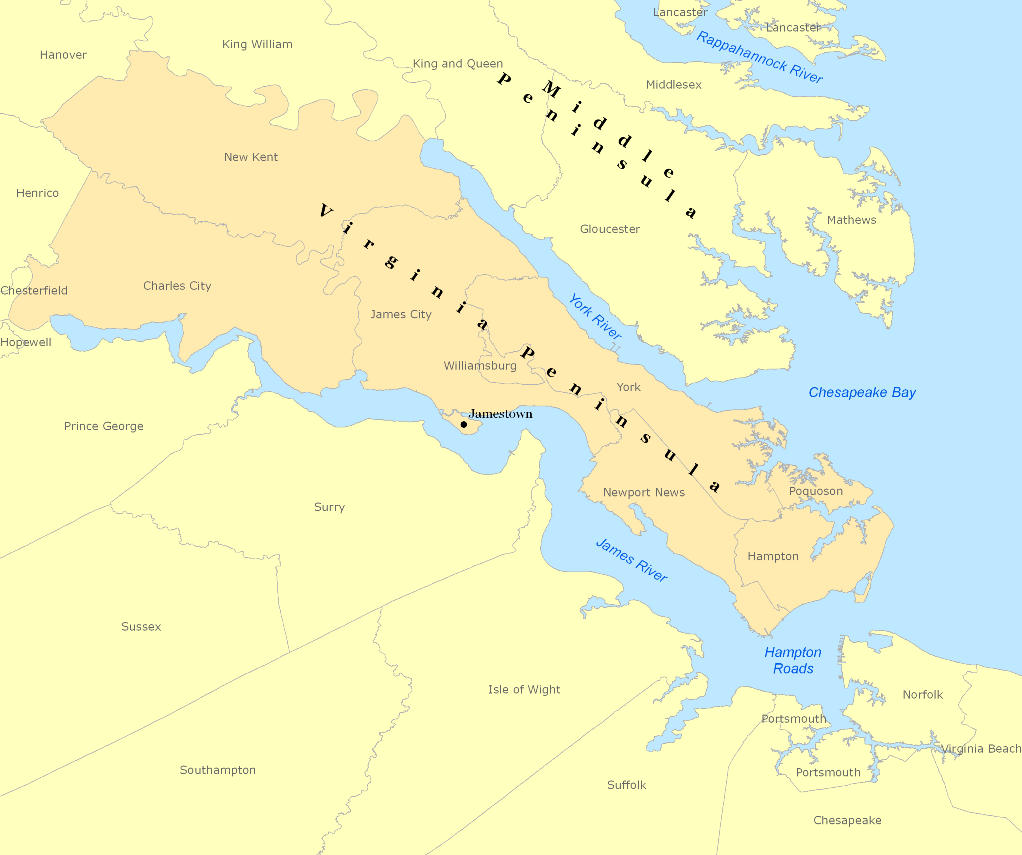
Virginia Peninsula
The Virginia Peninsula is a peninsula in southeast Virginia, USA, bounded by the York River, James River, Hampton Roads and Chesapeake Bay. It is sometimes known as the ''Lower Peninsula'' to distinguish it from two other peninsulas to the north, the Middle Peninsula and the Northern Neck. It is the site of historic Jamestown, founded in 1607 as the first English settlement in North America. Geographically located at the northwestern reaches, Charles City and New Kent counties are part of the Virginia Peninsula. In the 21st century, they are also considered part of the Richmond–Petersburg region. The rest of the Virginia Peninsula is all part of the Virginia Beach–Norfolk–Newport News, VA–NC MSA (metropolitan statistical area) with a population of about 1.8 million. The Hampton Roads MSA is the common name for the metropolitan area that surrounds the body of water of the same name. It is the seventh-largest metropolitan area in the Southeast and the 32nd larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Pier
A coal pier is a transloading facility designed for the transfer of coal between rail and ship. The typical facility for loading ships consists of a holding area and a system of conveyors for transferring the coal to dockside and loading it into the ship's cargo holds. Originally the holding area consisted of a rail yard in which the loaded cars were sorted by grade and held until needed for loading. Modern facilities are more likely to unload the cars immediately (for example, with rotary car dumpers) and store the coal in piles until the ship is loaded. This frees up the cars for immediate reuse and obviates rail yard maintenance. Dedicated coal piers began to be constructed in the 1880s at ports on the Atlantic Coast and Great Lakes in the United States, and many of these survive (though highly modified) to the present. In Virginia, beginning in 1881, coal piers, operated by the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway (C&O) on the Virginia Peninsula at Newport News and in South Hampto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bituminous Coal
Bituminous coal, or black coal, is a type of coal containing a tar-like substance called bitumen or asphalt. Its coloration can be black or sometimes dark brown; often there are well-defined bands of bright and dull material within the coal seam, seams. It is typically hard but friable. Its quality is Coal analysis#Coal classification by rank, ranked higher than lignite and sub-bituminous coal, but lesser than anthracite. It is the most abundant rank of coal, with deposits found around the world, often in rocks of Carboniferous age. Bituminous coal is formed from sub-bituminous coal that is buried deeply enough to be heated to or higher. Bituminous coal is used primarily for electrical power generation and in the steel industry. Bituminous coal suitable for smelting iron (''coking coal'' or ''metallurgical coal'' ) must be low in sulfur and phosphorus. It commands a higher price than other grades of bituminous coal (thermal coal) used for heating and power generation. Within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the Bureau of Labor Statistics classifies the state as a part of the Mid-Atlantic regionMid-Atlantic Home : Mid-Atlantic Information Office: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics" www.bls.gov. Archived. It is bordered by Pennsylvania to the north and east, Maryland to the east and northeast, Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, and Ohio to the northwest. West Virginia is the 10th-smallest state by area and ranks as the 12th-least populous state, with a population of 1,793,716 residents. The capital and largest city is Charleston. West Virginia was admitted to the Union on June 20, 1863, and was a key border state during the American Civil War. It was the only state to form by separating from a Confederate state, the second to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chesapeake And Ohio Railway
The Chesapeake and Ohio Railway was a Class I railroad formed in 1869 in Virginia from several smaller Virginia railroads begun in the 19th century. Led by industrialist Collis P. Huntington, it reached from Virginia's capital city of Richmond to the Ohio River by 1873, where the railroad town (and later city) of Huntington, West Virginia, was named for him. Tapping the coal reserves of West Virginia, the C&O's Peninsula Extension to new coal piers on the harbor of Hampton Roads resulted in the creation of the new City of Newport News. Coal revenues also led the forging of a rail link to the Midwest, eventually reaching Columbus, Cincinnati and Toledo in Ohio and Chicago, Illinois. By the early 1960s the C&O was headquartered in Cleveland, Ohio. In 1972, under the leadership of Cyrus Eaton, it became part of the Chessie System, along with the Baltimore and Ohio and Western Maryland Railway. The Chessie System was later combined with the Seaboard Coast Line and Louisvil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peninsula Extension
The Peninsula Extension which created the Peninsula Subdivision of the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway (C&O) was the new railroad line on the Virginia Peninsula from Richmond to southeastern Warwick County. Its principal purpose was to provide an important new pathway for coal mined in West Virginia to reach the harbor of Hampton Roads for coastal and export shipping on collier ships. Completed on October 16, 1881, the new double-tracked railroad and the other development visions of industrialist Collis Potter Huntington resulted in a 15-year transition of the rural farm village of Newport News into a new independent city which also became home to the world's largest shipyard. The railroad, one of the later developed in Virginia, became important to many communities, opening transportation options, and stimulating commerce and military operations on the Peninsula throughout the 20th century. Over 125 years after it opened, many of the stations are gone. Spur lines have both com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collis P
Collis may refer to: * Collis (surname) * Collis (planetary geology), a term used in planetary geology for a small hill or knob * Collis, Minnesota, an unincorporated community, United States * Collis, former name of Kerman, California, United States * Collis Potter Huntington Collis Potter Huntington (October 22, 1821 – August 13, 1900) was an American industrialist and railway magnate. He was one of the Big Four of western railroading (along with Leland Stanford, Mark Hopkins, and Charles Crocker) who invested ... (1821-1900), American railway executive *'' Collis'', a genus of Asian funnel weavers *'' Collis'', a genus of trilobites {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles I Of England
Charles I (19 November 1600 – 30 January 1649) was King of England, Scotland, and Ireland from 27 March 1625 until his execution in 1649. He was born into the House of Stuart as the second son of King James VI of Scotland, but after his father inherited the English throne in 1603, he moved to England, where he spent much of the rest of his life. He became heir apparent to the kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland in 1612 upon the death of his elder brother, Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales. An unsuccessful and unpopular attempt to marry him to the Spanish Habsburg princess Maria Anna culminated in an eight-month visit to Spain in 1623 that demonstrated the futility of the marriage negotiation. Two years later, he married the Bourbon princess Henrietta Maria of France. After his 1625 succession, Charles quarrelled with the English Parliament, which sought to curb his royal prerogative. He believed in the divine right of kings, and was determined to govern acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony Of Virginia
The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colonial empire, English colony in North America, following failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey GilbertGilbert (Saunders Family), Sir Humphrey" (history), ''Dictionary of Canadian Biography'' Online, University of Toronto, May 2, 2005 in 1583 and the colony of Roanoke (further south, in modern eastern North Carolina) by Sir Walter Raleigh in the late 1580s. The founder of the new colony was the Virginia Company, with the first two settlements in Jamestown, Virginia, Jamestown on the north bank of the James River and Popham Colony on the Kennebec River in modern-day Maine, both in 1607. The Popham colony quickly failed due to Starving Time, a famine, disease, and conflicts with local Native American tribes in the first two years. Jamestown occupied land belonging to the Powhatan Confederacy, and was also at the brink of failure before the arr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Burgesses
The House of Burgesses was the elected representative element of the Virginia General Assembly, the legislative body of the Colony of Virginia. With the creation of the House of Burgesses in 1642, the General Assembly, which had been established in 1619, became a bicameral institution. From 1642 to 1776, the House of Burgesses was an instrument of government alongside the royally-appointed colonial governor and the upper-house Council of State in the General House. When the Virginia colony declared its independence from the Kingdom of Great Britain at the Fifth Virginia Convention in 1776 and became the independent Commonwealth of Virginia, the House of Burgesses became the House of Delegates, which continues to serve as the lower house of the General Assembly. Title ''Burgess'' originally referred to a freeman of a borough, a self-governing town or settlement in England. Early years The Colony of Virginia was founded by a joint-stock company, the Virginia Company, as a pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shires Of Virginia
The eight Shires of Virginia were formed in 1634 in the Virginia Colony. These shires were based on a form of local government used in England at the time, and were redesignated as counties a few years later. As of 2007, five of the eight original shires were considered still extant in the Commonwealth of Virginia in essentially their same political form, although some boundaries and several names have changed in the almost 400 years since their creation. History In 1634, a new system of local government was created in the Virginia Colony by order of King Charles I of England. Eight shires were named by the House of Burgesses, each with its own local officers. The term shire in this system was officially renamed as county only a few years later. There were also several early individual name changes, notably Warrosquyoake, a Native American name with varied spellings that became Isle of Wight. Also, during the English Civil War, Charles River County and the Charles River were cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_at_Newport_News_Shipbuilding_on_20_March_1942_(NH_75592).jpg)