|
Newark Basin
The Newark Basin is a sediment-filled rift basin located mainly in northern New Jersey but also stretching into south-eastern Pennsylvania and southern New York. It is part of the system of Eastern North America Rift Basins. Geology Approximately 220 million years ago, during the late Triassic Period, the supercontinent Pangaea began to break apart. The focus of the rifting began somewhere between where present-day eastern North America and north-western Africa were joined. As in all rifting environments, grabens formed. Many of these grabens were created, but for some of them, extension stopped before full rifting occurred. Where only partial rifting occurred, basins formed, analogous to the present-day Basin and Range Province in western United States. By definition, a basin is any area that collects sediments. These "aborted rifts" (rifts that are tectonically inactive and no longer collecting sediments) extend from North Carolina to Newfoundland. Along certain basins, rif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredth an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newfoundland (island)
Newfoundland (, ; french: link=no, Terre-Neuve, ; ) is a large island off the east coast of the North American mainland and the most populous part of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It has 29 percent of the province's land area. The island is separated from the Labrador Peninsula by the Strait of Belle Isle and from Cape Breton Island by the Cabot Strait. It blocks the mouth of the Saint Lawrence River, creating the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, the world's largest estuary. Newfoundland's nearest neighbour is the French overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon. With an area of , Newfoundland is the world's 16th-largest island, Canada's fourth-largest island, and the largest Canadian island outside the North. The provincial capital, St. John's, is located on the southeastern coast of the island; Cape Spear, just south of the capital, is the easternmost point of North America, excluding Greenland. It is common to consider all directly neighb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of New Jersey
New Jersey is a very geologically and geographically diverse region in the United States' Middle Atlantic region, offering variety from the Appalachian Mountains and the Highlands in the state's northwest, to the Atlantic Coastal Plain region that encompasses both the Pine Barrens and the Jersey Shore. The state's geological features have impacted the course of settlement, development, commerce and industry over the past four centuries. New Jersey has four distinct physiographic provinces. They are: (listed from the south to the north) the Atlantic Coastal Plain Province, the Piedmont Province, the Highlands Province, and the Ridge and Valley Province. Coastal Plain The largest province in the state encompasses the southeast part of the state below the fall zone from Trenton to Carteret. It contains a large wedge of unconsolidated sediments that have been deposited since the Cretaceous Period. These sediments continue off-shore as far as the continental shelf edge in the At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of New Jersey
New Jersey is a state within the United States of America that lies on the north eastern edge of the North American continent. It shares a land border with the state of New York along the north, ratified by both states after the New York – New Jersey Line War, which is its only straight line border. New Jersey is slightly larger than the country of Kuwait. The Atlantic Ocean is east of the state. It is separated from New York, in particular the boroughs of the Bronx and Manhattan in New York City by the Hudson River, and from Staten Island by the Kill van Kull and the Arthur Kill. Liberty Island is an exclave of State of New York in New Jersey waters in Upper New York Bay. Ellis Island, also in the Upper Bay, and Shooter's Island, in Newark Bay, each have sections belonging to either of the two states. On its west, New Jersey is flanked by the Delaware River that forms its border with the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and Delaware Bay which separates New Jersey from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous Rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form natural glasses. Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces, extended crust and oceanic crust. Geological significance Igneous and metamorphic rocks make up 90–95% of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magmatism
Magmatism is the emplacement of magma within and at the surface of the outer layers of a terrestrial planet, which solidifies as igneous rocks. It does so through magmatic activity or igneous activity, the production, intrusion and extrusion of magma or lava. Volcanism is the surface expression of magmatism. Magmatism is one of the main processes responsible for mountain formation. The nature of magmatism depends on the tectonic setting. For example, andesitic magmatism is associated with the formation of island arcs at convergent plate boundaries while basaltic magmatism is found at mid-ocean ridges during sea-floor spreading at divergent plate boundaries. On Earth, magma forms by partial melting of silicate rocks either in the mantle, continental or oceanic crust. Evidence for magmatic activity is usually found in the form of igneous rocks formed from magma. Convergent boundaries Magmatism is associated with all stages of the development of convergent plate boundaries, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palisades Sill
The Palisades Sill is a Triassic, 200 Ma diabase intrusion. It extends through portions of New York and New Jersey. It is most noteworthy for The Palisades, the cliffs that rise steeply above the western bank of the Hudson River. The ideal location and accessibility of the sill, as well as its unique features, have generated much attention from nature enthusiasts, rock climbers, and geologists alike. Location The outcrop of the Palisades Sill is quite recognizable for its prominent cliffs above the Hudson River; it is easily seen from the western portions of Manhattan. The exposure is approximately long, most of it following the Hudson River. It first emerges in Staten Island in New York City. The sill then crosses the state line into New Jersey, where Jersey City, Union City, Fort Lee, and Englewood Cliffs all lie on it. The sill eventually crosses back into New York, following the Hudson River north until reaching Haverstraw. It is at this point that the sill makes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gettysburg Basin
Gettysburg may refer to: Events * Gettysburg Campaign, a series of American Civil War military engagements in the Main Eastern Theater. ** Battle of Gettysburg, July 1–3 military engagements during the 1863 Gettysburg Campaign ** Retreat from Gettysburg, the Confederate and Union armies' return to the South following the Battle of Gettysburg * Gettysburg Address, President Abraham Lincoln's speech at the November 19, 1863, Consecration of the National Cemetery at Gettysburg. Places ; Pennsylvania-related articles *Gettysburg, Pennsylvania ** Gettysburg Battlefield Historic District, of historic properties, buildings, and structures in Adams County, Pennsylvania ** Gettysburg National Military Park, protected by the National Park Service *** Gettysburg Museum and Visitor Center, the National Park Service's reception center *** Gettysburg National Cemetery, a district of the military park on Cemetery Hill *** Gettysburg National Museum, the 1921 museum used as the 1974-2008 NPS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between New York City and Jersey City, eventually draining into the Atlantic Ocean at Lower New York Bay. The river serves as a political boundary between the states of New Jersey and New York at its southern end. Farther north, it marks local boundaries between several New York counties. The lower half of the river is a tidal estuary, deeper than the body of water into which it flows, occupying the Hudson Fjord, an inlet which formed during the most recent period of North American glaciation, estimated at 26,000 to 13,300 years ago. Even as far north as the city of Troy, the flow of the river changes direction with the tides. The Hudson River runs through the Munsee, Lenape, Mohican, Mohawk, and Haudenosaunee homelands. Prior to European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike And Dip
Strike and dip is a measurement convention used to describe the orientation, or attitude, of a planar geologic feature. A feature's strike is the azimuth of an imagined horizontal line across the plane, and its dip is the angle of inclination measured downward from horizontal. They are used together to measure and document a structure's characteristics for study or for use on a geologic map. A feature's orientation can also be represented by dip and dip direction, using the azimuth of the dip rather than the strike value. Linear features are similarly measured with trend and plunge, where "trend" is analogous to dip direction and "plunge" is the dip angle. Strike and dip are measured using a compass and a clinometer. A compass is used to measure the feature's strike by holding the compass horizontally against the feature. A clinometer measures the features dip by recording the inclination perpendicular to the strike. These can be done separately, or together using a tool such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
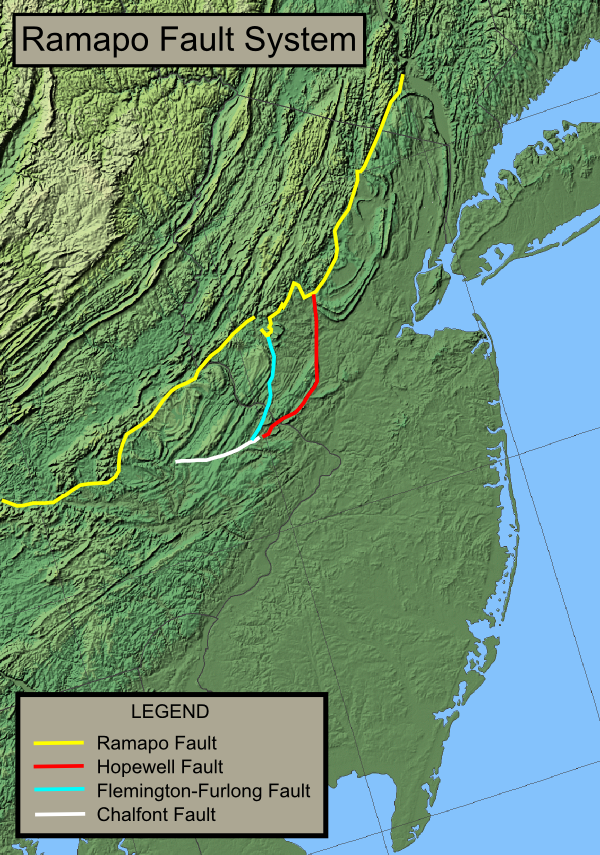
Ramapo Fault
The Ramapo Fault zone is a system of faults between the northern Appalachian Mountains and Piedmont areas to the east.Earthquakes and the Ramapo Fault System in Southeastern New York State Earth Institute News Archive, Columbia University, 2004. Accessed October 24, 2009. Spanning more than in , , and , it is perhaps the best known fault zone in the Mid-Atlantic regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A '' fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |