|
New Hebrides Trench
The New Hebrides Trench is an oceanic trench which extends to over deep in the Southern Pacific Ocean. It lies to the northeast of New Caledonia and the Loyalty Islands, to the southwest of Vanuatu, east of Australia, and south of Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands. The trench was formed as a result of the subduction zone. The Australian Plate is being subducted under the New Hebrides Plate causing volcanism which produced the Vanuatu archipelago. The trench was first explored in 2013 by the University of Aberdeen's Oceanlab team. They found cusk-eels, prawns, and other eels, and crustaceans. This is significantly different from other deep sea trenches that have been studied. Tectonics At the New Hebrides Trench, the Australian plate is being subducted underneath the New Hebrides microplate. The convergence rate ranges from /yr in the south, to /yr in the central section, to /yr in the north. The anomalous lack of convergence in the central section is caused by the subdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Hebrides Plate Map-fr
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created. New or NEW may refer to: Music * New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz Albums and EPs * ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013 * ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, 1995 Songs * "New" (Daya song), 2017 * "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013 * "New" (No Doubt song), 1999 *"new", by Loona from '' Yves'', 2017 *"The New", by Interpol from ''Turn On the Bright Lights'', 2002 Acronyms * Net economic welfare, a proposed macroeconomic indicator * Net explosive weight, also known as net explosive quantity * Network of enlightened Women, a conservative university women's organization * Next Entertainment World, a South Korean film distribution company Identification codes * Nepal Bhasa language ISO 639 language code * New Century Financial Corporation (NYSE stock abbreviation) * Northeast Wrestling, a professional wrestling promotion in the northeastern United States Transport * New Orleans Lakefront Air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called a vent. It includes all phenomena resulting from and causing magma within the crust or mantle of the body, to rise through the crust and form volcanic rocks on the surface. Magmas, that reach the surface and solidify, form extrusive landforms. Volcanic processes Magma from the mantle or lower crust rises through the crust towards the surface. If magma reaches the surface, its behavior depends on the viscosity of the molten constituent rock. Viscous (thick) magma produces volcanoes characterised by explosive eruptions, while non-viscous (runny) magma produce volcanoes characterised by effusive eruptions pouring large amounts of lava onto the surface. In some cases, rising magma can cool and solidify without reaching the surface. Inste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
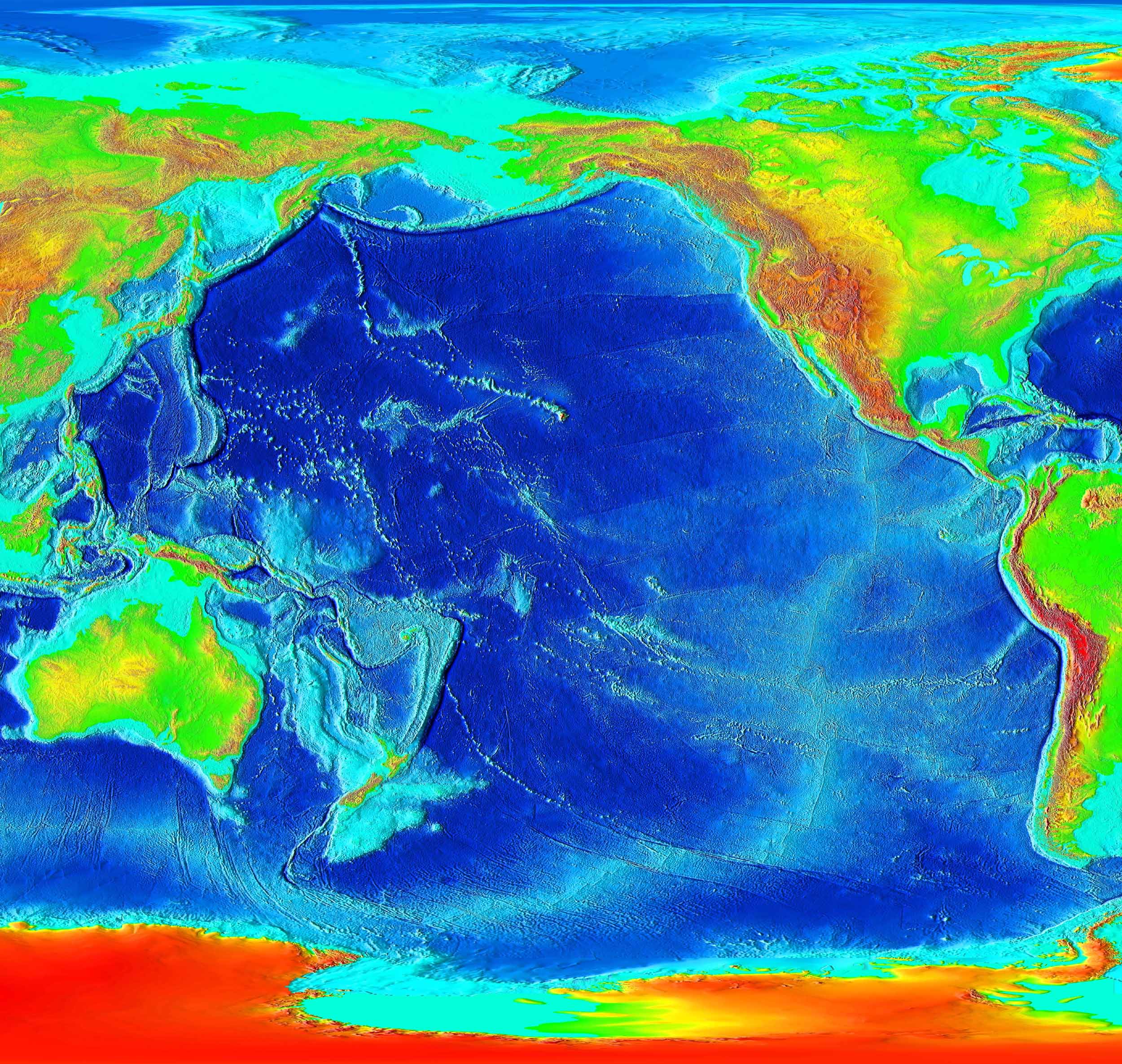
Geology Of The Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean evolved in the Mesozoic from the Panthalassic Ocean, which had formed when Rodinia rifted apart around 750 Ma. The first ocean floor which is part of the current Pacific Plate began 160 Ma to the west of the central Pacific and subsequently developed into the largest oceanic plate on Earth. The East Pacific Rise near Easter Island is the fastest spreading mid-ocean ridge, with a spreading rate of over 15 cm/yr. The Pacific Plate moves generally towards the northwest at between 7 and 11 cm/yr while the Juan De Fuca Plate has an east-northeasterly movement of some 4 cm/yr. Most subduction zones around the rim of the Pacific are directed away from a large area in the southern Pacific. At the core–mantle boundary below this area there is a large low-shear velocity province (LLSVP). Most of Pacific hotspots are located above the LLSVP while the longest Pacific hotspot tracks are located at or near its boundaries pointing at the positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of New Caledonia
The geology of New Caledonia includes all major rock types (igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic), which here range in age from ~290 million years old (Ma) to recent. Their formation is driven by alternate plate collisions and rifting. The mantle-derived Eocene Peridotite Nappe is the most significant and widespread unit (labelled as "Ophiolites" and coloured in bright green in Fig. 1). The igneous unit consists of ore-rich ultramafic rocks thrust onto the main island. Mining of valuable metals from this unit has been an economical pillar of New Caledonia for more than a century. Currently, New Caledonia is located on the Indo-Australian Plate and the largely submerged continent of Zealandia. After New Zealand, it is the second-largest subaerial landmass, and the northernmost part of this continent. As shown on the map, the landmass is elongated in a NW-SE orientation, which is similar to the distribution patterns of most of the geological units. Thrusting, exhumation and folding o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 Loyalty Islands Earthquake
The 2021 Loyalty Islands earthquake was a 7.7 magnitude earthquake that struck offshore between Vanuatu and New Caledonia on February 11, 2021 at 00:19 local time. It is the 4th largest earthquake of 2021. Tectonic setting Located about 415 km to the east of the island of New Caledonia in the southwest Pacific Ocean occurred as the result of low angle thrust faulting on or near the plate boundary interface between the Indo-Australian and Pacific plates. Focal mechanism solutions indicate the earthquake occurred on either a shallow fault striking west and dipping to the north, or on a steep fault striking east. The earthquake was preceded by two foreshocks of M 6.1 and M 6.0 in the hour before the earthquake. At the location of this earthquake, the Indo-Australian plate moves towards the east-northeast with respect to the Pacific at a rate of approximately 75 mm/yr. At the South New Hebrides Trench, Australia lithosphere converges with and sinks beneath the Pacific pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2013 Solomon Islands Earthquake
The 2013 Solomon Islands earthquake struck Temotu Province within Solomon Islands on 6 February with a Moment magnitude scale, moment magnitude of 8.0 and a maximum Mercalli intensity scale, Mercalli intensity of VIII (''Severe''). The epicentre was close to the Santa Cruz Islands within Temotu Province at the boundaries of the Indo-Australian Plate, Indo-Australian and Pacific plate, Pacific List of tectonic plates, tectonic plates, causing local evacuations, a tsunami of and killing at least nine people. Tectonic setting The whole of Solomon Islands, including Santa Cruz, is located on the plate boundary between the Indo-Australian and Pacific plates. This highly seismic region has a “near 90° bend in the boundary…" This area experiences much plate movement as the Santa Cruz Island “has upper plate strike-slip and normal faulting, plate boundary under-thrusting, Outer trench swell, outer rise extensional faulting, and intraplate faulting” and Solomon Islands i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2009 Vanuatu Earthquakes
The 2009 Vanuatu earthquakes were three earthquakes with magnitudes ranging from 7.4 to 7.8, constituting some of the largest earthquakes in Vanuatu's history. Tectonic Setting The Vanuatu earthquakes of October 7, 2009: M 7.7, Vanuatu, 22:03:14; M 7.8 Santa Cruz Islands, 22:18:51 UTC; and M 7.4, Vanuatu, 23:13:48; all occurred as a result of shallow reverse faulting on or near the plate boundary interface between the Indo-Australian Plate and Pacific Plates. In the region of these earthquakes, the Indo-Australian plate moves to the east-northeast with respect to the Pacific plate at a velocity of about 91 mm/yr. The Indo-Australian plate thrusts under the Pacific plate at the New Hebrides Trench and dips to the east-northeast. The locations, depths, and focal mechanism solutions for the October 7th events are all consistent with them resulting from reverse faulting associated with subduction along the Australia-Pacific plate boundary. The 7.8 earthquake of October 7, 2009 (22: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D'Entrecasteaux Ridge
The d'Entrecasteaux () Ridge (DER) is a double oceanic ridge in the south-west Pacific Ocean, north of New Caledonia and west of Vanuatu Islands. It forms the northern extension of the New Caledonia–Loyalty Islands arc, and is now actively subducting under the Vanuatu/New Hebrides arc. The subduction of the DER is responsible for the anomalous morphology of the central part of New Hebrides arc whose movement more closely matches the north-east direction of the subducting Australian Plate (the rest of the New Hebrides arc rotate west in front of the southward expanding North Fiji Basin). The name honours French naval officer Antoine Bruni d'Entrecasteaux, explorer of the south-west Pacific in the late 18th century. Geological setting The DER extends north from the New Caledonia ridge to the New Hebrides/Vanuatu Trench and thus separates the North Loyalty Basin ( ) to the south from the West Santos Basin ( bsl) to the north. The DER has a western and an eastern part with distin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cusk-eels
The cusk-eel family, Ophidiidae, is a group of marine bony fishes in the Ophidiiformes order. The scientific name is from the Greek ''ophis'' meaning "snake", and refers to their eel-like appearance. True eels, however, diverged from other ray-finned fish during the Jurassic, while cusk-eels are part of the Percomorpha clade, along with tuna, perch, seahorses, and others. Distribution Cusk-eels are found in temperate and tropical oceans throughout the world. They live close to the sea bottom, ranging from shallow water to the hadal zone. One species, ''Abyssobrotula galatheae'', was recorded at the bottom of the Puerto Rico trench, making it the deepest recorded fish at . Ecology Cusk-eels are generally very solitary in nature, but some species have been seen to associate themselves with tube worm communities. Liking to be hidden when they are not foraging, they generally associate themselves within muddy bottoms, sinkholes, or larger structures that they can hide in or aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Aberdeen
The University of Aberdeen ( sco, University o' 'Aiberdeen; abbreviated as ''Aberd.'' in List of post-nominal letters (United Kingdom), post-nominals; gd, Oilthigh Obar Dheathain) is a public university, public research university in Aberdeen, Scotland. It is an Ancient universities of Scotland, ancient university founded in 1495 when William Elphinstone, Bishop of Aberdeen and Lord Chancellor of Scotland, Chancellor of Scotland, petitioned Pope Alexander VI on behalf of James IV of Scotland, James IV, King of Scots to establish King's College, Aberdeen, King's College, making it Scotland's 3rd oldest university and the 5th oldest in the English-speaking world and the United Kingdom. Aberdeen is consistently ranked among the top 160 universities in the world and is ranked within the top 20 universities in the United Kingdom according to ''The Times'' and ''The Sunday Times'', and 13th in the UK according to ''The Guardian''. The university comprises three colleges—King's College ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Hebrides Plate
The New Hebrides Plate, sometimes called the Neo-Hebridean Plate, is a minor tectonic plate located in the Pacific Ocean, near the island country of Vanuatu. The plate is bounded on the southwest by the Indo-Australian Plate which is subducting below it. The New Hebrides Trench is seismically active, producing See also * List of earthquakes in Vanuatu Earthquakes in Vanuatu are frequent and are sometimes accompanied by tsunami, though these events are not often destructive. The archipelago, which was formerly known as New Hebrides, lies atop a complex and active plate boundary in the southwester ... References Citations * {{DEFAULTSORT:New Hebrides Plate Tectonic plates Geology of the Pacific Ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Trench
Oceanic trenches are prominent long, narrow topographic depressions of the ocean floor. They are typically wide and below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor, but can be thousands of kilometers in length. There are about of oceanic trenches worldwide, mostly around the Pacific Ocean, but also in the eastern Indian Ocean and a few other locations. The greatest ocean depth measured is in the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, at a depth of below sea level. Oceanic trenches are a feature of the Earth's distinctive plate tectonics. They mark the locations of convergent plate boundaries, along which lithospheric plates move towards each other at rates that vary from a few millimeters to over ten centimeters per year. Oceanic lithosphere moves into trenches at a global rate of about 3 km2/yr. A trench marks the position at which the flexed, subducting slab begins to descend beneath another lithospheric slab. Trenches are generally parallel to and about from a vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
.jpg)
