|
Neuzelle Kloster Interior-view
Neuzelle ( dsb, Nowa Cala) is a Municipalities of Germany, municipality in the Oder-Spree district of Brandenburg, Germany, the administrative seat of ''Amt (country subdivision), Amt'' (collective municipality) Neuzelle (Amt), Neuzelle. It is best known for Cistercians, Cistercian Neuzelle Abbey and its Neuzeller Kloster Brewery. Geography Neuzelle is situated in the north of the historic Lower Lusatia region near the border with Poland, about south of Eisenhüttenstadt. The municipal area along the Dorche creek, a tributary of the Oder River, since 2001 also comprises the villages of Bahro, Bomsdorf, Göhlen, Henzendorf, Kobbeln, Möbiskruge, Ossendorf, Schwerzko, Steinsdorf, Streichwitz, and Treppeln. In the west, it stretches up to the Schlaube Valley Nature Park. History The abbey was established as ''Nova Cella'' on 12 October 1268 by the House of Wettin, Wettin margrave Henry III, Margrave of Meissen, Henry III of Lusatia in remembrance of his deceased wife Agnes of Bohe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Germany
MunicipalitiesCountry Compendium. A companion to the English Style Guide European Commission, May 2021, pages 58–59. (german: Gemeinden, ) are the lowest level of official territorial division in . This can be the second, third, fourth or fifth level of territorial division, depending on the status of the municipality and the '''' (federal state) it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Wettin
The House of Wettin () is a dynasty of German kings, prince-electors, dukes, and counts that once ruled territories in the present-day German states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its origins can be traced back to the town of Wettin, Saxony-Anhalt. The Wettins gradually rose to power within the Holy Roman Empire. Members of the family became the rulers of several medieval states, starting with the Saxon Eastern March in 1030. Other states they gained were Meissen in 1089, Thuringia in 1263, and Saxony in 1423. These areas cover large parts of Central Germany as a cultural area of Germany. The family divided into two ruling branches in 1485 by the Treaty of Leipzig: the Ernestine and Albertine branches. The older Ernestine branch played a key role during the Protestant Reformation. Many ruling monarchs outside Germany were later tied to its cadet branch, the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. The Albertine branch, while less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szydłów, Lubusz Voivodeship
Szydłów (; german: Schiedlo) is an abandoned village in the administrative district of Gmina Cybinka, within Słubice County, Lubusz Voivodeship, in western Poland, close to the German border. History The area formed part of Poland since the establishment of the state in the 10th century. The settlement arose from a castle near the confluence of the Oder and Neisse rivers. Following Poland's fragmentation, it initially formed part of the Duchy of Silesia, and later of the Duchy of Legnica, both provincial duchies of Piast-ruled Poland. In 1249 the Silesian Duke Bolesław II the Bald of Legnica granted it to the Lusatian margrave Henry III the Illustrious from the House of Wettin, in turn for his mediation in the inheritance conflict with his brother Duke Henry III the White of Wrocław. It remained a village at the northeastern edge of Lower Lusatia, the only one east of the Oder River. From 1319 on it was a possession of Neuzelle Abbey. In the 14th century the village pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hall Church
A hall church is a church with a nave and aisles of approximately equal height, often united under a single immense roof. The term was invented in the mid-19th century by Wilhelm Lübke, a pioneering German art historian. In contrast to an architectural basilica, where the nave is lit from above by the clerestory, a hall church is lit by the windows of the side walls typically spanning almost the full height of the interior. Terms In English language, there are two problems of terminology on hall churches: * The term ''hall church'' is ambiguous because the term ''hall'' is ambiguous. In some cases, the church of a manor house ("hall") is called a hall church. Regarding the shapes of churches, ''hall church'' is also used for large aisleless churches, an entirely different type. Aisleless churches with a rectangular plan are called in Dutch and in German, ''/'', derived from French , marking large rooms of less extent than ''/''. * The obligatory distinction between ''nave'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brick Gothic
Brick Gothic (german: Backsteingotik, pl, Gotyk ceglany, nl, Baksteengotiek) is a specific style of Gothic architecture common in Northeast and Central Europe especially in the regions in and around the Baltic Sea, which do not have resources of standing rock, but in many places many glacial boulders. The buildings are essentially built using bricks. Buildings classified as Brick Gothic (using a strict definition of the architectural style based on the geographic location) are found in Belgium (and the very north of France), Netherlands, Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Kaliningrad (former East Prussia), Denmark, Sweden and Finland. As the use of baked red brick arrived in Northwestern and Central Europe in the 12th century, the oldest such buildings are classified as the Brick Romanesque. In the 16th century, Brick Gothic was superseded by Brick Renaissance architecture. Brick Gothic is characterised by the lack of figurative architectural sculpture, wides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convent
A convent is a community of monks, nuns, religious brothers or, sisters or priests. Alternatively, ''convent'' means the building used by the community. The word is particularly used in the Catholic Church, Lutheran churches, and the Anglican Communion. Etymology and usage The term ''convent'' derives via Old French from Latin ''conventus'', perfect participle of the verb ''convenio'', meaning "to convene, to come together". It was first used in this sense when the eremitical life began to be combined with the cenobitical. The original reference was to the gathering of mendicants who spent much of their time travelling. Technically, a monastery is a secluded community of monastics, whereas a friary or convent is a community of mendicants (which, by contrast, might be located in a city), and a canonry is a community of canons regular. The terms abbey and priory can be applied to both monasteries and canonries; an abbey is headed by an abbot, and a priory is a lesser dependent ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margraviate Of Meissen
The Margravate of Meissen (german: Markgrafschaft Meißen) was a medieval principality in the area of the modern German state of Saxony. It originally was a frontier march In medieval Europe, a march or mark was, in broad terms, any kind of borderland, as opposed to a national "heartland". More specifically, a march was a border between realms or a neutral buffer zone under joint control of two states in which diff ... of the Holy Roman Empire, created out of the vast ''Marca Geronis'' (Saxon Eastern March) in 965. Under the rule of the House of Wettin, Wettin dynasty, the margravate finally merged with the former Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg into the Electorate of Saxony, Saxon Electorate by 1423. Predecessors In the mid 9th century, the area of the later margravate was part of an eastern frontier zone of the Carolingian Empire called Sorbian March (''Limes Sorabicus''), after Sorbs, Sorbian tribes of Polabian Slavs settling beyond the Saale river. In 849, a margrave named Thachulf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nossen
Nossen ( hsb, Nosyn) is a town in the Meißen (district), district of Meissen, in Saxony, Germany. It is located 80 km southeast of Leipzig. The town is dominated by a large Renaissance castle. Nossen is best known for its proximity to a motorway junction where the Bundesautobahn 14, A14 merges onto the Bundesautobahn 4, A4. Geography Neighboring towns Nearest towns are Roßwein, Großschirma, Reinsberg, Germany, Reinsberg and Striegistal in Mittelsachsen districts and Käbschütztal, Lommatzsch and Klipphausen in the Meißen district. History During World War II, a subcamp of Flossenbürg concentration camp was located here. Historical population From 1995, recorded on 31 December, unless otherwise noted:Datenquelle ab 1998: Statistisches Landesamt Sachsen Personalities Sons and daughters of the city * Friedrich Funcke (1642-1699), clergyman, cantor and composer * Paul Richter (1859-1944), architect * Friedrich Wilhelm Quintscher (1883-1945), founder of the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altzella Abbey
Altzella Abbey, also Altzelle Abbey (german: Kloster Altzella or ''Altzelle'', previously ''Cella'' or ''Cella Sanctae Mariae''), is a former Cistercian monastery near Nossen in Saxony, Germany. The former abbey contains the tombs of the Wettin margraves of Meissen from 1190 to 1381. The premises and gardens, surrounded by the precinct wall of the former monastery, and known as the ''Klosterpark Altzella'', are now maintained by the Schloss Nossen/Kloster Altzella Administration, and consist of a Romantic park, ruins and restored buildings, used for various cultural and religious functions, such as Corpus Christi processions. It also hosts conferences and private functions. History In 1162 Emperor Frederick I acquired 800 ''Hufen'' of cleared land from a monastery founded by Otto II, Margrave of Meissen, some of which was exchanged after the discovery of silver in 1168. In the following years,the foundation year is taken as 1170 - see Janauschek, ''Originum Cisterciensium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
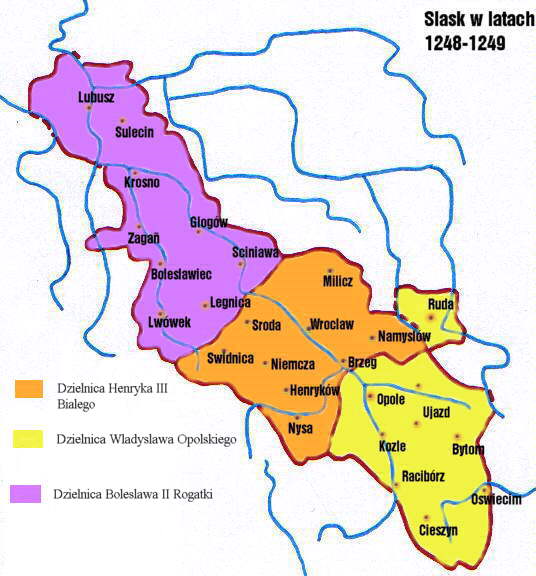
Henry III The White
Henry III the White ( pl, Henryk III Biały) ( – 3 December 1266), a member of the Silesian Piasts, was Duke of Silesia at Wrocław from 1248 until his death, as co-ruler with his brother Władysław. Life He was the third son of the Polish high duke Henry II the Pious, by his wife Princess Anna, daughter of the Přemyslid king Ottokar I of Bohemia. After the heroic death of his father at the Battle of Legnica on 9 April 1241, Henry III was still a minor and found himself under the care of the mother together with his youngest brothers Konrad and Władysław. In 1242, the unexpected death of his brother Mieszko, placed him in the second place immediately after his oldest brother Bolesław II the Bald. Since then, he became in the head of the political opposition in the Lower Silesia against the government of Bolesław II. Duke of Wrocław The first appearance of Henry III as adult was found only in 1247; however, Bolesław II didn't have any intentions to share the power wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesian Piasts
The Silesian Piasts were the elder of four lines of the Polish Piast dynasty beginning with Władysław II the Exile (1105–1159), eldest son of Duke Bolesław III of Poland. By Bolesław's testament, Władysław was granted Silesia as his hereditary province and also the Lesser Polish Seniorate Province at Kraków according to the principle of agnatic seniority. Early history The history of the Silesian Piasts began with the feudal fragmentation of Poland in 1138 following the death of the Polish duke Bolesław III Wrymouth. While the Silesian province and the Kraków seniorate were assigned to Władysław II the Exile, his three younger half–brothers Bolesław IV the Curly, Mieszko III the Old, and Henry of Sandomierz received Masovia, Greater Poland and Sandomierz, respectively, according to the Testament of Boleslaw III. Władysław soon entered into fierce conflicts with his brothers and the Polish nobility. When in 1146 he attempted to take control of the whole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolesław II Rogatka
Boleslav or Bolesław may refer to: In people: * Boleslaw (given name) In geography: * Bolesław, Dąbrowa County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland * Bolesław, Olkusz County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland * Bolesław, Silesian Voivodeship, Poland *Brandýs nad Labem-Stará Boleslav, Czech Republic *Mladá Boleslav, Czech Republic See also * Pulß * Václav (other) * Wenceslaus (other) Wenceslaus, Wenceslas, Wenzeslaus and Wenzslaus (and other similar names) are Latinized forms of the Czech name Václav. The other language versions of the name are german: Wenzel, pl, Wacław, Więcesław, Wieńczysław, es, Wenceslao, russian: ... {{disambig, geo de:Bolesław ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)