|
Neurosymbolic AI
Neuro-symbolic AI is a type of artificial intelligence that integrates neural and symbolic AI architectures to address the weaknesses of each, providing a robust AI capable of reasoning, learning, and cognitive modeling. As argued by Leslie Valiant and others, the effective construction of rich computational cognitive models demands the combination of symbolic reasoning and efficient machine learning. Gary Marcus argued, "We cannot construct rich cognitive models in an adequate, automated way without the triumvirate of hybrid architecture, rich prior knowledge, and sophisticated techniques for reasoning." Further, "To build a robust, knowledge-driven approach to AI we must have the machinery of symbol manipulation in our toolkit. Too much useful knowledge is abstract to proceed without tools that represent and manipulate abstraction, and to date, the only known machinery that can manipulate such abstract knowledge reliably is the apparatus of symbol manipulation." Angelo Dall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that enable machines to machine perception, perceive their environment and use machine learning, learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals. High-profile applications of AI include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google Search); recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon (company), Amazon, and Netflix); virtual assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Siri, and Amazon Alexa, Alexa); autonomous vehicles (e.g., Waymo); Generative artificial intelligence, generative and Computational creativity, creative tools (e.g., ChatGPT and AI art); and Superintelligence, superhuman play and analysis in strategy games (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
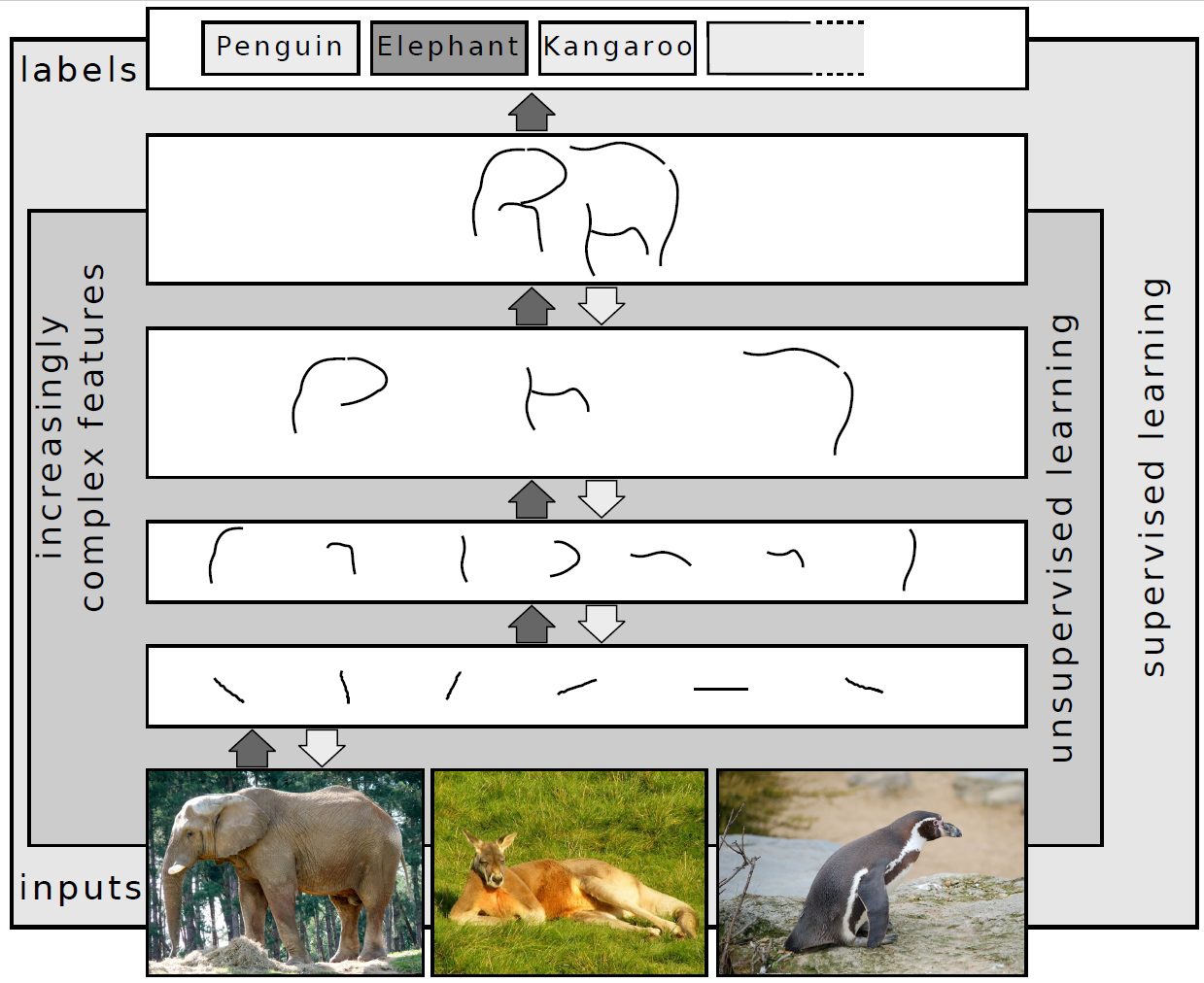
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural networks to perform tasks such as classification, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from biological neuroscience and is centered around stacking artificial neurons into layers and "training" them to process data. The adjective "deep" refers to the use of multiple layers (ranging from three to several hundred or thousands) in the network. Methods used can be either supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised. Some common deep learning network architectures include fully connected networks, deep belief networks, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks, generative adversarial networks, transformers, and neural radiance fields. These architectures have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plug-in (computing)
In computing, a plug-in (also spelled plugin) or add-in (also addin, add-on, or addon) is a software component that extends the functionality of an existing software system without requiring the system to be software build, re-built. A plug-in software feature, feature is one way that a system can be customizable. Applications support plug-ins for a variety of reasons including: * Enable third-party developers to extend an application * Support easily adding new features * Reduce the size of an application by not loading unused features * Separate source code from an application because of incompatible software licenses Examples Examples of plug-in use for various categories of applications: * Digital audio workstations and audio editing software use audio plug-ins to generate, process or analyze sound. Ardour (software), Ardour, Audacity (audio editor), Audacity, Cubase, FL Studio, Logic Pro, Logic Pro X and Pro Tools are examples of such systems. * Email clients use plug-i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is a generative artificial intelligence chatbot developed by OpenAI and released on November 30, 2022. It uses large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4o as well as other Multimodal learning, multimodal models to create human-like responses in text, speech, and images. It has access to features such as searching the web, using apps, and running programs. It is credited with accelerating the AI boom, an ongoing period of rapid investment in and public attention to the field of artificial intelligence (AI). Some observers have raised concern about the potential of ChatGPT and similar programs to displace human intelligence, enable plagiarism, or fuel misinformation. ChatGPT is built on OpenAI's proprietary series of generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) models and is Fine-tuning (machine learning), fine-tuned for conversational applications using a combination of supervised learning and reinforcement learning from human feedback. Successive user AI prompt, prompts an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
And–or Tree
An and–or tree is a graphical representation of the reduction of problems (or goals) to conjunctions and disjunction In logic, disjunction (also known as logical disjunction, logical or, logical addition, or inclusive disjunction) is a logical connective typically notated as \lor and read aloud as "or". For instance, the English language sentence "it is ...s of subproblems (or subgoals). Example The and–or tree: represents the search space for solving the problem P, using the goal-reduction methods: :P if Q and R :P if S :Q if T :Q if U Definitions Given an initial problem P0 and set of problem solving methods of the form: :P if P1 and … and Pn the associated and–or tree is a set of labelled nodes such that: # The root of the tree is a node labelled by P0. # For every node N labelled by a problem or sub-problem P and for every method of the form P if P1 and ... and Pn, there exists a set of children nodes N1, ..., Nn of the node N, such that each nod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Net
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks. A neural network consists of connected units or nodes called ''artificial neurons'', which loosely model the neurons in the brain. Artificial neuron models that mimic biological neurons more closely have also been recently investigated and shown to significantly improve performance. These are connected by ''edges'', which model the synapses in the brain. Each artificial neuron receives signals from connected neurons, then processes them and sends a signal to other connected neurons. The "signal" is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs, called the '' activation function''. The strength of the signal at each connection is determined by a ''weight'', which adjusts during the learning process. Typically, neuro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Algebra
In mathematics and computer science, computer algebra, also called symbolic computation or algebraic computation, is a scientific area that refers to the study and development of algorithms and software for manipulating expression (mathematics), mathematical expressions and other mathematical objects. Although computer algebra could be considered a subfield of scientific computing, they are generally considered as distinct fields because scientific computing is usually based on numerical computation with approximate floating point numbers, while symbolic computation emphasizes ''exact'' computation with expressions containing variable (mathematics), variables that have no given value and are manipulated as symbols. Software applications that perform symbolic calculations are called ''computer algebra systems'', with the term ''system'' alluding to the complexity of the main applications that include, at least, a method to represent mathematical data in a computer, a user programm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macsyma
Macsyma (; "Project MAC's SYmbolic MAnipulator") is one of the oldest general-purpose computer algebra systems still in wide use. It was originally developed from 1968 to 1982 at MIT's Project MAC. In 1982, Macsyma was licensed to Symbolics and became a commercial product. In 1992, Symbolics Macsyma was spun off to Macsyma, Inc., which continued to develop Macsyma until 1999. That version is still available for Microsoft's Windows XP operating system. The 1982 version of MIT Macsyma remained available to academics and US government agencies, and it is distributed by the US Department of Energy (DOE). That version, DOE Macsyma, was maintained by Bill Schelter. Under the name of Maxima, it was released under the GPL in 1999, and remains under active maintenance. Development The project was initiated in July, 1968 by Carl Engelman, William A. Martin (front end, expression display, polynomial arithmetic) and Joel Moses (simplifier, indefinite integration: heuristic/Risch). M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Training Data
In machine learning, a common task is the study and construction of algorithms that can learn from and make predictions on data. Such algorithms function by making data-driven predictions or decisions, through building a mathematical model from input data. These input data used to build the model are usually divided into multiple data sets. In particular, three data sets are commonly used in different stages of the creation of the model: training, validation, and test sets. The model is initially fit on a training data set, which is a set of examples used to fit the parameters (e.g. weights of connections between neurons in artificial neural networks) of the model. The model (e.g. a naive Bayes classifier) is trained on the training data set using a supervised learning method, for example using optimization methods such as gradient descent or stochastic gradient descent. In practice, the training data set often consists of pairs of an input vector (or scalar) and the correspondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monte Carlo Tree Search
In computer science, Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS) is a heuristic search algorithm for some kinds of decision processes, most notably those employed in software that plays board games. In that context MCTS is used to solve the game tree. MCTS was combined with neural networks in 2016 and has been used in multiple board games like Chess, Shogi, Checkers, Backgammon, Contract Bridge, Go, Scrabble, and Clobber as well as in turn-based-strategy video games (such as Total War: Rome II's implementation in the high level campaign AI) and applications outside of games. History Monte Carlo method The Monte Carlo method, which uses random sampling for deterministic problems which are difficult or impossible to solve using other approaches, dates back to the 1940s. In his 1987 PhD thesis, Bruce Abramson combined minimax search with an ''expected-outcome model'' based on random game playouts to the end, instead of the usual static evaluation function. Abramson said the expected-out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AlphaGo
AlphaGo is a computer program that plays the board game Go. It was developed by the London-based DeepMind Technologies, an acquired subsidiary of Google. Subsequent versions of AlphaGo became increasingly powerful, including a version that competed under the name Master. After retiring from competitive play, AlphaGo Master was succeeded by an even more powerful version known as AlphaGo Zero, which was completely self-taught without learning from human games. AlphaGo Zero was then generalized into a program known as AlphaZero, which played additional games, including chess and shogi. AlphaZero has in turn been succeeded by a program known as MuZero which learns without being taught the rules. AlphaGo and its successors use a Monte Carlo tree search algorithm to find its moves based on knowledge previously acquired by machine learning, specifically by an artificial neural network (a deep learning method) by extensive training, both from human and computer play. A neural ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPT-3
Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3 (GPT-3) is a large language model released by OpenAI in 2020. Like its predecessor, GPT-2, it is a decoder-only transformer model of deep neural network, which supersedes recurrence and convolution-based architectures with a technique known as "attention". This attention mechanism allows the model to focus selectively on segments of input text it predicts to be most relevant. GPT-3 has 175 billion parameters, each with 16-bit precision, requiring 350GB of storage since each parameter occupies 2 bytes. It has a context window size of 2048 tokens, and has demonstrated strong " zero-shot" and " few-shot" learning abilities on many tasks. On September 22, 2020, Microsoft announced that it had licensed GPT-3 exclusively. Others can still receive output from its public API, but only Microsoft has access to the underlying model. Background According to ''The Economist'', improved algorithms, more powerful computers, and a recent increase i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |