|
Neuromuscular Blocking Agents
Neuromuscular blocking agents, or in abbreviation, NMBAs, are chemical agents that paralyse skeletal muscles by blocking the movement of neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction. They are often used during general anesthesia to optimize intubating and surgical conditions, specifically to facilitate endotracheal intubation. This class of medications helps to reduce patient movement, breathing, or ventilator dyssynchrony and allows lower insufflation pressures during laparoscopyBlobner M, Frick CG, Stäuble RB, et al. Neuromuscular block-ade improves surgical conditions (NISCO). Surg Endosc.2015;29:627–636. including the generation of nerve impulses. It has several indications for use in the intense care unit. It can help reduce hoarseness in voice as well as injury to the vocal cord during intubation. In addition, it plays an important role in facilitating mechanical ventilation in patients with poor lung function. In the following section, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Bernard
Claude Bernard (; 12 July 1813 – 10 February 1878) was a French physiologist. Historian I. Bernard Cohen of Harvard University called Bernard "one of the greatest of all men of science". He originated the term ''milieu intérieur'', and the associated concept of homeostasis (the latter term being coined by Walter Cannon). Life and career Bernard was born in 1813 in the village of Saint-Julien near Villefranche-sur-Saône. He received his early education in the Jesuit school of that town, and then proceeded to the college at Lyon, which, however, he soon left to become assistant in a druggist's shop. He is sometimes described as an agnostic and even humorously referred to by his colleagues as a "great priest of atheism". Despite this, after his death Cardinal Ferdinand Donnet claimed Bernard was a fervent Catholic, with a biographical entry in the ''Catholic Encyclopedia''. His leisure hours were devoted to the composition of a vaudeville comedy, and the success it achieved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancuronium
Pancuronium (trademarked as Pavulon) is an aminosteroid muscle relaxant with various medical uses. It is used in euthanasia and is used in some states as the second of three drugs administered during lethal injections in the United States. Mechanism of action Pancuronium is a typical non-depolarizing curare-mimetic muscle relaxant. It competitively inhibits the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor at the neuromuscular junction by blocking the binding of acetylcholine. It has slight vagolytic activity, causing an increase in heart rate, but no ganglioplegic (i.e., blocking ganglions) activity. It is a very potent muscle relaxant drug, with an ED95 (i.e., the dose that causes 95% depression of muscle twitch response) of only 60 µg/kg body weight. Onset of action is relatively slow compared to other similar drugs, in part due to its low dose: an intubating dose takes 3–6 minutes for full effect. Clinical effects (muscle activity lower than 25% of physiological) last for abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suxamethonium
Suxamethonium chloride, also known as suxamethonium or succinylcholine, or simply sux by medical abbreviation, is a medication used to cause short-term paralysis as part of general anesthesia. This is done to help with tracheal intubation or electroconvulsive therapy. It is administered by injection, either into a vein or into a muscle. When used in a vein, onset of action is generally within one minute and effects last for up to 10 minutes. Common side effects include low blood pressure, increased saliva production, muscle pain, and rash. Serious side effects include malignant hyperthermia and allergic reactions. It is not recommended in people who are at risk of high blood potassium or a history of myopathy. Use during pregnancy appears to be safe for the baby. Suxamethonium is in the neuromuscular blocker family of medications and is of the depolarizing type. It works by blocking the action of acetylcholine on skeletal muscles. Side effects of succinylcholine chloride i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocuronium
Rocuronium bromide (brand names Zemuron, Esmeron) is an aminosteroid non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocker or muscle relaxant used in modern anaesthesia to facilitate tracheal intubation by providing skeletal muscle relaxation, most commonly required for surgery or mechanical ventilation. It is used for standard endotracheal intubation, as well as for rapid sequence induction (RSI). Pharmacology Mechanism of action Rocuronium bromide is a competitive antagonist for the Nicotinic acetyl-choline receptors at the neuromuscular junction. Of the Neuromuscular-blocking drugs it is considered to be a non-depolarizing neuromuscular junction blocker, because it acts by dampening the receptor action causing muscle relaxation, instead of continual depolarisation which is the mechanism of action of the depolarizing neuromuscular junction blockers, like succinylcholine. It was designed to be a weaker antagonist at the neuromuscular junction than pancuronium; hence its monoquaternary s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atracurium
Atracurium besilate, also known as atracurium besylate, is a medication used in addition to other medications to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation. It can also be used to help with endotracheal intubation but suxamethonium (succinylcholine) is generally preferred if this needs to be done quickly. It is given by injection into a vein. Effects are greatest at about 4 minutes and last for up to an hour. Common side effects include flushing of the skin and low blood pressure. Serious side effects may include allergic reactions; however, it has not been associated with malignant hyperthermia. Prolonged paralysis may occur in people with conditions like myasthenia gravis. It is unclear if use in pregnancy is safe for the baby. Atracurium is in the neuromuscular-blocker family of medications and is of the non-depolarizing type. It works by blocking the action of acetylcholine on skeletal muscles. Atracurium was approved for medical use in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallamine
Gallamine triethiodide (Flaxedil) is a non-depolarising muscle relaxant. It acts by combining with the cholinergic receptor sites in muscle and competitively blocking the transmitter action of acetylcholine. Gallamine is a non-depolarising type of blocker as it binds to the acetylcholine receptor but does not have the biological activity of acetyl choline. Gallamine triethiodide has a parasympatholytic effect on the cardiac vagus nerve, which causes tachycardia and occasionally hypertension. Very high doses cause histamine release. Gallamine triethiodide is commonly used to stabilize muscle contractions during surgical procedures. It was developed by Daniel Bovet in 1947. The pharmaceutical is no longer marketed in the United States, according to the FDA Orange Book. See also * Neuromuscular-blocking drug * Curare Curare ( /kʊˈrɑːri/ or /kjʊˈrɑːri/; ''koo-rah-ree'' or ''kyoo-rah-ree'') is a common name for various alkaloid arrow poisons originating from plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appendectomy
An appendectomy, also termed appendicectomy, is a Surgery, surgical operation in which the vermiform appendix (a portion of the intestine) is removed. Appendectomy is normally performed as an urgent or emergency procedure to treat complicated acute appendicitis. Appendectomy may be performed Laparoscopic surgery, laparoscopically (as minimally invasive surgery) or as an open operation. Over the 2010s, surgical practice has increasingly moved towards routinely offering laparoscopic appendicectomy; for example in the United Kingdom over 95% of adult appendicectomies are planned as laparoscopic procedures. Laparoscopy is often used if the diagnosis is in doubt, or in order to leave a less visible surgical scar. Recovery may be slightly faster after laparoscopic surgery, although the laparoscopic procedure itself is more expensive and resource-intensive than open surgery and generally takes longer. Advanced pelvic sepsis occasionally requires a lower midline laparotomy. Complicated ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harold Randall Griffith
Harold Randall Griffith (July 25, 1894 – 1985) was a Canadian anesthesiologist and a leader in the fields of anesthesiology. History Griffith was born in Montreal the son of Alexander Randall Griffith, a medical doctor and homeopathic practitioner. His medical studies at McGill University were interrupted by World War I, where he served in the No 6. Field Ambulance and was awarded the Military Medal for bravery at Vimy Ridge. He received his MDCM from McGill University in 1922, and an MD in homeopathic medicine from Hahnemann Medical College in Philadelphia in 1923. He developed his interest in anaesthesia as a medical student during which time he administered many anaesthetics and developed an acute awareness of the subtleties essential for safe anaesthesia practice with the drugs and techniques available at that time. Anaesthesia became his professional career and he served as Anaesthetist-in-Chief at the Montreal Homeopathic Hospital, subsequently renamed the Queen Elizab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intocostrin
Curare ( /kʊˈrɑːri/ or /kjʊˈrɑːri/; ''koo-rah-ree'' or ''kyoo-rah-ree'') is a common name for various alkaloid arrow poisons originating from plant extracts. Used as a paralyzing agent by indigenous peoples in Central and South America for hunting and for therapeutic purposes, curare only becomes active when it contaminates a wound. These poisons cause weakness of the skeletal muscles and, when administered in a sufficient dose, eventual death by asphyxiation due to paralysis of the diaphragm. Curare is prepared by boiling the bark of one of the dozens of plant sources, leaving a dark, heavy paste that can be applied to arrow or dart heads. In medicine, curare has been used as a treatment for tetanus or strychnine poisoning and as a paralyzing agent for surgical procedures. History The word 'curare' is derived from ''wurari'', from the Carib language of the Macusi of Guyana. It has its origins in the Carib phrase "mawa cure" meaning of the Mawa vine, scientif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
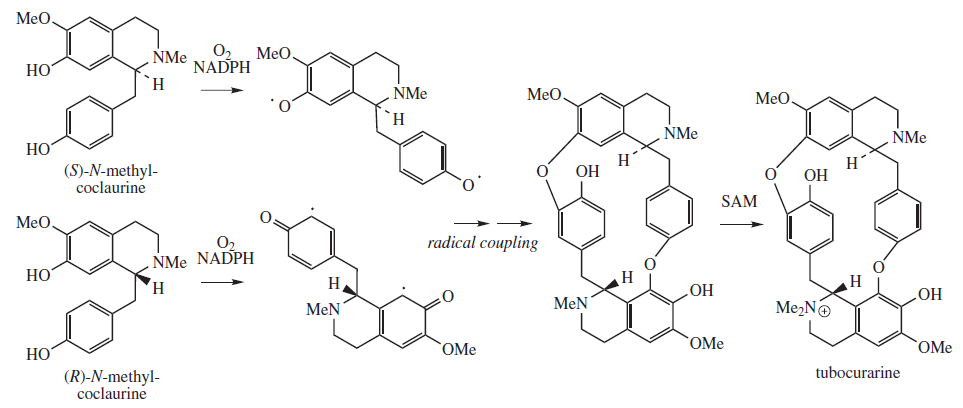
D-tubocurarine
Tubocurarine (also known as ''d''-tubocurarine or DTC) is a toxic alkaloid historically known for its use as an arrow poison. In the mid-1900s, it was used in conjunction with an anesthetic to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or mechanical ventilation. It is now rarely used as an adjunct for clinical anesthesia because safer alternatives, such as cisatracurium and rocuronium, are available. History Tubocurarine is a naturally occurring mono-quaternary alkaloid obtained from the bark of the Menispermaceous South American plant ''Chondrodendron tomentosum'', a climbing vine known to the European world since the Spanish conquest of South America. Curare had been used as a source of arrow poison by South American natives to hunt animals, and they were able to eat the animals' contaminated flesh subsequently without any adverse effects because tubocurarine cannot easily cross mucous membranes. Thus, tubocurarine is effective only if given parenterally, as demonstrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |