|
Netrins
Netrins are a class of proteins involved in axon guidance. They are named after the Sanskrit word "netr", which means "one who guides". Netrins are genetically conserved across nematode worms, fruit flies, frogs, mice, and humans. Structurally, netrin resembles the extracellular matrix protein laminin. Netrins are chemotropic; a growing axon will either move towards or away from a higher concentration of netrin. Though the detailed mechanism of axon guidance is not fully understood, it is known that netrin attraction is mediated through UNC-40/DCC cell surface receptors and repulsion is mediated through UNC-5 receptors. Netrins also act as growth factors, encouraging cell growth activities in target cells. Mice deficient in netrin fail to form the hippocampal comissure or the corpus callosum. A proposed model for netrin activity in the spinal column of developing human embryos is that netrins are released by the floor plate and then are picked up by receptor proteins embe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netrin 1 Knockout Model Cropped
Netrins are a class of proteins involved in axon guidance. They are named after the Sanskrit word "netr", which means "one who guides". Netrins are Conserved sequence, genetically conserved across Caenorhabditis elegans, nematode worms, Drosophila, fruit flies, Xenopus laevis, frogs, Mus musculus, mice, and Human, humans. Structurally, netrin resembles the extracellular matrix protein laminin. Netrins are chemotropism, chemotropic; a growing axon will either move towards or away from a higher concentration of netrin. Though the detailed mechanism of axon guidance is not fully understood, it is known that netrin attraction is mediated through UNC-40/DCC cell surface receptors and repulsion is mediated through UNC-5 receptors. Netrins also act as growth factors, encouraging cell growth activities in target cells. Mice deficient in netrin fail to form the hippocampal comissure or the corpus callosum. A proposed Scientific modelling, model for netrin activity in the spinal column of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floor Plate (biology)
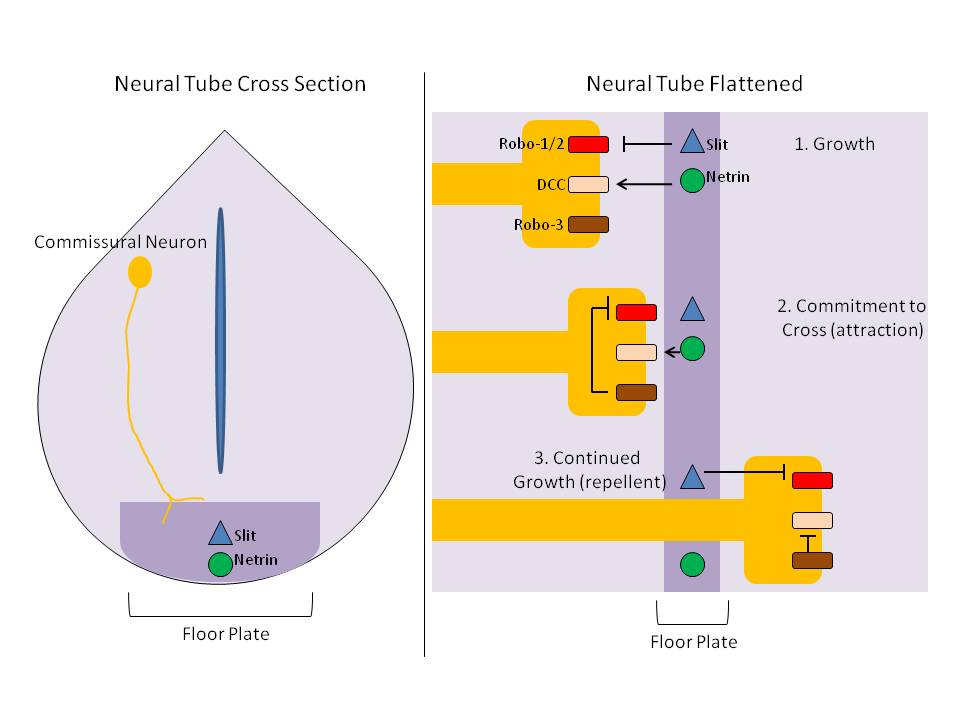
The floor plate is a structure integral to the developing nervous system of vertebrate organisms. Located on the ventral midline of the embryonic neural tube, the floor plate is a specialized glial structure that spans the anteroposterior axis from the midbrain to the tail regions. It has been shown that the floor plate is conserved among vertebrates, such as zebrafish and mice, with homologous structures in invertebrates such as the fruit fly ''Drosophila'' and the nematode ''Caenorhabditis elegans, C. elegans''. Functionally, the structure serves as an organizer to ventralize tissues in the embryo as well as to guide neuronal positioning and differentiation along the dorsoventral axis of the neural tube. Induction Induction of the floor plate during embryogenesis of vertebrate embryos has been studied extensively in chick and zebrafish and occurs as a result of a complex signaling network among tissues, the details of which have yet to be fully refined. Currently there are s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNC-5
UNC-5 is a receptor for netrins including UNC-6. Netrins are a class of proteins involved in axon guidance. UNC-5 uses repulsion to direct axons while the other netrin receptor UNC-40 attracts axons to the source of netrin production. Discovery of netrins The term netrin was first used in a study done in 1990 in Caenorhabditis elegans and was called UNC-6. Studies performed on rodents in 1994 have determined that netrins are vital to guidance cues. The vertebrate orthologue of UNC-6, netrin-1 was determined to be a key guidance cue for axons moving toward the ventral midline in the rodent embryo spinal cord. Netrin-1 has been identified as a critical component of embryonic development with functions in axon guidance, cell migration, morphogenesis and angiogenesis. The most recent studies have found that there are 5 types of netrins expressed in animals. Ectotopic expression of UNC-5 can result in short or long range repulsion. Axon guidance The guidance of axons to their t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon Guidance
Axon guidance (also called axon pathfinding) is a subfield of neural development concerning the process by which neurons send out axons to reach their correct targets. Axons often follow very precise paths in the nervous system, and how they manage to find their way so accurately is an area of ongoing research. Axon growth takes place from a region called the growth cone and reaching the axon target is accomplished with relatively few guidance molecules. Growth cone receptors respond to the guidance cues. Mechanisms Growing axons have a highly motile structure at the growing tip called the growth cone, which responds to signals in the extracellular environment that instruct the axon in which direction to grow. These signals, called guidance cues, can be fixed in place or diffusible; they can attract or repel axons. Growth cones contain receptors that recognize these guidance cues and interpret the signal into a chemotropic response. The general theoretical framework is that wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
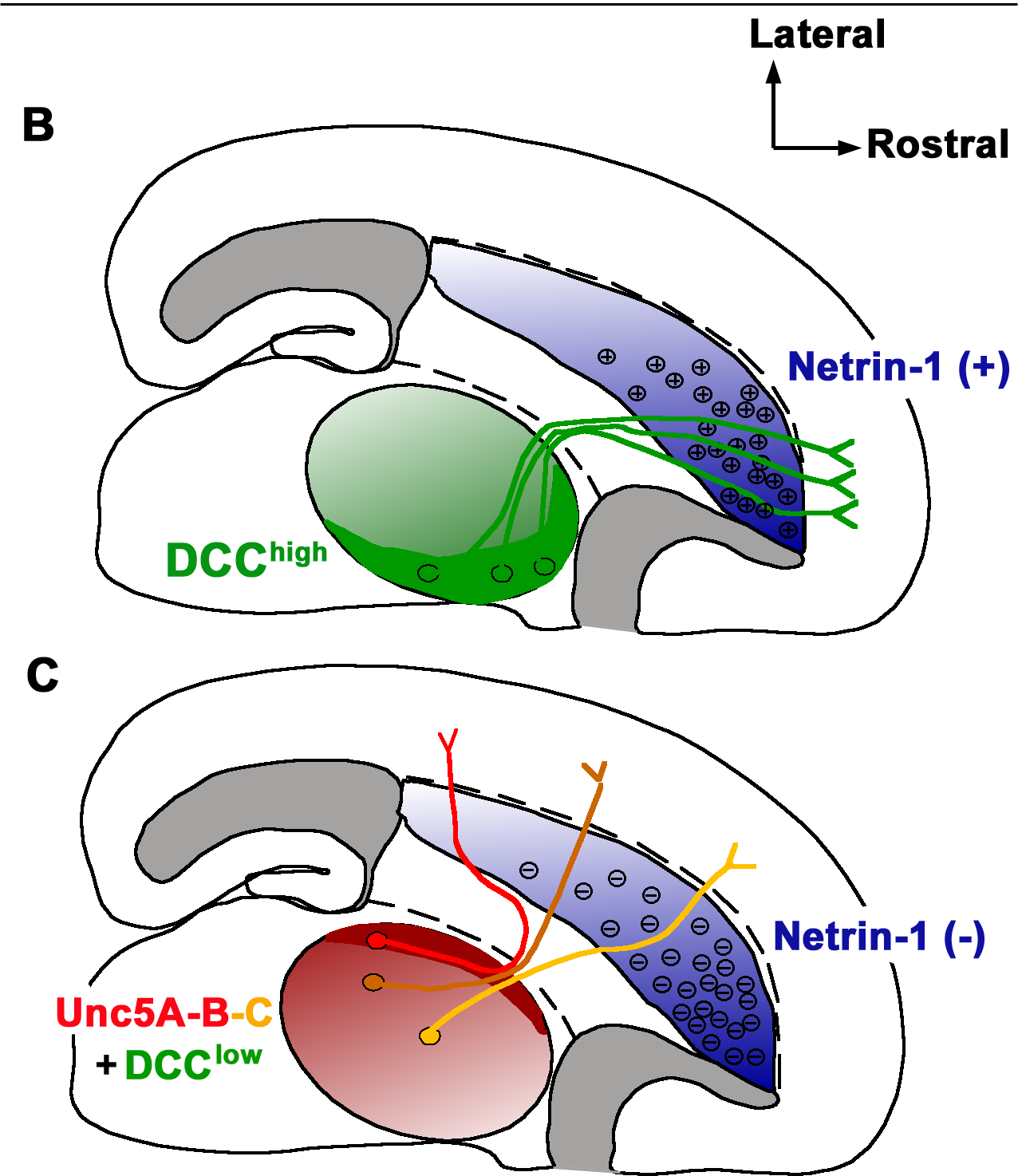
Netrin-1
Netrin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NTN1'' gene. Netrin is included in a family of laminin-related secreted proteins. The function of this gene has not yet been defined; however, netrin is thought to be involved in axon guidance and cell migration during development. Mutations and loss of expression of netrin suggest that variation in netrin may be involved in cancer development. Interactions NTN1 has been shown to interact with Deleted in Colorectal Cancer, and components of the extracellular matrix and the tumor microenvironment. Midline crossing of commissural axons During the development of the central nervous system, when the dorsal and ventral signaling is being established, the floor plate is an important site for crossing for groups of neural processes at the dorsal midline. Once crossed through the floor plate, these groups are now referred to as commissural axons. These neuronal cell bodies are signaled by Netrin 1 to be attracted to the floor pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
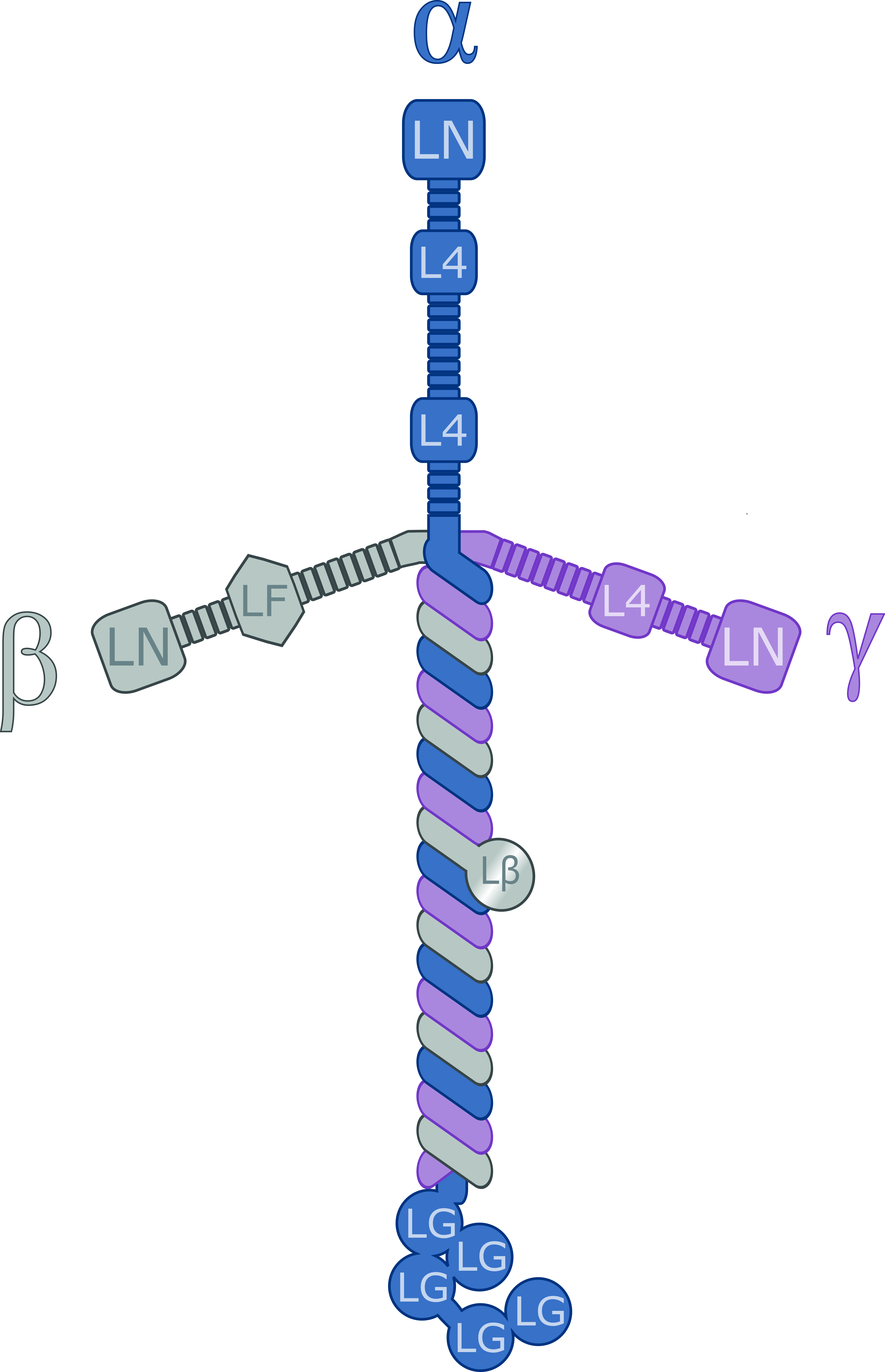
Laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major constituents of the basement membrane, namely the basal lamina (the protein network foundation for most cells and organs). Laminins are vital to biological activity, influencing cell differentiation, migration, and adhesion. Laminins are heterotrimeric proteins with a high molecular mass (~400 to ~900 kDa) and possess three different chains (α, β, and γ) encoded by five, four, and three paralogous genes in humans, respectively. The laminin molecules are named according to their chain composition, e.g. laminin-511 contains α5, β1, and γ1 chains. Fourteen other chain combinations have been identified ''in vivo''. The trimeric proteins intersect, composing a cruciform structure that is able to bind to other molecules of the extracellular matrix and cell membrane. The three short arms have an affinity for binding to other laminin molecules, conducing sheet formation. The long ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deleted In Colorectal Cancer
Netrin receptor DCC, also known as DCC, or colorectal cancer suppressor is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''DCC'' gene. DCC has long been implicated in colorectal cancer and its previous name was ''Deleted in colorectal carcinoma''. Netrin receptor DCC is a single transmembrane receptor. Since it was first discovered in a colorectal cancer study in 1990, ''DCC'' has been the focus of a significant amount of research. ''DCC'' held a controversial place as a tumour suppressor gene for many years, and is well known as an axon guidance receptor that responds to netrin-1. More recently DCC has been characterized as a dependence receptor, and many hypotheses have been put forward that have revived interest in ''DCCs candidacy as a tumour suppressor gene, as it may be a ligand-dependent suppressor that is frequently epigenetically silenced. Background Early studies of colorectal tumours found that allelic deletions of segments of chromosome 18q occur in a very high per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryos
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres (4-cell stage) are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, (16-cell stage) takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of the body. Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Cones
Growth may refer to: Biology *Auxology, the study of all aspects of human physical growth *Bacterial growth *Cell growth *Growth hormone, a peptide hormone that stimulates growth *Human development (biology) *Plant growth *Secondary growth, growth that thickens woody plants *A tumor or other such neoplasm Economics * Economic growth, the increase in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services * Growth investing, a style of investment strategy focused on capital appreciation Mathematics * Exponential growth, also called geometric growth * Hyperbolic growth * Linear function, Linear growth, refers to two distinct but related notions * Logistic function, Logistic growth, characterized as an S curve Social science * Developmental psychology * Erikson's stages of psychosocial development * Human development (humanity) * Personal development * Population growth Other uses * Growth (film), ''Growth'' (film), a 2010 American horror film * Izaugsme (''Growth''), a Latv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycophosphatidylinositol
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol () or glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI) is a phosphoglyceride that can be attached to the C-terminus of a protein during posttranslational modification. The resulting GPI-anchored proteins play key roles in a wide variety of biological processes. GPI is composed of a phosphatidylinositol group linked through a carbohydrate-containing linker (glucosamine and mannose glycosidically bound to the inositol residue) and via an ethanolamine phosphate (EtNP) bridge to the C-terminal amino acid of a mature protein. The two fatty acids within the hydrophobic phosphatidyl-inositol group anchor the protein to the cell membrane. Synthesis Glycosylated (GPI-anchored) proteins contain a signal sequence, thus directing them to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The protein is co-translationally inserted in the ER membrane via a translocon and is attached to the ER membrane by its hydrophobic C terminus; the majority of the protein extends into the ER lumen. The hydro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapses
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that allows a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or a target effector cell. Synapses can be classified as either chemical or electrical, depending on the mechanism of signal transmission between neurons. In the case of electrical synapses, neurons are coupled bidirectionally with each other through gap junctions and have a connected cytoplasmic milieu. These types of synapses are known to produce synchronous network activity in the brain, but can also result in complicated, chaotic network level dynamics. Therefore, signal directionality cannot always be defined across electrical synapses. Chemical synapses, on the other hand, communicate through neurotransmitters released from the presynaptic neuron into the synaptic cleft. Upon release, these neurotransmitters bind to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, inducing an electrical or chemical response in the target neuron. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |