|
Nephelometry (medicine)
Nephelometry is a technique used in immunology to determine the levels of several blood plasma proteins. For example the total levels of antibodies isotypes or classes: Immunoglobulin M, Immunoglobulin G, and Immunoglobulin A. It is important in quantification of free light chains in diseases such as multiple myeloma. Quantification is important for disease classification and for disease monitoring once a patient has been treated (increased skewing of the ratio between kappa and lambda light chains after a patient has been treated is an indication of disease recurrence). It is performed by measuring the scattered light at an angle from the sample being measured. In diagnostic nephelometry, the ascending branch of the Heidelberger-Kendall curve is extended by optimizing the course of the reaction so that most plasma proteins’ (from human blood) measurement signals fall at the left side of the Heidelberger-Kendall curve, even at very high concentrations. This technique is widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunology
Immunology is a branch of medicineImmunology for Medical Students, Roderick Nairn, Matthew Helbert, Mosby, 2007 and biology that covers the medical study of immune systems in humans, animals, plants and sapient species. In such we can see there is a difference of human immunology and comparative immunology in veterinary medicine and animal biosciences. Immunology measures, uses charts and differentiate in context in medicine the studies of immunity on cell and molecular level, and the immune system as part of the physiological level as its functioning is of major importance. In the different states of both health, occurring symptoms and diseases; the functioning of the immune system and immunological responses such as autoimmune diseases, allergic hypersensitivities, or in some cases malfunctioning of immune system as for example in immunological disorders or in immune deficiency, and the specific transplant rejection) Immunology has applications in numerous disciplines of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
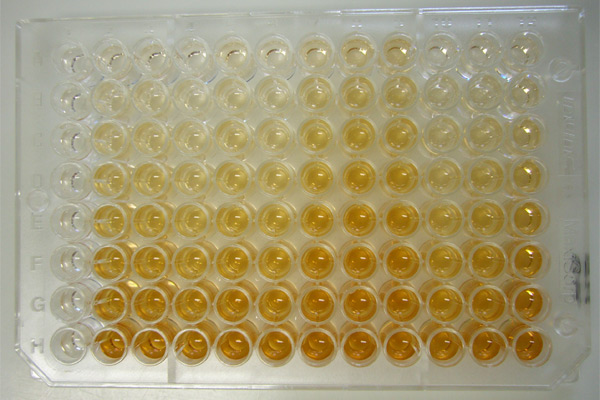
Immunologic Tests
An immunoassay (IA) is a biochemical test that measures the presence or concentration of a macromolecule or a small molecule in a solution through the use of an antibody (usually) or an antigen (sometimes). The molecule detected by the immunoassay is often referred to as an "analyte" and is in many cases a protein, although it may be other kinds of molecules, of different sizes and types, as long as the proper antibodies that have the required properties for the assay are developed. Analytes in biological liquids such as serum or urine are frequently measured using immunoassays for medical and research purposes. Immunoassays come in many different formats and variations. Immunoassays may be run in multiple steps with reagents being added and washed away or separated at different points in the assay. Multi-step assays are often called separation immunoassays or heterogeneous immunoassays. Some immunoassays can be carried out simply by mixing the reagents and sample and making a phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerosol Measurement
An aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog or mist, dust, forest exudates, and geyser steam. Examples of anthropogenic aerosols include particulate air pollutants, mist from the discharge at hydroelectric dams, irrigation mist, perfume from atomizers, smoke, steam from a kettle, sprayed pesticides, and medical treatments for respiratory illnesses. When a person inhales the contents of a vape pen or e-cigarette, they are inhaling an anthropogenic aerosol. The liquid or solid particles in an aerosol have diameters typically less than 1 μm (larger particles with a significant settling speed make the mixture a suspension, but the distinction is not clear-cut). In general conversation, ''aerosol'' often refers to a dispensing system that delivers a consumer product from a can. Diseases can spread by means of small droplets in the breath, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbidimetry
Turbidimetry (the name being derived from ''turbidity'') is the process of measuring the loss of intensity of transmitted light due to the scattering effect of particles suspended in it. Light is passed through a filter creating a light of known wavelength which is then passed through a cuvette containing a solution. A photoelectric cell collects the light which passes through the cuvette. A measurement is then given for the amount of absorbed light. Turbidimetry can be used in biology to find the number of cells in a suspension. Turbidity-is an expression of optical look of a suspension caused by radiation to the scattered and absorbed wavelength. Scattering of light is elastic so both incident and scattered radiation have same wavelength. A turbidometer measures the amount of radiation that passes through a fluid in forward direction, analogous to absorption spectrphotoometry. Standard for turbidimetry is prepared by dissolving 5g of hydrazinium (2+) sulfate(N2H4H2SO4) and 50g of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitin Reaction
A precipitin is an antibody which can precipitate out of a solution upon antigen binding. Precipitin reaction The precipitin reaction provided the first quantitative assay for antibody. The precipitin reaction is based upon the interaction of antigen with antibody leading to the production of antigen-antibody complexes. To produce a precipitin reaction, varying amounts of soluble antigen are added to a fixed amount of serum containing antibody. As the amount of antigen added: * In the zone of antibody excess, each molecule of antigen is bound extensively by antibody and crosslinked to other molecules of antigen. The average size of antibody-antigen complex is small; cross-linking between antigen molecules by antibody is rare. * In the zone of equivalence, the formation of precipitin complexes is optimal. Extensive lattices of antigen and antibody are formed by cross-linking. * At high concentrations of antigen, the average size of antibody-antigen complexes is once again small be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |