|
Neotectonic
Neotectonics, a subdiscipline of tectonics, is the study of the motions and deformations of Earth's crust (geological and geomorphological processes) that are current or recent in geologic time. The term may also refer to the motions/deformations in question themselves. Geologists refer to the corresponding time-frame as the neotectonic period, and to the preceding time as the palaeotectonic period. Vladimir Obruchev coined the term ''neotectonics'' in his 1948 article, defining the field as "recent tectonic movements occurred in the upper part of Tertiary ( Neogene) and in the Quaternary, which played an essential role in the origin of the contemporary topography". Since then geologists have disagreed as to how far back to date "geologically recent" time, with the common meaning being that neotectonics is the youngest, not yet finished stage in Earth tectonics. Some authors consider neotectonics to be basically synonymous with "active tectonics", while others date the start of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonics
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents known as cratons, and the ways in which the relatively rigid plates that constitute the Earth's outer shell interact with each other. Tectonics also provide a framework for understanding the earthquake and volcanic belts that directly affect much of the global population. Tectonic studies are important as guides for economic geologists searching for fossil fuels and ore deposits of metallic and nonmetallic resources. An understanding of tectonic principles is essential to geomorphologists to explain erosion patterns and other Earth surface features. Main types of tectonic regime Extensional tectonics Extensional tectonics is associated with the stretching and thinning of the crust or the lithosphere. This type of tectonics is found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonic Set-up
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents known as cratons, and the ways in which the relatively rigid plates that constitute the Earth's outer shell interact with each other. Tectonics also provide a framework for understanding the earthquake and volcanic belts that directly affect much of the global population. Tectonic studies are important as guides for economic geologists searching for fossil fuels and ore deposits of metallic and nonmetallic resources. An understanding of tectonic principles is essential to geomorphologists to explain erosion patterns and other Earth surface features. Main types of tectonic regime Extensional tectonics Extensional tectonics is associated with the stretching and thinning of the crust or the lithosphere. This type of tectonics is found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the . The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
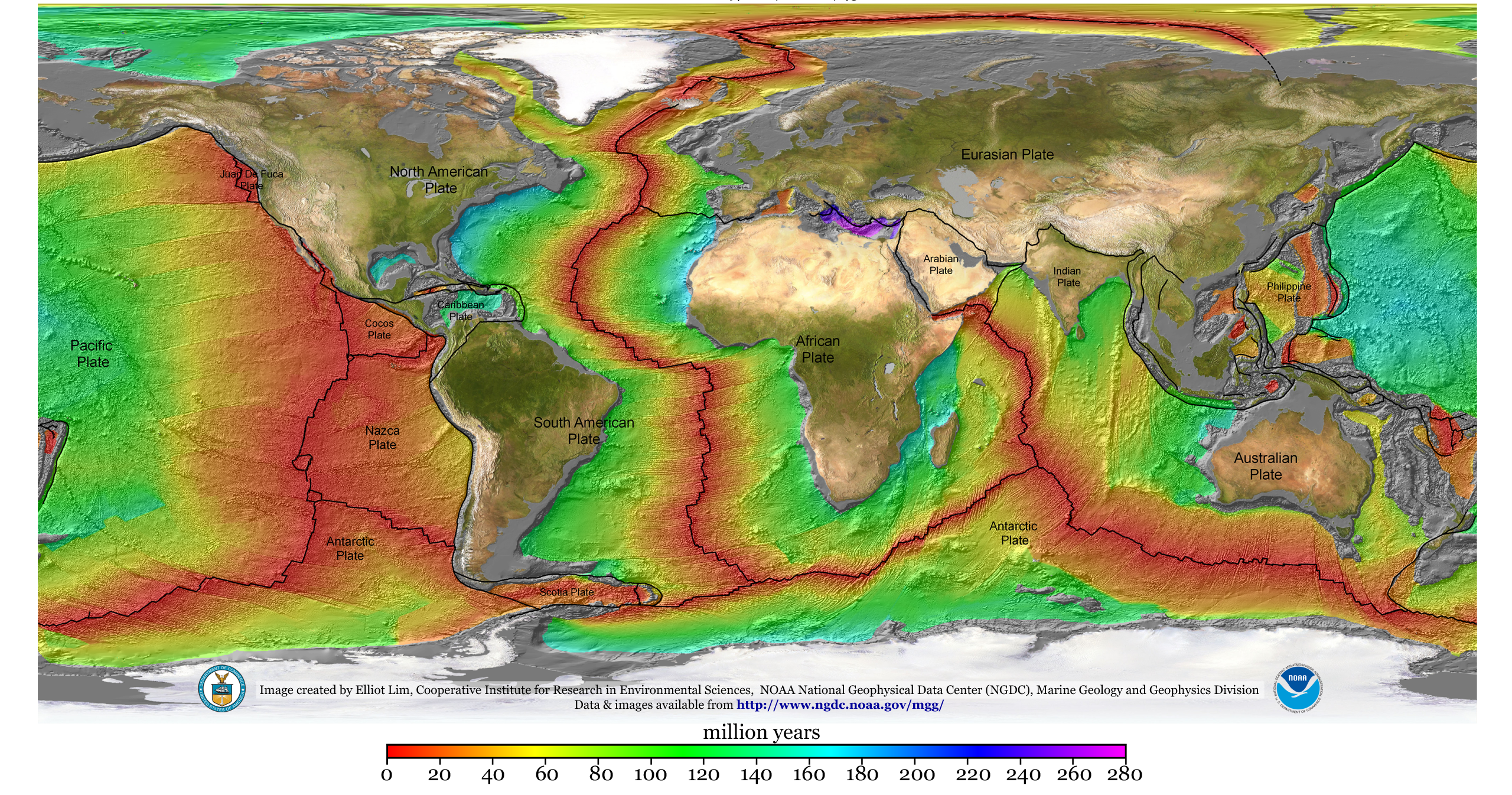
Tectonic Plate
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large tectonic plates which have been slowly moving since about 3.4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of ''continental drift'', an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be generally accepted by geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid to late 1960s. Earth's lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of the planet (the crust and upper mantle), is broken into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary: '' convergent'', '' divergent'', or ''transform''. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic tren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletus (c. 585 BCE), Anaximenes of Miletus (c. 550 BCE), Aristotle (c. 340 BCE), and Zha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited Summit (topography), summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are Monadnock, isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountain formation, Mountains are formed through Tectonic plate, tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through Slump (geology), slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce Alpine climate, colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the Montane ecosystems, ecosys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysics
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term ''geophysics'' sometimes refers only to solid earth applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial physics; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets. Gutenberg, B., 1929, Lehrbuch der Geophysik. Leipzig. Berlin (Gebruder Borntraeger). Runcorn, S.K, (editor-in-chief), 1967, International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for Episodic tremor and slip, non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crust (geology)
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. It is usually distinguished from the underlying mantle by its chemical makeup; however, in the case of icy satellites, it may be distinguished based on its phase (solid crust vs. liquid mantle). The crusts of Earth, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Io, the Moon and other planetary bodies formed via igneous processes and were later modified by erosion, impact cratering, volcanism, and sedimentation. Most terrestrial planets have fairly uniform crusts. Earth, however, has two distinct types: continental crust and oceanic crust. These two types have different chemical compositions and physical properties and were formed by different geological processes. Types of crust Planetary geologists divide crust into three categories based on how and when it formed. Primary crust / primordial crust This is a planet's "original" crust. It forms from solidification of a magma ocean. Towa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Nevada, Reno
The University of Nevada, Reno (Nevada, the University of Nevada, or UNR) is a public land-grant research university in Reno, Nevada. It is the state's flagship public university and primary land grant institution. It was founded on October 12, 1874, in Elko, Nevada. The university is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity" by the Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education. According to the National Science Foundation, the university spent $144 million on research and development in 2018, ranking it 139th in the nation. The university has a medical school. The university is also home to the Donald W. Reynolds School of Journalism, which includes six Pulitzer Prize winners among its alumni. History The Nevada State Constitution established the State University of Nevada in Elko on October 12, 1874. In 1881, it became Nevada State University. In 1885, the Nevada State University moved from Elko to Reno. In 1906, it was ren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogeny
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word "orogeny" () comes from Ancient Greek (, , + , , ). Although it was used before him, the term was employed by the American geologist G. K. Gilbert in 1890 to describe the process of mountain-building as distinguished f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The lithosphere is broken into tectonic plates whose motion allows heat to escape from the interior of the Earth into space. The crust lies on top of the mantle, a configuration that is stable because the upper mantle is made of peridotite and is therefore significantly denser than the crust. The boundary between the crust and mantle is conventionally placed at the Mohorovičić discontinuity, a boundary defined by a contrast in seismic velocity. The temperature of the crust increases with depth, reaching values typically in the range from about to at the boundary with the underlying mantle. The temperature increases by as much as for every kilometer locally in the upper part of the crust Composition File:Elemental abundances.svg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |