|
Neonematherium
''Neonematherium'' is an extinct genus of scelidotheriid ground sloths that lived in Argentina, Chile, and Colombia during the Early to Late Miocene. Fossils have been found in the Honda Group of Colombia, and the Río Frías Formation of Chile. Taxonomy ''Neonematherium'' is a member of the Scelidotheriidae, a family of ground sloths known from the Oligocene, Miocene Pliocene, Pleistocene, and the Early Holocene epochs and are characterized by an elongated snout. Scelidotheres themselves part are usually placed as a subfamily of the Mylodontidae, although they are sometimes considered a separate family, Scelidotheriidae. Below is a phylogenetic tree of the Scelidotheriidae Scelidotheriidae is a family of extinct ground sloths within the order Pilosa, suborder Folivora and superfamily Mylodontoidea, related to the other extinct mylodontoid family, Mylodontidae, as well as to the living two-toed sloth family C ..., based on the work of Nieto ''et al''. 2021, showi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laventan
The Laventan ( es, Laventense) age is a period of geologic time (13.8 to 11.8 Ma) within the Middle Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically within the SALMA classification in South America. It follows the Colloncuran and precedes the Mayoan age.Madden et al., 1997 Etymology The age is named after the Miocene Lagerstätte La Venta, where a rich biodiversity from the Middle Miocene has been recovered from the Honda Group. Formations Fossil content Correlations The Laventan (13.8 to 11.8 Ma) correlates with: * NALMA ** latest Barstovian (15.97-13.65 Ma)Barstovian at Fossilworks.org ** early |
Honda Group, Colombia
The Honda Group ( es, Grupo Honda, Tsh, Ngh) is a geological group of the Upper and Middle Magdalena Basins and the adjacent Central and Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The group, in older literature also defined as formation, is in its present-day type section in the Tatacoa Desert in the department of Huila subdivided into two main formations; La Victoria and Villavieja. The group was originally defined in and named after Honda, Tolima, but has been redefined based on the many fossil finds in the Tatacoa Desert, to the south. In the original type section of its occurrence, the thick group is subdivided into three formations, from old to young; Cambrás, San Antonio and Los Limones. The group dates to the Neogene period; in its broadest definition from the Late Oligocene to Late Miocene, and in the redefined type section restricted to the Laventan age of the South American Land Mammal Ages (SALMA), equivalent to the Middle Miocene Serravallian epoch. The Honda Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
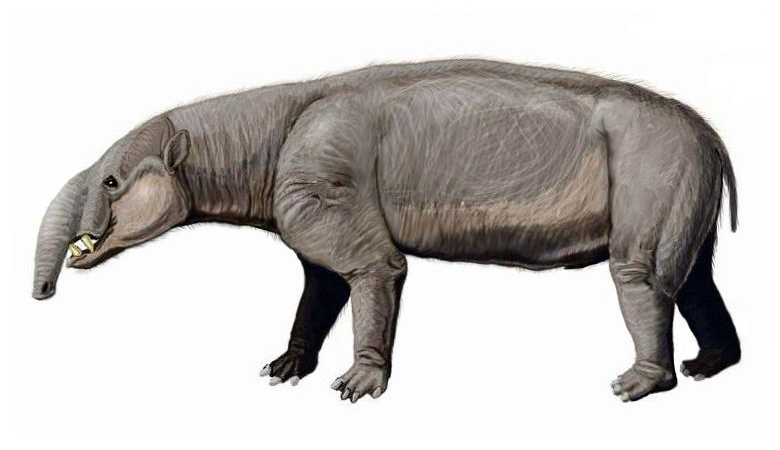
Scelidotheriidae
Scelidotheriidae is a family of extinct ground sloths within the order Pilosa, suborder Folivora and superfamily Mylodontoidea, related to the other extinct mylodontoid family, Mylodontidae, as well as to the living two-toed sloth family Choloepodidae. The only other extant family of the suborder Folivora is the distantly related Bradypodidae. Erected as the family Scelidotheriidae by Ameghino in 1889, the taxon was demoted to a subfamily by Gaudin in 1995. However, recent collagen sequence data indicates the group is less closely related to ''Mylodon'' and ''Lestodon'' than '' Choloepus'' is, and thus it has been elevated back to full family status by Presslee ''et al.'' (2019). Taxonomy Together with Mylodontidae, and the two-toed sloths, the scelidotheriids form the superfamily Mylodontoidea. ''Chubutherium'' is an ancestral and very plesiomorph In phylogenetics, a plesiomorphy ("near form") and symplesiomorphy are synonyms for an ancestral character shared by all m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friasian
The Friasian age is a period of geologic time (16.3–15.5 Ma) within the Early Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically within the SALMA classification of South America. It follows the Santacrucian and precedes the Colloncuran age. Etymology The age is named after the Río Frías Formation in the Aysén Basin, Patagonia, Chile Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a .... Formations Fossils References Bibliography ;Río Frías Formation * * * * * ;Castilletes Formation * * * * * * * * ;Cerdas Beds * ;Chilcatay Formation * * * * ;Cura-Mallín Group * * * ;Gran Bajo del Gualicho Formation * ;Parángula Formation * ;Pebas Formation * * ;Río Foyel Formation * * ;Río Yuca Formation * {{SALMA Miocene S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Río Frías Formation
Río Frías Formation ( es, Formación Río Frías) is a Miocene, Middle Miocene geologic formation made up sedimentary rock located in Aysén Region, western Patagonia. The formation crops out along the upper couse of Cisnes River ( es, Río Cisnes).Marshall & Salinas, 1990 Marsupial fossils have been found in the formation.Marshall, 1990 The Friasian period in the South American Land Mammal Ages is named after the formation. Description Río Frías Formation was discovered by Santiago Roth in the summer of 1897–98. Roth was a Swiss immigrant who had been sent to survey the area by Francisco Moreno. Moreno was director of La Plata Museum and was involved in the Cordillera of the Andes Boundary Case 1902 (Argentina, Chile), Cordillera of the Andes Boundary Case between Chile and Argentina, thus there was both a political and scientific motivation behind the exploration of Patagonia. Santiago Roth called the upper course of Río Cisnes for Río Frías being unaware that it was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catonyx
''Catonyx'' is an extinct genus of ground sloth of the family Scelidotheriidae, endemic to South America during the Pliocene and Pleistocene epochs. It lived from 2.5 Ma to about 10,000 years ago, existing for approximately . The most recent date obtained is about 9600 B.P. Description This animal, like many other terrestrial sloths, was of conspicuous size and mighty build. It had to reach and exceed 4 meters in length, and the skull alone was at least 50 centimeters long. Its weight has been estimated at over 1500 kg. The snout of ''Catonyx'' was elongated, although not as in some similar forms (e.g., ''Scelidotherium''). Unlike the latter, ''Catonyx'' possessed shorter premaxillae that formed a triangular (and not rectangular like ''Scelidotherium'') snout tip, a pronounced rostrum bulge, a palate equipped with a median groove, and larger teeth. In addition, the mandibular symphysis was elongated and elevated, and the posterior lobe of the lower fourth molar was more curve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valgipes
''Valgipes'' is an extinct genus of scelidotheriid ground sloth, endemic to intertropical Brazil and Uruguay during the Late Pleistocene. Thought to have been a forest-dwelling browser, ''Valgipes'' is a monotypic genus with a complex and long taxonomic history, and is a close relative of '' Catonyx'' and '' Proscelidodon''. Taxonomy The taxonomic history of Scelidotheriidae in Brazil is convoluted, and only one species of ''Valgipes'', ''V. bucklandi'', is recognised today, named in honour of William Buckland. Based on the remains of 23 individuals discovered in Lagoa Santa, Minas Gerais, in 1846 Peter Wilhelm Lund described two Brazilian scelidotheriids, ''Scelidotherium owenii'' and ''Scelidotherium bucklandi'', while Winge (1915) named them as ''Scelidotherium magnum'' and '' Catonyx giganteus''. In 1874, Paul Gervais erected the genus ''Valgipes'' for a different species, ''V. deformis'', which he based on a calcaneum bone which he classified as scelidotheriid. Based on c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Sloths
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Placental Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burdigalian First Appearances
The Burdigalian is, in the geologic timescale, an age or stage in the early Miocene. It spans the time between 20.43 ± 0.05 Ma and 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma (million years ago). Preceded by the Aquitanian, the Burdigalian was the first and longest warming period of the MioceneEdward Petuch, Ph.D. Florida Atlantic University, Department of Geosciences. and is succeeded by the Langhian. Stratigraphic definition The name Burdigalian comes from ''Burdigala'', the Latin name for the city of Bordeaux, France. The Burdigalian Stage was introduced in scientific literature by Charles Depéret in 1892. The base of the Burdigalian is at the first appearance of foram species ''Globigerinoides altiaperturus'' and the top of magnetic chronozone C6An. , an official GSSP for the Burdigalian had not yet been assigned. The top of the Burdigalian (the base of the Langhian) is defined by the first appearance of foram species ''Praeorbulina glomerosa'' and is also coeval with the top of magnetic chronozo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langhian Extinctions
The Langhian is, in the ICS geologic timescale The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronol ..., an age (geology), age or stage (stratigraphy), stage in the middle Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch/series (stratigraphy), Series. It spans the time between 15.97 ± 0.05 annum, Ma and 13.65 ± 0.05 Ma (million years ago) during the Middle Miocene.GeoWhen (2007) The Langhian was a continuing warming period defined by Lorenzo Pareto in 1865, it was originally established in the Langhe area north of Ceva in northern Italy, hence the name. The Langhian is preceded by the Burdigalian and followed by the Serravallian Stage. Stratigraphic definition The base of the Langhian is defined by the first appearance of foraminifer species ''Praeorbulina glomerosa'' and is also coeval with the top o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |