|
Neoceratiidae
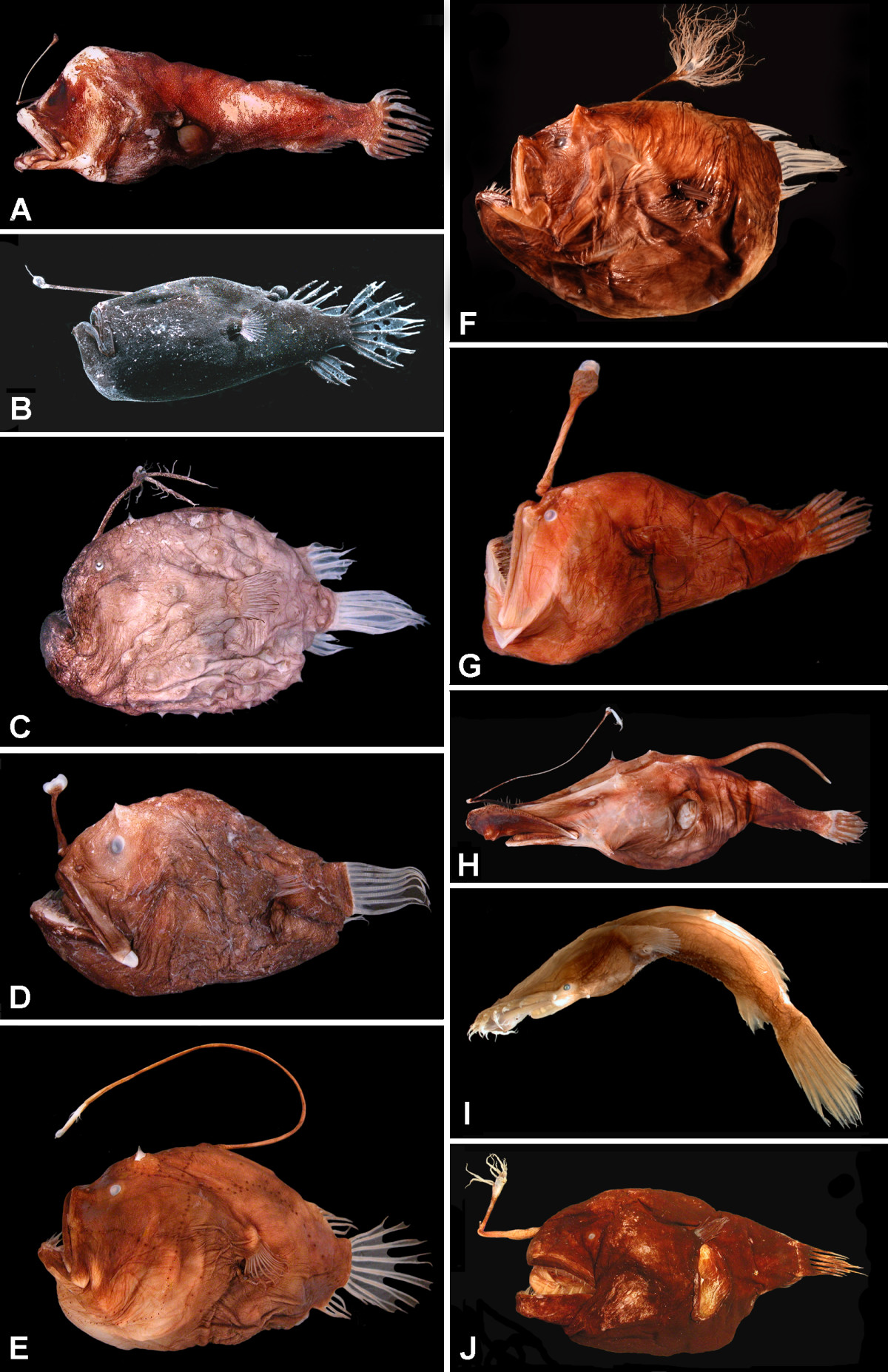
The toothed seadevil, spiny seadevil or netbeard seadevil, ''(Neoceratias spinifer)'', is a rarely seen deep-sea anglerfish found in the mesopelagic and bathypelagic zones of the western central Pacific Ocean. It is the only species in the family Neoceratidae, and is unique amongst the deep-sea anglerfish in lacking an illicium and esca (the "fishing rod" and "lure"), and in having large teeth placed on the outside of its jaws.Pietsch, Theodore W. (2005)Neoceratias spinifer. Needlebeard Seadevils.Version 6 November 2005 (under construction)Tree of Life Web Project Description Adult female toothed seadevils have slender, elongate bodies up to long. They are dark red-brown to black in color, with naked skin. The mouth is large and extends well past the small eye; the jaws have an inner row of short, straight, widely spaced, immobile teeth. On the outside of the jaws, there are prominent conical outgrowths that bear 2-3 straight teeth, the longest of which reach almost 15% the leng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglerfish
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence comes from symbiotic bacteria, which are thought to be acquired from seawater, that dwell in and around the sea. Some anglerfish are notable for extreme sexual dimorphism and sexual symbiosis of the small male with the much larger female, seen in the suborder Ceratioidei, the deep sea anglerfish. In these species, males may be several orders of magnitude smaller than females. Anglerfish occur worldwide. Some are pelagic (dwelling away from the sea floor), while others are benthic (dwelling close to the sea floor). Some live in the deep sea (such as the Ceratiidae), while others on the continental shelf, such as the frogfishes and the Lophiidae (monkfish or goosefish). Pelagic forms are most often laterally compressed, whereas th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophiiformes
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence comes from symbiotic bacteria, which are thought to be acquired from seawater, that dwell in and around the sea. Some anglerfish are notable for extreme sexual dimorphism and sexual symbiosis of the small male with the much larger female, seen in the suborder Ceratioidei, the deep sea anglerfish. In these species, males may be several orders of magnitude smaller than females. Anglerfish occur worldwide. Some are pelagic (dwelling away from the sea floor), while others are benthic (dwelling close to the sea floor). Some live in the deep sea (such as the Ceratiidae), while others on the continental shelf, such as the frogfishes and the Lophiidae (monkfish or goosefish). Pelagic forms are most often laterally compressed, whereas the be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Pappenheim
Paul may refer to: *Paul (given name), a given name (includes a list of people with that name) * Paul (surname), a list of people People Christianity *Paul the Apostle (AD c.5–c.64/65), also known as Saul of Tarsus or Saint Paul, early Christian missionary and writer * Pope Paul (other), multiple Popes of the Roman Catholic Church * Saint Paul (other), multiple other people and locations named "Saint Paul" Roman and Byzantine empire * Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus (c. 229 BC – 160 BC), Roman general * Julius Paulus Prudentissimus (), Roman jurist * Paulus Catena (died 362), Roman notary *Paulus Alexandrinus (4th century), Hellenistic astrologer * Paul of Aegina or Paulus Aegineta (625–690), Greek surgeon Royals *Paul I of Russia (1754–1801), Tsar of Russia *Paul of Greece (1901–1964), King of Greece Other people *Paul the Deacon or Paulus Diaconus (c. 720 – c. 799), Italian Benedictine monk *Paul (father of Maurice), the father of Maurice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopelagic
The mesopelagic zone (Greek μέσον, middle), also known as the middle pelagic or twilight zone, is the part of the pelagic zone that lies between the photic epipelagic and the aphotic bathypelagic zones. It is defined by light, and begins at the depth where only 1% of incident light reaches and ends where there is no light; the depths of this zone are between approximately 200 to 1,000 meters (~656 to 3,280 feet) below the ocean surface. The mesopelagic zone occupies about 60% of the planet's surface and about 20% of the ocean's volume, amounting to a large part of the total biosphere. It hosts a diverse biological community that includes bristlemouths, blobfish, bioluminescent jellyfish, giant squid, and a myriad of other unique organisms adapted to live in a low-light environment. It has long captivated the imagination of scientists, artists and writers; deep sea creatures are prominent in popular culture. Physical conditions The mesopelagic zone includes the regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathypelagic Zone
The bathypelagic zone or bathyal zone (from Greek βαθύς (bathýs), deep) is the part of the open ocean that extends from a depth of below the ocean surface. It lies between the mesopelagic above, and the abyssopelagic below. The bathypelagic is known as the midnight zone because of the lack of sunlight; this feature does not allow for photosynthesis-driven primary production, preventing growth of phytoplankton or aquatic plants. Although larger by volume than the photic zone, our knowledge of the bathypelagic zone remains limited by our ability to explore the deep ocean. Physical characteristics The bathypelagic zone is characterized by a nearly constant temperature of approximately and a salinity range of 33-35 g/kg. This region has little to no light, because sunlight does not reach this deep in the ocean and bioluminescence is limited. The hydrostatic pressure in this zone ranges 100-400 atmospheres (atm), due to the increase of 1 atm for every 10 m depth. It is beli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nostril
A nostril (or naris , plural ''nares'' ) is either of the two orifices of the nose. They enable the entry and exit of air and other gasses through the nasal cavities. In birds and mammals, they contain branched bones or cartilages called turbinates, whose function is to warm air on inhalation and remove moisture on exhalation. Fish do not breathe through noses, but they do have two (but cyclostomes have merged into one) small holes used for smelling, which can also be referred to as nostrils. In humans, the nasal cycle is the normal ultradian cycle of each nostril's blood vessels becoming engorged in swelling, then shrinking. The nostrils are separated by the septum. The septum can sometimes be deviated, causing one nostril to appear larger than the other. With extreme damage to the septum and columella, the two nostrils are no longer separated and form a single larger external opening. Like other tetrapods, humans have two external nostrils (anterior nares) and tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamella (zoology)
Lamellae on a gecko's foot. In surface anatomy, a lamella is a thin plate-like structure, often one amongst many lamellae very close to one another, with open space between. Aside from respiratory organs, they appear in other biological roles including filter feeding and the traction surfaces of geckos. In fish, gill lamellae are used to increase the surface area in contact with the environment to maximize gas exchange (both to attain oxygen and to expel carbon dioxide) between the water and the blood. In fish gills there are two types of lamellae, primary and secondary. The primary gill lamellae (also called gill filament) extends from the gill arch, and the secondary gill lamellae extends from the primary gill lamellae. Gas exchange primarily occurs at the secondary gill lamellae, where the tissue is notably only one cell layer thick. Furthermore, countercurrent gas exchange at the secondary gill lamellae further maximizes oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide release. See a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, colour, markings, or behavioural or cognitive traits. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is ''monomorphism'', which is when both biological sexes are phenotypically indistinguishable from each other. Overview Ornamentation and coloration Common and easily identified types of dimorphism consist of ornamentation and coloration, though not always apparent. A difference in coloration of sexes within a given species is called sexual dichromatism, which is commonly seen in many species of birds and reptiles. Sexual selection leads to the exaggerat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioluminescent
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria, and terrestrial arthropods such as fireflies. In some animals, the light is bacteriogenic, produced by symbiotic bacteria such as those from the genus ''Vibrio''; in others, it is autogenic, produced by the animals themselves. In a general sense, the principal chemical reaction in bioluminescence involves a light-emitting molecule and an enzyme, generally called luciferin and luciferase, respectively. Because these are generic names, luciferins and luciferases are often distinguished by the species or group, e.g. firefly luciferin. In all characterized cases, the enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of the luciferin. In some species, the luciferase requires other cofactors, such as calcium or magnesium ions, and some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include arthropods, mollusks, annelids, echinoderms and cnidarians. The majority of animal species are invertebrates; one estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata. Invertebrates vary widely in size, from 50 μm (0.002 in) rotifers to the 9–10 m (30–33 ft) colossal squid. Some so-called invertebrates, such as the Tunicata and Cephalochordata, are more closely related to vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the invertebrates paraphyletic, so the term has little meaning in taxonomy. Etymology The word "invertebrate" comes from the Latin word ''vertebra' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


