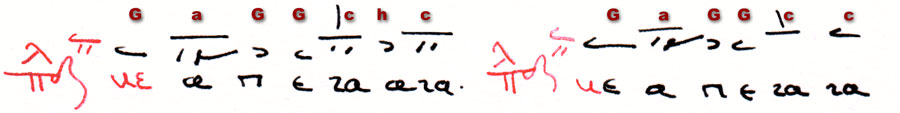|
Nenano
Phthora nenano (Medieval Greek: , also νενανώ) is the name of one of the two "extra" modes in the Byzantine Octoechos—an eight mode system, which was proclaimed by a synod of . The phthorai nenano and nana were favoured by composers at the Monastery Agios Sabas, near Jerusalem, while hymnographers at the Stoudiou-Monastery obviously preferred the diatonic mele. The ''phthora nenano'' as part of the Hagiopolitan ''octoechos'' Today the system of eight diatonic modes and two ' ("destroyers") is regarded as the modal system of Byzantine chant, and during the eighth century it became also model for the Latin '' tonaries''—introductions into a proper diatonic eight mode system and its psalmody, created by Frankish cantores during the Carolinigian reform. While φθορά νενανῶ was often called "chromatic", the second ' was named "nana" (gr. φθορά νανὰ) and called "enharmonic", the names were simply taken from the syllables used for the intonation (enechem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enechema
Echos (Greek: "sound", pl. echoi ; Old Church Slavonic: "voice, sound") is the name in Byzantine music theory for a mode within the eight-mode system (oktoechos), each of them ruling several melody types, and it is used in the melodic and rhythmic composition of Byzantine chant ("thesis of the melos"), differentiated according to the chant genre and according to the performance style ("method of the thesis"). It is akin to a Western medieval tonus, an Andalusian tab', an Arab naġam (since 1400 "maqam"), or a Persian parde (since 18th-century dastgah). Overview and semantics The noun ''echos'' in Greek means "sound" in general. It acquired the specialized meaning of ''mode'' early on in the development of Byzantine music theory since the Octoechos reform in 692. In general, the concept of echos denotes a certain octave species, its intervallic structure as well as a set of more or less explicitly formulated melodic rules and formulae that represent a certain category of me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echos
Echos (Greek: "sound", pl. echoi ; Old Church Slavonic: "voice, sound") is the name in Byzantine music theory for a mode within the eight-mode system (oktoechos), each of them ruling several melody types, and it is used in the melodic and rhythmic composition of Byzantine chant ("thesis of the melos"), differentiated according to the chant genre and according to the performance style ("method of the thesis"). It is akin to a Western medieval tonus, an Andalusian tab', an Arab naġam (since 1400 "maqam"), or a Persian parde (since 18th-century dastgah). Overview and semantics The noun ''echos'' in Greek means "sound" in general. It acquired the specialized meaning of ''mode'' early on in the development of Byzantine music theory since the Octoechos reform in 692. In general, the concept of echos denotes a certain octave species, its intervallic structure as well as a set of more or less explicitly formulated melodic rules and formulae that represent a certain category of me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papadic Octoechos
Oktōēchos (here transcribed "Octoechos"; Greek: , pronounced in Constantinopolitan: ; from ὀκτώ "eight" and ἦχος "sound, mode" called echos; Slavonic: Осмогласие, ''Osmoglasie'' from о́смь "eight" and гласъ "voice, sound") is the name of the eight mode system used for the composition of religious chant in Byzantine, Syriac, Armenian, Georgian, Latin and Slavic churches since the Middle Ages. In a modified form the octoechos is still regarded as the foundation of the tradition of monodic Orthodox chant today. Until 1204 neither the Hagia Sophia nor any other cathedral of the Byzantine Empire did abandon its habits, and the Hagiopolitan eight mode system came into use not earlier than in the mixed rite of Constantinople, after the patriarchate and the court had returned from their exile in Nikaia in 1261. Middle Byzantine Round notation In the history of the Byzantine rite the Hagiopolitan reform was described as a synthesis of the cathedra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hagiopolitan Octoechos
Oktōēchos (here transcribed ""; Greek: pronounced in koine: ; from ὀκτώ "eight" and ἦχος "sound, mode" called echos; Slavonic: Осмогласие, ''Osmoglasie'' from о́смь "eight" and гласъ "voice, sound") is the name of the eight mode system used for the composition of religious chant in most Christian churches during the Middle Ages. In a modified form the octoechos is still regarded as the foundation of the tradition of monodic Orthodox chant today (Neobyzantine Octoechos). The Octoechos as a liturgical concept which established an organization of the calendar into eight-week cycles, was the invention of monastic hymnographers at Mar Saba in Palestine and in Constantinople. It was formally accepted in the Quinisext Council of 692, which also aimed to replace the exegetic poetry of the kontakion and other homiletic poetry, as it was sung during the morning service (Orthros) of the cathedrals. A similar eight-mode system was established in Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Music
Byzantine music (Greek: Βυζαντινή μουσική) is the music of the Byzantine Empire. Originally it consisted of songs and hymns composed to Greek texts used for courtly ceremonials, during festivals, or as paraliturgical and liturgical music. The ecclesiastical forms of Byzantine music are the best known forms today, because different Orthodox traditions still identify with the heritage of Byzantine music, when their cantors sing monodic chant out of the traditional chant books such as the Sticherarion, which in fact consisted of five books, and the Irmologion. Byzantine music did not disappear after the fall of Constantinople. Its traditions continued under the Patriarch of Constantinople, who after the Ottoman conquest in 1453 was granted administrative responsibilities over all Eastern Orthodox Christians in the Ottoman Empire. During the decline of the Ottoman Empire in the 19th century, burgeoning splinter nations in the Balkans declared autonomy or autocephaly fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nana (echos)
Phthora nana (Medieval Greek ) is one of the ten modes of the Hagiopolitan Octoechos consisting of 8 diatonic echoi and two additional phthorai. It is used in different traditions of Orthodox chant until today (→ Neobyzantine Octoechos). The name "nana" is taken from the syllables (written in ligatures "ʅʅ") sung during the intonation which precedes a melody composed in this mode. The name "phthora" derived from the verb and means "destroy" or "corrupt". It was usually referred to the diatonic genus of the eight mode system and as a sign used in Byzantine chant notation it indicated a "change to another genus" (), in the particular case of phthora nana a change to the enharmonic genus. Today the "nana" intonation has become the standard name of the third authentic mode which is called "echos tritos" () in Greek and "third glas" () in Old Church Slavonic. The different functions of phthora nana In the theory and notation of Byzantine and Orthodox chant nana is the name of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nana (echos)
Phthora nana (Medieval Greek ) is one of the ten modes of the Hagiopolitan Octoechos consisting of 8 diatonic echoi and two additional phthorai. It is used in different traditions of Orthodox chant until today (→ Neobyzantine Octoechos). The name "nana" is taken from the syllables (written in ligatures "ʅʅ") sung during the intonation which precedes a melody composed in this mode. The name "phthora" derived from the verb and means "destroy" or "corrupt". It was usually referred to the diatonic genus of the eight mode system and as a sign used in Byzantine chant notation it indicated a "change to another genus" (), in the particular case of phthora nana a change to the enharmonic genus. Today the "nana" intonation has become the standard name of the third authentic mode which is called "echos tritos" () in Greek and "third glas" () in Old Church Slavonic. The different functions of phthora nana In the theory and notation of Byzantine and Orthodox chant nana is the name of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octoechos (liturgy)
The Octoechos (from the Greek: ; from ὀκτώ 'eight' and ἦχος 'sound, mode' called echos; cu, Осмѡгласникъ, from о́смь 'eight' and гласъ 'voice, sound') is a liturgical book containing a repertoire of hymns ordered in eight parts according to eight echoi ( tones or modes). Originally created in the Monastery of Stoudios during the 9th century as a hymnal complete with musical notation, it is still used in many rites of Eastern Christianity. The book with similar function in the Western Church is the tonary, and both contain the melodic models of an octoechos system; however, while the tonary serves simply for a modal classification, the octoechos is organized as a cycle of eight weeks of services. The word itself can also refer to the repertoire of hymns sung during the celebrations of the Sunday Office. Role of meter in the Octoechos Many hymns in the Octoechos, such as Kathismata, Odes, and Kontakia are set in a strict meter—a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Damascus
John of Damascus ( ar, يوحنا الدمشقي, Yūḥanna ad-Dimashqī; gr, Ἰωάννης ὁ Δαμασκηνός, Ioánnēs ho Damaskēnós, ; la, Ioannes Damascenus) or John Damascene was a Christian monk, priest, hymnographer, and apologist. Born and raised in Damascus c. 675 or 676; the precise date and place of his death is not known, though tradition places it at his monastery, Mar Saba, near Jerusalem on 4 December 749. A polymath whose fields of interest and contribution included law, theology, philosophy, and music, he was given the by-name of Chrysorroas (Χρυσορρόας, literally "streaming with gold", i.e. "the golden speaker"). He wrote works expounding the Christian faith, and composed hymns which are still used both liturgically in Eastern Christian practice throughout the world as well as in western Lutheranism at Easter. He is one of the Fathers of the Eastern Orthodox Church and is best known for his strong defence of icons. The Catholic Church ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmas Of Maiuma
Saint Cosmas of Maiuma, also called Cosmas Hagiopolites ("of the Holy City"), Cosmas of Jerusalem, Cosmas the Melodist, or Cosmas the Poet (d. 773 or 794), was a bishop and an important hymnographer in the East. He is venerated as a saint by the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church. Life Saint Cosmas ( el, Κοσμάς) was born in Jerusalem, but he was orphaned at a young age. He was adopted by Sergius, the father of St. John of Damascus (ca.676 - 749), and became John's foster-brother. The teacher of the two boys was an elderly Calabrian monk, also named Cosmas (known as "Cosmas the Monk" to distinguish him), who had been freed from slavery to the Saracens by St. John's father. John and Cosmas went from Damascus to Jerusalem, where both became monks in the Lavra (monastery) of St. Sabbas the Sanctified near that city.''Byzantine Music and Liturgy'', E. Wellesz, ''The Cambridge Medieval History: The Byzantine Empire, Part II'', Vol. IV, ed. J.M. Hussey, D.M. Nicol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5th–6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople in 1453. From the 7th century onwards, Greek was the only language of administration and government in the Byzantine Empire. This stage of language is thus described as Byzantine Greek. The study of the Medieval Greek language and literature is a branch of Byzantine studies, the study of the history and culture of the Byzantine Empire. The beginning of Medieval Greek is occasionally dated back to as early as the 4th century, either to 330 AD, when the political centre of the Roman Empire was moved to Constantinople, or to 395 AD, the division of the empire. However, this approach is rather arbitrary as it is more an assumption of political, as opposed to cultural and linguistic, developments. Indeed, by this time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)