|
Nematocarcinoidea
Nematocarcinoidea is a superfamily of shrimp, comprising four families – Eugonatonotidae, Nematocarcinidae, Rhynchocinetidae and Xiphocarididae. They share the presence of strap-like epipods on at least the first three pairs of pereiopod The decapod (crustaceans such as a crab, lobster, shrimp or prawn) is made up of 20 body segments grouped into two main body parts: the cephalothorax and the pleon (abdomen). Each segment may possess one pair of appendages, although in various g ...s, and a blunt molar process. References External links * * Caridea Taxa named by Sidney Irving Smith Arthropod superfamilies {{Caridea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caridea
The Caridea, commonly known as caridean shrimp or true shrimp, are an infraorder of shrimp within the order Decapoda. This infraorder contains all species of true shrimp. They are found widely around the world in both fresh and salt water. Many other animals with similar names – such as the mud shrimp of Axiidea and the boxer shrimp of Stenopodidea – are not true shrimp, but many have evolved features similar to true shrimp. Biology Carideans are found in every kind of aquatic habitat, with the majority of species being marine. Around a quarter of the described species are found in fresh water, however, including almost all the members of the species-rich family Atyidae and the Palaemonidae subfamily Palaemoninae. They include several commercially important species, such as ''Macrobrachium rosenbergii'', and are found on every continent except Antarctica. The marine species are found at depths to , and from the tropics to the polar regions. In addition to the great variety in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhynchocinetes Durbanensis
''Rhynchocinetes durbanensis'', commonly known as the camel shrimp and the hingebeak prawn, is a species of shrimp (family Rhynchocinetidae) found in the Indo-Pacific. Up to in length, the shrimp has large black eyes, and features red and white lines on a translucent body. It has many white ''ocelli'' (spots) as well as a Y-shaped white mark on the upper front part of its carapace. It is strongly sexually dimorphic, and dominant males have larger first pair of chelipeds. The shrimp is found in hollows and crevices from deep, where it forms groups consisting of dozens of individuals. One study determined that the ovigerous females carry from 267 to 1764 eggs, and the eggs take 9 days to hatch after spawning at a temperature of , or 18 days when the temperature is under . ''R. durbanensis'' has been frequently confused with '' R. uritai'', and also closely resembles '' R. brucei''. ''R. durbanensis'' was first described scientifically by Isabella Gordon Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidney Irving Smith
Sidney Irving Smith (February 18, 1843 in Norway, Maine – May 6, 1926 in New Haven, Connecticut) was an American zoologist. Private life Sidney Smith was the son of Elliot Smith and Lavinia Barton. His brother in law was Addison Emery Verrill. Smith married Eugenia Pocahontas Barber in New Haven, Connecticut on June 29, 1882. The couple had no children, and Eugenia died on March 14, 1916. Smith suffered from hereditary glaucoma, rendering him partially sighted from 1906, and completely blind some years before his death. He died on May 6, 1926 of throat cancer. Education and career In his youth, Sidney Irving Smith became expert on the fauna around his home town, and an expert at making collections, particularly of insects. He studied at the Sheffield Scientific School of Yale University, and received his Ph.B. in 1867. Yale University conferred upon him the honorary degree of M.A. in 1887. He stayed on at Yale, initially as an assistant, but from 1875 as the first professor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugonatonotidae
''Eugonatonotus'' is a genus of decapods and is the only genus in the monotypic family Eugonatonotidae. The species of this genus are found in Central America, Southeastern Asia and Australia. Species: *''Eugonatonotus chacei ''Eugonatonotus'' is a genus of decapods and is the only genus in the monotypic family Eugonatonotidae. The species of this genus are found in Central America, Southeastern Asia and Australia. Species: *'' Eugonatonotus chacei'' Chan & Yu, 199 ...'' Chan & Yu, 1991 *'' Eugonatonotus crassus'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q11843284, from2=Q15730610 Decapods Decapod genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematocarcinidae
Nematocarcinidae is a family of crustaceans belonging to the order Decapoda The Decapoda or decapods (literally "ten-footed") are an order of crustaceans within the class Malacostraca, including many familiar groups, such as crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp and prawns. Most decapods are scavengers. The order is esti .... Genera: * '' Lenzicarcinus'' Burukovsky, 2005 * '' Macphersonus'' Burukovsky, 2012 * '' Nematocarcinus'' Milne-Edwards, 1881 * '' Nigmatullinus'' Burukovsky, 1991 * '' Segonzackomaius'' Burukovsky, 2011 References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4481640 Decapods Decapod families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhynchocinetidae
The family Rhynchocinetidae are a group of small, reclusive red-and-white shrimp. This family typically has an upward-hinged foldable rostrum, hence its taxon name ''Rhynchocinetidae'', which means ''movable beak''; this gives these shrimps their common name of hinge-beak shrimps. The family contains only two genera, '' Cinetorhynchus'' and '' Rhynchocinetes''. Taxonomy Rhynchocinetidae has historically been considered to include the single genus ''Rhynchocinetes'', which was subdivided into two sub-genera. However, in 1995, Holthuis elevated the subgenus ''Cinetorhynchus'' to full generic status based on morphology. Members of ''Rhynchocinetes'' have two acute teeth on the central carina of the carapace, a supraorbital spine and no spine on the margins of the fourth and fifth abdominal somites. ''Cinetorhynchus'' differs in having three teeth on the carapace, no supraorbital spine and a single spine each on the margins of the fourth and fifth abdominal somites. Description Mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiphocarididae
''Xiphocaris'' is a genus of crustaceans belonging to the monotypic family Xiphocarididae. The species of this genus are found in the Caribbean The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se .... Species: *'' Xiphocaris elongata'' *'' Xiphocaris gomezi'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q11849255, from2=Q18615830 Crustaceans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoologische Mededelingen
''Zoologische Mededelingen'' was a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal publishing papers and monographs on animal systematics. The publisher was the National Museum of Natural History Naturalis in the Netherlands. The first issue appeared in 1915, as the official journal of Naturalis' predecessor, the Rijks Museum van Natuurlijke Historie. Earlier, the museum published ''Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle des Pays-Bas'' (volumes I-XIV, 1862-1908) and ''Notes from the Leyden Museum'' (volumes I-XXXVI, 1879-1914), which mainly covered the fauna of the Netherlands and the former Dutch colonies. ''Zoologische Mededelingen'' was indexed in ''The Zoological Record'' and ''BIOSIS''. A complete backlist of published volumes is presented on the institutional repository of Naturalis. The last article was published in 2014 and the journal was merged into the ''European Journal of Taxonomy The ''European Journal of Taxonomy'' is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal for descrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Register Of Marine Species
The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) is a taxonomic database that aims to provide an authoritative and comprehensive list of names of marine organisms. Content The content of the registry is edited and maintained by scientific specialists on each group of organism. These taxonomists control the quality of the information, which is gathered from the primary scientific literature as well as from some external regional and taxon-specific databases. WoRMS maintains valid names of all marine organisms, but also provides information on synonyms and invalid names. It is an ongoing task to maintain the registry, since new species are constantly being discovered and described by scientists; in addition, the nomenclature and taxonomy of existing species is often corrected or changed as new research is constantly being published. Subsets of WoRMS content are made available, and can have separate badging and their own home/launch pages, as "subregisters", such as the ''World List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
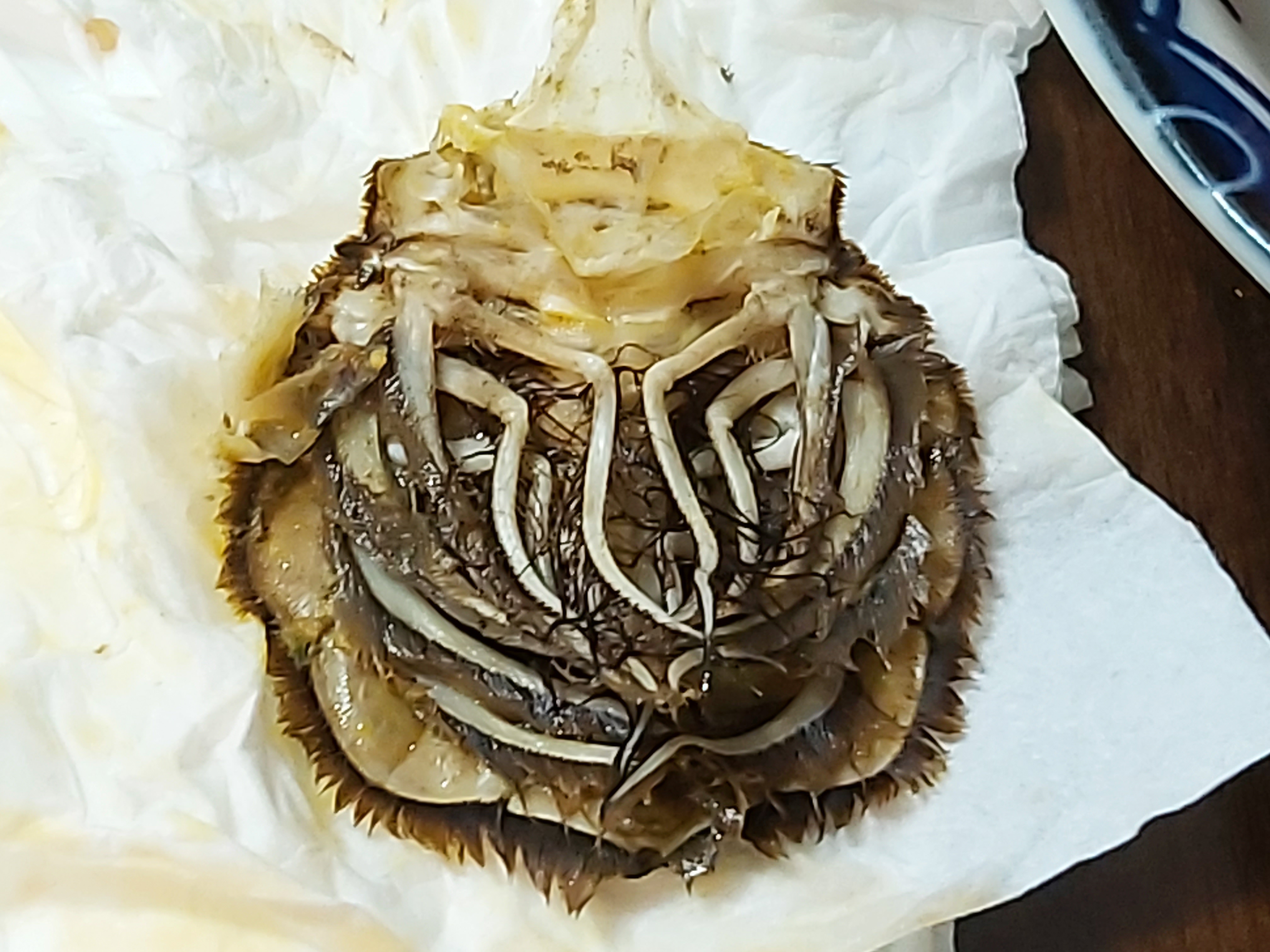
Pereiopod
The decapod (crustaceans such as a crab, lobster, shrimp or prawn) is made up of 20 body segments grouped into two main body parts: the cephalothorax and the pleon (abdomen). Each segment may possess one pair of appendages, although in various groups these may be reduced or missing. They are, from head to tail: Cephalothorax Head # antennules # antennae #mandibles # first maxillae # second maxillae The head also bears the (usually stalked) compound eyes. The distal portion of a mandible or maxilla which has a sensory function is known as a palp. Thorax / pereon #first maxillipeds #second maxillipeds #third maxillipeds #first pereiopods #second pereiopods #third pereiopods #fourth pereiopods #fifth pereiopods Maxillipeds are appendages modified to function as mouthparts. Particularly in the less advanced decapods, these can be very similar to the pereiopods. Pereiopods are primarily walking legs and are also used for gathering food. They are also the ten legs from which decapods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSIRO Publishing
CSIRO Publishing is an Australian-based science and technology publisher. It publishes books, journals and magazines across a range of scientific disciplines, including agriculture, chemistry, plant and animal sciences, natural history and environmental management. It also produces interactive learning modules for primary school students and provides writing workshops for researchers. CSIRO Publishing operates within the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO). It was established as a stand-alone business unit in 1995. Books CSIRO Publishing publishes books in a number of categories, including: * Animals: behaviour; birds; domesticated; ecology and management; field guides; fish; genetics and evolution; health and welfare; invasive; invertebrates; mammals and marsupials; reproduction and physiology; reptiles and amphibians; and wildlife. * Built Environment: architecture; building; codes and standards; engineering; landscape architecture; and pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Sidney Irving Smith
In biology, a taxon ( back-formation from '' taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |